- Pipamazine
-
Pipamazine 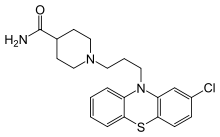
Systematic (IUPAC) name 1-[3-(2-chloro-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)propyl]piperidine-4-carboxamide Clinical data Pregnancy cat. Formerly used for morning sickness Legal status Withdrawn Routes Oral, intramuscular injection Identifiers CAS number 84-04-8 ATC code None PubChem CID 6761 ChemSpider 6503 
UNII 653552FH1N 
KEGG D02606 
Chemical data Formula C21H24ClN3OS Mol. mass 401.95 g/mol  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Pipamazine (INN; trade names Mornidine, Mometine, Nausidol) is a drug of the phenothiazine class formerly used as an antiemetic. It is chemically related to chlorpromazine, but has negligible antipsychotic activity and produces few extrapyramidal side effects.[1]
Pipamazine was introduced to the U.S. market in 1959 by G. D. Searle & Company. It was advertised for morning sickness[2] and postoperative nausea and vomiting, and was claimed to reduce the need for postoperative analgesia.[3] It was eventually withdrawn from the U.S. market in 1969, after reports of hepatotoxicity (liver injury).[4][5]
There is very little published information on pipamazine; it is mostly absent from modern-day sources, apart from a few passing mentions in the pharmacological literature.[1]
Adverse effects
Mornidine advertisements for postoperative recovery claimed "unusually low side effects".[3] However, contemporary comparative trials found that hypotension (low blood pressure) was a substantial concern when the drug was given at normal dosages for this indication; blood pressure reductions of up to 70 mmHg were reported.[6] Reductions in dosage mitigated hypotension while maintaining antiemetic efficacy.
In his book The Creation of Psychopharmacology, Irish psychiatrist David Healy states that the failure of pipamazine to perform as a neuroleptic and its negative side effect profile helped Searle lose interest in the antipsychotic sector, and contributed to the company's refusal to market haloperidol in the United States.[7]
References
- ^ a b Frota LH (2003) (in Portuguese). Cinqüenta anos de medicamentos antipsicóticos em psiquiatria. Rio de Janeiro: UFRJ. pp. 486. ISBN 8590382710. http://www.medicina.ufrj.br/cursos/LH%20FROTA%20-%201%20Ed%20-%2050%20ANOS%20DE%20MEDICAMENTOS%20ANTIPSICOTICOS.pdf.
- ^ [No authors listed] (July 1959). "Now she can cook breakfast again..." (PDF). Canadian Medical Association Journal 81 (1): 59. PMC 1830735. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1830735. Advertisement.
- ^ a b [No authors listed] (April 1960). "Lessened postoperative vomiting with MORNIDINE®" (PDF). Annals of Surgery 151 (4). PMC 1613578. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1613578. Advertisement.
- ^ 34 F.R. 12051. July 17, 1969.
- ^ Wysowski DK, Swartz L (June 2005). "Adverse drug event surveillance and drug withdrawals in the United States, 1969–2002: the importance of reporting suspected reactions". Archives of Internal Medicine 165 (12): 1363–9. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.12.1363. PMID 15983284.
- ^ Blatchford E (March 1961). "Studies of anti-emetic drugs: A comparative study of cyclizine (Marzine®), pipamazine (Mornidine®), trimethobenzamide (Tigan®), and hyoscine". Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 8 (2): 159–65. doi:10.1007/BF03021345.
- ^ Healy D (2002). "Explorations in a new world". The creation of psychopharmacology. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. pp. 123–4. ISBN 0-674-01599-1.
Antiemetics (A04) 5-HT3 Antagonists Alosetron • Azasetron • Bemesetron • Cilansetron • Clozapine • Dazopride • Dolasetron • Granisetron • Lerisetron • Metoclopramide • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Olanzapine • Ondansetron • Palonosetron • Ramosetron • Ricasetron • Tropisetron • ZatosetronCB1 Agonists (Cannabinoids) D2/D3 Antagonists H1 Antagonists (Antihistamines) mACh Antagonists (Anticholinergics) NK1 Antagonists Others Categories:- Antiemetics
- Phenothiazines
- Piperidines
- Withdrawn drugs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
