- Orange River
-
For other uses, see Orange River (disambiguation).
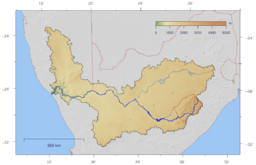
Orange Gariep, Oranje, Senqu River Sunset over the Orange River near Upington in the Northern CapeCountries Lesotho, South Africa, Namibia Tributaries - right Caledon River, Vaal River, Fish River (Namibia) Landmarks Gariep Dam, Augrabies Falls Source Senqu - location Drakensberg mountains, Lesotho Mouth Alexander Bay - location Atlantic Ocean Length 2,200 km (1,367 mi) Basin 973,000 km2 (375,677 sq mi) The course and watershed of the Orange River. This map shows a conservative border for the watershed. Specifically, the Kalahari basin is excluded, as some sources say it is endorheic.[1] Some other sources using computational methods show a basin which includes parts of Botswana (and hence of the Kalahari).[2]The Orange River (Afrikaans/Dutch: Oranjerivier), Gariep River, Groote River or Senqu River is the longest river in South Africa. It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho, flowing westwards through South Africa to the Atlantic Ocean. The river forms part of the international borders between South Africa and Namibia and between South Africa and Lesotho, as well as several provincial borders within South Africa. Although the river does not pass through any major cities, it plays an important role in the South African economy by providing water for irrigation, as well as hydroelectric power. The river was named by Robert Jacob Gordon after the Dutch Royal House.
Contents
Course
The Orange rises in the Drakensberg mountains along the border between South Africa and Lesotho, about 193 km (120 mi) west of the Indian Ocean and at an altitude of over 3,000 m. While in Lesotho, the river is known as the Senqu and parts of it freeze in winter, because of the altitude there.
The river then runs westwards through South Africa, forming the south-western boundary of the Free State province. In this section the river flows into first the Gariep Dam (the largest in the country), and on to the Vanderkloof Dam. From the border of Lesotho to below the Van der Kloof Dam the river bed is deeply incised. Further downstream the land is flatter, and the river is used extensively for irrigation.
At the western point of the Free State, southwest of Kimberley, the Orange meets with its main tributary, the Vaal River, which itself forms much of the northern border of the province. From here the river flows further westwards through the arid wilderness of the southern Kalahari region and Namaqualand in the Northern Cape Province to meet with Namibia at the 20th degree of east longitude. From here it flows westwards for 550 km,[3] forming the international border between the province and Namibia's Karas Region. On the border, the river passes the town of Vioolsdrif, the Customs and Excise post between South Africa and Namibia.
In the last 800 km (500 mi) of its course the Orange receives many intermittent streams and several large wadis lead into it. In this section, the Namib Desert terminates on the north bank of the river, so under normal circumstances the volume of water added by these tributaries is negligible. Here the bed of the river is once again deeply incised. The Hundred Falls or Augrabies Falls are located on this section of the Orange, where the river descends 122 m (400 ft) in a course of 26 km (16 mi).
The Orange empties into the Atlantic Ocean at Alexander Bay, which lies about equidistant between Cape Town and Walvis Bay. Some 33 km (21 mi) from its mouth it is completely obstructed by rapids and sand bars and is generally not navigable for long stretches.
The river has a total length of 2,200 km (1,400 mi).
Tributaries of the Orange River
The river starts at the border between KwaZulu-Natal and Lesotho, high in the Drakensberg Mountains as the Senqu River. Tributaries in Lesotho include: the Koakoatsi River, Tlhanyaku River, Moremoholo River, Mokhotlon River, Sehonghong River, Khubelu River, Makhoaba River, Bobatsi River, Mphelebeko River, Semena River, Nashai River, Litsoeyse River, Matebeng River, Liboleng River, Tsoelike River, Linakeng River, Qabane River, Kolo-La-Tsoene River, Senqunyane River, Qhoali River, Meletsunyane River, Qhuasing River, Outing River, Sebapala River, Thaling River, Masitise River and the Tele River (the border river between South Africa and Lesotho. Tributaries in South Africa include: the Makhaleng River (the west border of Lesotho), Kromspruit, Bamboesspruit, Gryskopspruit, Winnaarspruit, Knoffelspruit, Wilgespruit, Nuwejaarspruit, Kraai River, Melkspruit, Sanddrifspruit, Stormbergspruit, Moddelbulspruit, Palmietspruit, Caledon River, Oudagspruit, Broekspruit, Bossiespruit, Brakspruit, Suurbergspruit, Donkerpoortspruit, Oorlogspoort River, Rietkuilspruit, Vanderwaltsfonteinspruit, Otterspoortspruit, Paaiskloofspruit, Seekoei River, Kattegatspruit, Knapsak River, Hondeblaf River, Berg River, Lemoenspruit, Vaal River, Withoekskloof, Lanyonspruit, Diep River, Brak River, Karabeeloop River, Prieska River, Rooiloop River, Kat River, Marydale River, Soutloop River, Elmboog Sloot, Eselfontein River, Matjies River, Donkerhoekspruit, Helbrandkloofspruit, Hartbeer River, Slang River, Brabees River, Molopo River, Bul River, Kourop River, Bak River, Kraalputs de Loop, Narrie se Loop, Samoep River, Kaboep River, Mik River, Hartbees River, Brak River, Matjies River, Groen River, Kahams River. Tributaries in Namibia include: the Kleinap River, Ham River, Udabis River, Velloor River, Sambok River, Eendoorn River, Girtus River, Hom River, Davignab River, Haib River, Sambok River, Gamkap River.
Catchment and rainfall
 The Augrabies Falls in full flow.
The Augrabies Falls in full flow.
In the dry winter months the volume of the water in the river is considerably reduced because of the rapid run-off and evaporation. At the source of the Orange the rainfall is approximately 2,000 mm per annum but precipitation decreases as the river flows westward; at its mouth the rainfall is less than 50 mm per annum. The factors that support evaporation, on the other hand, tend to increase in a westerly direction. However, in the wet season (summer) the Orange river becomes an impetuous, brown torrent. The huge mass of sediment carried constitutes a long-term threat to all engineering projects on the river.
The total catchment of the Orange River (including the Vaal) extends over 973,000 km², i.e. equivalent to about 77% of the land area of South Africa (1,268,5358 km²). Approximately 366,000 km² (38%), however, is situated outside the country in Lesotho, Botswana and Namibia.
History
Name of the river
The river was first discovered by indigenous Nama people, who called it the Nu Gariep.[3] The river was named the Orange River by Colonel Robert Gordon, commander of the Dutch East India Company garrison at Cape Town, on a trip to the interior in 1779[3]. Gordon named the river in honour of William V of Orange.[3] A popular but incorrect belief is that the river was named after the supposedly orange colour of its water, as opposed to the colour its tributary, the Vaal River ( 'vaal' being Afrikaans for pale or grey).[citation needed] Since the end of apartheid, the original name, "Gariep" has had greater favour in official correspondence in South Africa, although the name "Orange" has greater international recognition.[3] In Lesotho, where the river rises, it is known as the Senqu River.
 Panorama taken from a fluorspar-rich hill overlooking a bend in the River, which was in flood due to above-normal rains.
Panorama taken from a fluorspar-rich hill overlooking a bend in the River, which was in flood due to above-normal rains.
Economy
 The General Hertzog Bridge over the Orange River at Aliwal North on the southwestern border with the Free State. Note the remains of the Frere Bridge on the left.
The General Hertzog Bridge over the Orange River at Aliwal North on the southwestern border with the Free State. Note the remains of the Frere Bridge on the left.
As the collection point for the majority of South Africa's water, the Orange River plays a major role in supporting agriculture, industry and mining. To assist in this, two large water schemes have been created, the Orange River Project and the Lesotho Highlands Water Project. Historically, the river played an important role in the South African diamond rush, with the first diamonds in the country being discovered in alluvial deposits on the Orange. Today, several commercial diamond mines operate along the final stretch of the Orange River and around its mouth. Finally, because of the lack of dangerous animals and high water levels during summer, the river is used for recreational canoeing and rafting.
Orange River Project
The Orange River Project (ORP) was one of the largest and most imaginative projects of its kind in South Africa. It was constructed by Hendrik Verwoerd's government at the height of the apartheid era. The ORP was built to utilise the unused water of the Orange River — which, without the Vaal River, represents some 14.1% of the total runoff in South Africa — and in the process, to satisfy an increasing demand for water. The main objectives of the project were:
- to stabilise river flow,
- the generation and transmission of hydro-electric power,
- to provide a reliable water supply for users in the Orange river basin, and
- to give a new lease of life to water-deficient areas in the Eastern Cape such as the Great Fish and Sundays River valleys.
The Gariep Dam near Colesberg, named the Hendrik Verwoerd Dam when built, is the main storage structure within the Orange River. From here the water is supplied in two directions: westward along the Orange River (via hydro-electric power generators) to the Vanderkloof Dam which was previously named the PK le Roux Dam , and southward through the Orange-Fish Tunnel to the Eastern Cape.
 The Gariep Dam on the Orange River is the largest dam in South Africa, and was a key part of the Orange River Project.
The Gariep Dam on the Orange River is the largest dam in South Africa, and was a key part of the Orange River Project.
Hydro-electricity
Eskom operates hydro-electric power-stations at both the Gariep Dam and the Vanderkloof Dam. The hydro-electric power station at the Vanderkloof Dam was the first power-generation station in South Africa situated entirely underground. The towns Oviston and Oranjekrag were established to facilitate the construction and operation of the new infrastructure.
Irrigation
 A vinyard on the Orange River
A vinyard on the Orange River
Irrigation in the vast area downstream of the Vanderkloof Dam, which has turned thousands of hectares of arid veld into highly productive agricultural land, was made possible by the construction of the Gariep Dam and the Vanderkloof Dam. Old, established irrigation schemes such as those at Buchuberg, Upington, Kakamas and Vioolsdrif have also benefitted because regulation of the flow is now possible.
In recent years the wine producing areas along the Orange River have also grown in importance. See the article Northern Cape wine.
Irrigation in the Eastern Cape has also received a tremendous boost, not only from the additional water that is being made available but also owing to improvement in water quality. Without this improvement the citrus farmers along the Lower Sundays River would almost certainly have continued to suffer losses of productivity.
Lesotho Highlands Water Project
Main article: Lesotho Highlands Water ProjectThe Lesotho Highlands Water Project was conceived to supplement the water supply in the Vaal River System. Water is delivered to South Africa by means of the Delivery Tunnel which passes under the Lesotho South Africa border at the Caledon River and then under the Little Caledon River south of Clarens in the Free State and discharges into the Ash River about 30 km further to the north. The scheme became viable when water demands in Gauteng reached levels that could no longer be supported economically by alternative schemes such as the Tugela River-Vaal River pumped storage scheme, which utilized the Sterkfontein Dam, located near Harrismith in the Free State.
Alluvial diamonds
In 1867, the first diamond discovered in South Africa, the Eureka Diamond, was found near Hopetown on the Orange River. Two years later, a much larger diamond known as the Star of South Africa was found in the same area, causing a diamond rush. This was soon eclipsed by the diamond rush to mine diamonds directly from kimberlite at Kimberley in 1871, although alluvial diamonds continued to be found in the Orange. Today, several commercial diamond mines operate on the last stretch of the river, as well as the beaches around its mouth. Diamond mines also operate on the middle stretch of the river.
Rafting and canoeing
During the temperate months of March and April, given good rains and the sluices of the dams being open a canoeist (or rafter) can easily travel 30 km per day. The lower reaches of the river are most popular, because of the spectacular topography. Commercial tours are available and these expeditions depart from the border town of Vioolsdrif.
Miscellaneous
- Because of the river's geographical position, it is too cold in winter to support crocodiles.
See also
 Twin Falls in Augrabies Falls National Park
Twin Falls in Augrabies Falls National Park
- List of rivers in South Africa
- List of international border rivers
- List of crossings of the Orange River
- Dams on the Orange River
- Armenia Dam
- Egmont Dam
- Gariep Dam
- Newberry Dam
- Vanderkloof Dam
- Welbedacht Dam
- Waterfalls on the Orange River
- Augrabies Falls
- Twin falls
References
- ^ Swanevelder, C. J. (1981), Utilising South Africa's largest river: The physiographic background to the Orange River scheme, GeoJournal vol 2 supp 2 pg 29-40
- ^ Revenga, C.; Murray, S.; Abramovitz, J. and Hammond, A . (1998) Watersheds of the world: Ecological value and vulnerability, World Resources Institute, ISBN 1-56973-254-X
- ^ a b c d e Earle, Anton et al. (2005), A preliminary basin profile of the Orange/Senqu River (pdf), African Centre for Water Research, retrieved 30 June 2007
External links
- Orange-Senqu River Commission (ORASECOM)
- Orange-Senqu River Awareness Kit - knowledge hub for the Orange-Senqu River basin
- Map of the Orange River basin at Water Resources eAtlas
- Map of portion of Orange River basin forming part of South Africa
- Information on the Orange River from the South African Department of Water Affairs and Forestry
Rivers of Lesotho Rivers Caledon · Makhaleng · Malibamat'so · Orange · Senqu · Senqunyane
Categories:- Rivers of Lesotho
- Orange River
- Rivers of South Africa
- Rivers of Namibia
- International rivers of Africa
- Geography of Karas Region
- Vaal River
- Namibia–South Africa border
- Karoo
- Lesotho–South Africa border
- Internal borders of South Africa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.