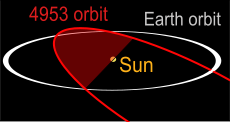
- Minimum orbit intersection distance
-
Minimum orbit intersection distance (MOID) is a measure used in astronomy to assess collision risk between astronomical objects.[1] It is defined as the distance between the closest points of the osculating orbits of the two bodies in question. Of greatest interest is the risk of a collision with Earth; the MOID between an object and Earth is called Earth MOID. Earth MOID is often listed on comet and asteroid databases such as the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Small-body Database.[2] However, MOID can be defined with respect to other bodies as well: Jupiter MOID, Venus MOID and so on.
An object is classified as a potentially hazardous object (PHO) – that is, posing a possible risk to Earth – if, among other conditions, its Earth MOID is less than 0.05 AU. For larger bodies than Earth, there is a risk of collision with a somewhat larger MOID; for instance, Jupiter MOIDs less than 1 AU are considered noteworthy.[3]
A low MOID does not mean that a collision is inevitable, however. It is also necessary that the two bodies reach that point in their orbits at the same time, which will happen eventually unless the two objects are gravitationally locked in orbital resonance. However, this point may be very far in the future, and the orbit of the smaller body may be disturbed by other planets. Calculations become increasingly inaccurate as trajectories are projected further forward in time, especially beyond times where the body is disturbed in passing a planet. MOID has the advantage that it is obtained directly from the orbital elements of the body and no projection into the future is required.[4] Because MOID is used as a snapshot of current risk, it is calculated from the simple Keplerian orbits of the bodies with no adjustment for perturbations.[3]
The only object that has ever been rated at 4 on the Torino scale (since downgraded), the Aten asteroid 99942 Apophis, has a MOID of 0.00017 AU. This is not the smallest MOID in the catalogues; many bodies with smaller MOID are not classed as PHO's because of their small size. For comparison, the only object that has been detected and had its MOID calculated before it hit the Earth was the small meteoroid 2008 TC3. This object was listed with a MOID of 0.00001 AU in the Minor Planet Center database, and is the smallest MOID calculated for an Apollo asteroid.[5] It is even smaller at the more precise JPL Small Body Database (0.0000078 AU).[6]
See also
- List of Mercury-crossing minor planets
- List of Venus-crossing minor planets
- List of Earth-crossing minor planets
- List of Mars-crossing minor planets
- List of Jupiter-crossing minor planets
- List of Saturn-crossing minor planets
- List of Uranus-crossing minor planets
- List of Neptune-crossing minor planets
References
- ^ Basics of Space Flight: The Solar System, p3, NASA JPL, retrieved 14th May 2009.
- ^ JPL Small-body Database Browser
- ^ a b Bruce Koehn, "Minimum Orbital Intersection Distance", Lowell Observatory, retrieved online 14th May 2009.
- ^ Brian G. Marsden, "Press Information Sheet:Potentially Hazardous Asteroids", Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, retrieved online 3rd May 2009.
- ^ List Of Apollo Minor Planets, International Astronomical Union: Minor Planet Center, retrieved 14th May 2009.
- ^ 2008 TC3 at JPL Small Body Database. Retrieved 14th May 2009.
External links
- Sentry Risk Table (current) by NEO Program
- List of the Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs)
- MBPL - Minor Body Priority List ( PHA Asteroids )
- SAEL - Small Asteroids Encounters List
- TECA Table of Asteroids Next Closest Approaches to the Earth
The Solar System 
Small Solar System bodies Minor planets - Designation
- Groups
- Moons
- Meanings of names
- Pronunciation of names
Comets Meteoroids Lists / categories - Asteroid groups and families
- Asteroid moons
- Binary asteroids
- Minor planets
Categories:- Near-Earth objects
- Space hazards
- Orbits
- Astrodynamics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.