- North East (London sub region)
-
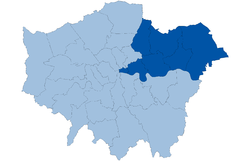
North East London — London Plan sub region — Coordinates: 51°34′N 0°04′E / 51.56°N 0.07°ECoordinates: 51°34′N 0°04′E / 51.56°N 0.07°E Sovereign state United Kingdom Country England Region London Established 2008 Comprises Barking and Dagenham
Havering
Newham
Redbridge
Tower Hamlets
Waltham Forest
City of LondonArea – Total 115.8 sq mi (300 km2) Population – Total 1,400,000 – Density 12,086.6/sq mi (4,666.7/km2) The North East is a sub-region of the London Plan corresponding to the London Boroughs of Tower Hamlets, Newham, Waltham Forest, Redbridge, Havering, Barking and Dagenham, and the City of London.[1] The sub region was established in 2008 and replaced the larger East sub region that had been established in 2004. The north east has a population of 1.4 million and is the location of 900,000 jobs.[1] It is an area that has undergone extensive regeneration as part of the London Docklands and continues as part of the Thames Gateway. It will be the location of the 2012 Summer Olympics.[2] A substantial increase in population is expected in the area.[3]
Contents
Settlement
There are two metropolitan centres in the sub region, at Romford and Ilford; with major centres at Walthamstow, Stratford, Canary Wharf, East Ham and Barking. Large swathes of the south and west of the sub region are planned for regeneration as part of the Thames Gateway project. Opportunity areas are designated at the City Fringe, Canary Wharf, Lower Lea Valley including Stratford, the Royal Docks, Ilford and London Riverside.[4] A total opportunity area of 5,836 hectares.
Metropolitan centres are yellow, major centres pink[4] History
The oldest parts of the sub-region are Tower Hamlets and Hackney. These areas, originally in Middlesex, officially became part of London with the creation of the County of London in 1888. The eastern limit of London at this time became the River Lea which was the traditional boundary between Middlesex and Essex.
Because the strict planning laws of London were not in force on the eastern side of the river the area began to industrialise quickly in places such as Canning Town and Silvertown, now in the borough of Newham. This area became known as 'London over the Border'. In 1965 the boroughs of Newham, Waltham Forest, Redbridge, Barking & Dagenham and Havering were incorporated into Greater London. As a legacy of not being in the original County of London, Newham receives less funding, than for example Tower Hamlets, and is campaigning to be officially recognised as an Inner London borough.
Changing face of the region
Northeast London is today an area of regeneration, with a rising population. The redevelopment of the Docklands area began in the early 1980s, and the Thames Gateway project is now extending regeneration further east, with the London Thames Gateway Development Corporation responsible for planning and delivery of the project in East London. London's successful bid to host the Olympics has kick-started regeneration programmes in the area, and is likely to have an impact on house prices.
Transport
Existing transport routes in the area are the A12 and A13 roads, the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway and the Great Eastern Main Line, part of a large network of suburban National Rail routes operated by National Express East Anglia and c2c; and the London Underground services of the Central Line, District Line, Hammersmith and City Line, and Docklands Light Railway (DLR).
Northeast London has seen considerable improvement with transport in recent years and is the focus for further development over the years leading up to the Olympics and beyond:[4]
- The A12 and A13 have been upgraded.
- A new extension to the DLR to connect with London City Airport opened in December 2005, while work on an extension under the Thames to connect with Woolwich has been completed. Further DLR projects include an extension to Barking Reach and Dagenham Dock, and a direct route to connect with Stratford International station, via West Ham, where High Speed 1 will serve the heart of Stratford City.
- Further connecting the sub-region with the rest of London, an east-west rail route known as Crossrail is currently under construction.
- The East London Transit, a part-segregated bus rapid transit, had its first phase open in 2010, and an additional phase is planned to open in 2013.
Places of interest
- Art: The Diver, Whitechapel Gallery
- Buildings and structures: Canary Wharf, Dagenham wind turbines, ExCeL Exhibition Centre, Limehouse Town Hall, London City Airport, Thames Barrier, Pioneer Point
- Education: University of East London, Queen Mary, University of London
- Markets: Billingsgate, Brick Lane, Columbia Road, New Spitalfields
- Museums: London Gas Museum, Museum in Docklands, North Woolwich Old Station Museum, Upminster Tithe Barn, Upminster Windmill, V&A Museum of Childhood, Ragged School Museum, Walthamstow Pump House Museum, Vestry House Museum, William Morris Gallery.
- Open spaces: Barking Abbey, Langtons, Lower Lea Valley and Lee Valley Park, Thames Chase, Victoria Park, Epping Forest, Mile End Park, Wanstead Park, Valentines Park
- Sports venues: Boleyn Ground, Romford Greyhound Stadium, Romford Ice Arena, Walthamstow Stadium, Brisbane Road, Redbridge Cycling Centre
- Theatre: Queens Theatre, Stratford Circus, Theatre Royal Stratford East
References
- ^ a b GLA, London Plan (2008) - North East London policies
- ^ "University of East London Olympic Partnerships". http://www.uel.ac.uk/2012/office/partners.htm.
- ^ GLA, London Plan (2008) - The strategic priorities for North East London
- ^ a b c GLA, London Plan (2008) - North East London sub region
Sub-regions of London Official London Plan North · North East · South East · South West · West
Other Categories:- London sub regions
- Geography of Barking and Dagenham
- Geography of Havering
- Geography of Newham
- Geography of Tower Hamlets
- Geography of Waltham Forest
- Geography of the City of London
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.