- Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
-
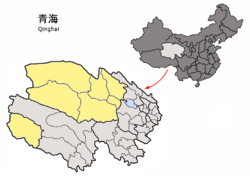
Haixi Prefecture — Autonomous Prefecture — 海西蒙古族藏族自治州
ᠬᠠᠶᠢᠰᠢ ᠶᠢᠨ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠲᠥᠪᠡᠳ ᠦᠨᠳᠦᠰᠦᠲᠡᠨ ᠦ ᠥᠪᠡᠷᠲᠡᠭᠡᠨ ᠵᠠᠰᠠᠬᠤ ᠵᠧᠦChinese transcription(s) – Chinese characters 海西蒙古族藏族自治州 – Hanyu pinyin Hǎixī Měnggǔzú Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu Tibetan transcription(s) – Tibetan script མཚོ་ནུབ་སོག་རིགས་ཆ་བོད་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་ཁུལ་ – Wylie Mtsho-nub Sog-rigs dang Bod-rigs rang-skyong-khul – Tibetan pinyin Conub Sogrig Poirig Ranggyong Kü Location of the prefecture within Qinghai Coordinates: 37°24′N 97°24′E / 37.4°N 97.4°ECoordinates: 37°24′N 97°24′E / 37.4°N 97.4°E Country China Province Qinghai Prefecture Seat Delingha Area – Total 325,785 km2 (125,786.3 sq mi) Population (2010)[1] – Total 489,338 – Density 1.5/km2 (3.9/sq mi) – Major Ethnic Groups Han-64.95%
Tibetan-12.16%
Hui-11.94%
Mongols- 7.23%Time zone China Standard (UTC+8) Postal code 817000 Area code(s) 0977 Website http://www.haixi.gov.cn/ Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in northern Qinghai province of Western China. It has an area of 325,785 square kilometres (125,786 sq mi) and its capital is Delingha. The name of the prefecture literally means "west of Qinghai Lake."
Geladandong Mountain, the source of the Yangtze River, is located here.
Contents
History
After 1949, the People's Government of Dulan County was founded and the area was renamed Dulan Autonomous District (都兰自治区); in 1954, Dulan was renamed Haixi Mongol, Tibetan and Kazakh Autonomous District (海西蒙藏哈萨克族自治区) and in 1955, Haixi Mongol, Tibetan and Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture (海西蒙藏哈萨克族自治州). In 1963, it was renamed "海西蒙古族藏族哈萨克族自治州" (English the same, "蒙藏哈萨克族"->"蒙古族藏族哈萨克族"). In 1985, after the Kazakhs had returned to Xinjiang, it was again renamed Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture.[2]
Demographics
As of the 2010 census, Haixi had 489,338 inhabitants, giving it a population density of 1.5 inhabitants per km².
The following is a list of ethnic groups in the prefecture, taken in the 2000 Census
Nationality Population Percentage Han 215,706 64.95% Tibetan 40,371 12.16% Hui 39,644 11.94% Mongol 24,020 7.23% Tu 5,792 1.74% Salar 3,569 1.07% Dongxiang 1,026 0.31% Manchu 544 0.16% Tujia 422 0.13% Kazakh 380 0.11% Others 620 0.2% Subdivisions
Haixi directly governs 2 county-level cities and 3 counties.
Map 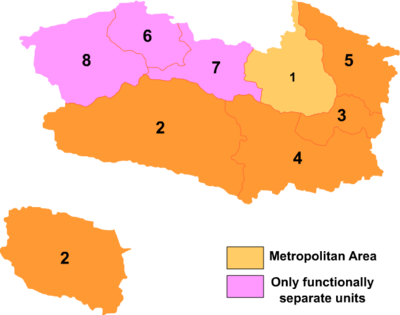
# Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Tibetan Wylie Population
(2010)Area (km²) Density
(/km²)1 Delingha City 德令哈市 Délìnghā Shì 78,184 27,613 2.83 2 Golmud City 格尔木市 Gé'ěrmù Shì ན་གོར་མོ་གྲོང་ཁྱེར་ na gor mo
grong khyer215,213 123,460 1.74 3 Wulan County 乌兰县 Wūlán Xiàn ཝུའུ་ལན་རྫོང་ wu'u lan rdzong 38,723 10,784 3.59 4 Dulan County 都兰县 Dūlán Xiàn ཏུའུ་ལན་རྫོང་ tu'u lan rdzong 76,623 50,000 1.53 5 Tianjun County 天峻县 Tiānjùn Xiàn ཐེན་ཅུན་རྫོང་ then cun rdzong 33,923 20,000 1.70 6 Lenghu Administrative Committee 冷湖行政委员会 Lěnghú Xíngzhèng
Wěiyuánhuì2,434 21,000 0.12 7 Da Qaidam Administrative committee 大柴旦行政委员会 Dàcháidàn Xíngzhèng
Wěiyuánhuì13,671 34,000 0.40 8 Magnya Administrative committee 茫崖行政委员会 Mángyá Xíngzhèng
Wěiyuánhuì31,017 32,000 0.97 The southwestern exclave of the Haixi Prefecture, separated from the rest of the prefecture by a "panhandle" of the Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, is the Tanggulashan Town of Golmud City.
Gallery
A picture taken in the southwestern part of the prefectureThe Qingzang Railway can be seen on the far leftNotable Features
- Delingha city
- Geladandong mountain
- Headwaters of the Yangtze River
- The Baigong Pipes
Notes
- ^ According to 2010 China National Census
- ^ 海西州 (青海省民政厅网站).
For details, see: 海西蒙古族藏族自治州 (行政区划网站).
Further reading
- A. Gruschke: The Cultural Monuments of Tibet’s Outer Provinces: Amdo - Volume 1. The Qinghai Part of Amdo, White Lotus Press, Bangkok 2001. ISBN 974-480-049-6
- Tsering Shakya: The Dragon in the Land of Snows. A History of Modern Tibet Since 1947, London 1999, ISBN 0-14-019615-3
External links
Qinghai Province county-level divisions Xining: Chengzhong District · Chengdong District · Chengxi District · Chengbei District · Datong County · Huangyuan County · Huangzhong County
Haidong: Ping'an County · Ledu County · Minhe County · Huzhu County · Hualong County · Xunhua County
Haibei: Haiyan County · Qilian County · Gangca County · Menyuan County
Hainan: Gonghe County · Tongde County · Guide County · Xinghai County · Guinan County
Huangnan: Tongren County · Jainca County · Zêkog County · Henan County
Golog: Maqên County · Baima County · Gadê County · Darlag County · Jigzhi County · Madoi County
Yushu: Yushu County · Zadoi County · Chindu County · Zhidoi County · Nangqên County · Qumarleb County
Haixi: Delingha City · Golmud City · Wulan County · Dulan County · Tianjun CountyAdministrative Committees: Lenghu · Da Qaidam · Mangya1
^1 — The administrative committees are not standard units of local government, though they do function as such.
■ = Prefecture-level city ■ = Prefecture ■ = Autonomous prefecturesMongol autonomous areas in the People's Republic of China Regions Prefectures
and countiesFuxin · Harqin Left WingOther provincesDorbod (Heilongjiang) · Qian Gorlos (Jilin) · Subei (Gansu) · Weichang (Manchu and Mongol) (Hebei)Tibetan autonomous areas in the People's Republic of China Regions 
Prefectures
and countiesGannan · Tenzhu
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.