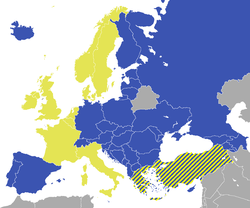
- Member states of the Council of Europe
-
Notes on table;
aGreece and Turkey also considered as founders of the organisation.
bIn 1950, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany), est. 23 May 1949, and then French-occupied Saar (protectorate) became associate members. (West) Germany became a full member in 1951, while the Saarland withdrew from its associate membership in 1956 after acceding to the Federal Republic after a referendum in 1955. The Soviet-occupied eastern part of Germany and later East German Democratic Republic never became a member of the Council of Europe. Through German reunification in 1990, the five Länder (i.e. states/regions) of East Germany acceded to the Federal Republic of Germany and thus gained representation in the Council of Europe.
c Joined under the provisional reference "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (including quotation marks).[1] Majority of countries recognise the country with its constitutional name.
dOriginally joined as Serbia and Montenegro.
eWithdrew from Council in September, 1967, until 1974 during the Regime of the Colonels.The Council of Europe has 47 member states.
The Council of Europe was founded on 5 May 1949 by Belgium, Denmark, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Greece and Turkey joined three months later, and Iceland and Germany the next year. It now has 47 member states, with Montenegro being the latest to join.
Article 4 of the Council of Europe Statute specifies that membership is open to any "European" State. As a result, nearly all European states have acceded to the Council of Europe, with the exception of Belarus (human rights concerns), Kazakhstan (human rights concerns/not sufficient democratization[citation needed]), Vatican City (a theocracy) and some of the states with limited recognition.
Flag State Date joined 
Belgium Founder 
Denmark Founder 
France Founder 
Ireland Founder 
Italy Founder 
Luxembourg Founder 
Netherlands Founder 
Norway Founder 
Sweden Founder 
United Kingdom Founder 
Greecea, e 9 August 1949 
Turkeya 9 August 1949 
Iceland 7 March 1950 
Germanyb 13 July 1950 
Austria 16 April 1956 
Cyprus 24 May 1961 
Switzerland 6 May 1963 
Malta 29 April 1965 
Portugal 22 September 1976 
Spain 24 November 1977 
Liechtenstein 23 November 1978 
San Marino 16 November 1988 
Finland 5 May 1989 
Hungary 6 November 1990 
Czechoslovakia 21 January 1991 – 31 December 1992 
Poland 26 November 1991 
Bulgaria 7 May 1992 
Estonia 14 May 1993 
Lithuania 14 May 1993 
Slovenia 14 May 1993 
Czech Republic 30 June 1993 
Slovakia 30 June 1993 
Romania 7 October 1993 
Andorra 10 November 1994 
Latvia 10 February 1995 
Albania 13 July 1995 
Moldova 13 July 1995 
Macedoniac 9 November 1995 
Ukraine 9 November 1995 
Russia 28 February 1996 
Croatia 6 November 1996 
Georgia 27 April 1999 
Armenia 25 January 2001 
Azerbaijan 25 January 2001 
Bosnia and Herzegovina 24 April 2002 
Serbiad 3 April 2003 
Monaco 5 October 2004 
Montenegro 11 May 2007 Following its declaration of independence on 3 June 2006, Montenegro submitted a request to accede to the Council of Europe. The Committee of Ministers transmitted the request to the Parliamentary Assembly for opinion, in accordance with the usual procedure.[2] Eleven days later, on 14 June 2006, the Committee of Ministers declared that the Republic of Serbia would continue the membership of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro.[3] On 11 May 2007, Montenegro joined the Council of Europe as the 47th member state.
 This coin was issued in Armenia to commemorate Armenia's accession to the Council in 2001
This coin was issued in Armenia to commemorate Armenia's accession to the Council in 2001
Contents
Applicants
Special Guest status with the Assembly was established as a provisional status for parliaments of European non-member states which applied for membership in the Council of Europe.[4]
The Parliament of Belarus held special guest status with the Parliamentary Assembly from September 1992 to January 1997, but this has been suspended as a consequence of the November 1996 constitutional referendum and parliament by-elections which the CoE found to be undemocratic, as well as limits on democratic freedoms such as freedom of expression (cf. Belarusian media) under the administration of President Alexander Lukashenko. The constitution changed by the referendum "does not respect minimum democratic standards and violates the principles of separation of powers and the rule of law.[5] Belarus applied for full membership on 12 March 1993 (still open).
Kazakhstan applied for the Special Guest status with the Parliamentary Assembly in 1999. The Assembly found that Kazakhstan could apply for full membership, because 4% of its territory, west of the Ural river, is located in Europe,[6] but granting Special Guest status would require improvements in the fields of democracy and human rights. Kazakhstan signed a co-operation agreement with the Assembly in April 2004. In November 2006, the Kazakhstan Parliament officially asked to be granted observer status with the Assembly. On 15 to 16 March 2010, the President of the Council of Europe's Parliamentary Assembly (PACE) made an official visit to Kazakhstan,[7] resulting in the conclusion that the Council of Europe and Kazakhstan strengthen their relations. This milestone emboldens Kazakhstan's "Path to Europe" programme, as outlined by Kazakh president Nursultan Nazarbayev in Astana in 2008.[8]
Observers
Observer status was designed for non-European democracies willing to contribute to democratic transitions in Europe.[4]
Canada, Japan, Mexico, the U.S. and the Holy See have observer status with the Council of Europe and can participate in the Committee of Ministers and all intergovernmental committees. They may contribute financially to the activities of the Council of Europe on a voluntary basis.
The parliaments of Canada, Israel and Mexico have observer status with the Parliamentary Assembly and their delegations can participate in Assembly sessions and committee meetings. Representatives of the Palestinian Legislative Council may participate in Assembly debates concerning the Middle East as well as Turkish-Cypriot representatives from Northern Cyprus concerning this island.
There has been criticism concerning the observer status of Japan and the United States because both countries apply the death penalty.[9] The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe has been lobbying for the United States and Japan to abolish the death penalty or lose their observer status. The Council also voted to restore Special Guest status to Belarus, on condition that Belarus declare a moratorium on the death penalty.
Partners
In 2009 Assembly established a new status for institutional co-operation with parliaments of non-member states in neighboring regions wishing to be supported by the Assembly in their democratic transitions and to participate in the political debate on common challenges.[4]
The new status is called "Partner for democracy" and interested states could obtain it if they commit to embrace the values of the Council of Europe such as pluralist democracy, the rule of law and respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms; to encourage a moratorium on executions and abolish the death penalty; to organize free and fair elections; to become party to the relevant CoE conventions; to utilize the expertize of the Assembly and the Venice Commission in its institutional and legislative work.[4]
CoE has adopted the policy of dialogue with the neighboring regions of the southern Mediterranean, the Middle East and Central Asia – based on respect for universal human rights. Following this policy the Assembly has already established working contacts with parliaments of neighbouring countries other than those of the CoE Observers: Algeria, Kazakhstan, Morocco, Tunisia and the Palestinian Legislative Council. Several of these parliaments have expressed interest in upgrading the status of the existing co-operation, and in establishing a relationship on a permanent basis. Since 1994 the parliaments of the countries bordering the Council of Europe member states have the possibility of concluding special co-operation agreements with the Assembly, but it has not generated much interest among the parliaments concerned, which suggests that it does not offer sufficient clarity and visibility. So far only the Kazakhstan Parliament had taken advantage of it since 2004. In November 2006, the Kazakhstan Parliament officially asked to be granted observer status with the Assembly. Such formal or informal requests are made by a number of parliaments that are already co-operating with it but think that the institutionalized recognition of that co-operation could make it more visible, more coherent and more effective. However the observer status is considered inappropriate in these cases, as it requires that the state receiving it already complies with the CoE core values and principles, which is not the case for the states currently requesting it, who are in the early stages of democratic transition.[4]
The newly established "Partner for democracy" status is similar to the co-operation initiatives of other intergovernmental organizations of mostly European states such as the European Neighbourhood Policy of the EU, the partners for co-operation of OSCE, the cooperation with non-member states of NATO.
Morocco and Palestine have been given "Partner for Democracy Status".[10][11]
The national parliaments eligible to request a "Partner for democracy" status are from the following countries:[4]
- southern Mediterranean and Middle East participants in the Union for the Mediterranean: Mauritania, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and maybe Libya[12]
- Central Asian participants in the OSCE: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
- other states if the Bureau of the Assembly so decides
As of 2010 no parliament has applied for "Partner for democracy" status, but initial discussion are held with Kazakhstan.[7]
References
- ^ "Statute of the Council of Europe". Council of Europe. 5 May 1949. http://conventions.coe.int/Treaty/en/Treaties/Html/001.htm. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- ^ "Request by the Republic of Montenegro for accession to the Council of Europe". Council of Europe. 14 June 1949. https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?id=1010157. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- ^ "Continuation by the Republic of Serbia of membership of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro in the Council of Europe". Council of Europe. 14 June 2006. https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?id=1010125. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f Establishment of a “Partner for democracy” status with the Parliamentary Assembly
- ^ "Belarus : a referendum under a 'hardening dictatorial regime'". Council of Europe. 2004. http://assembly.coe.int/ASP/APFeaturesManager/defaultArtSiteView.asp?ArtId=362. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- ^ II General information, point 11 on Council of Europe document 11007 dated 07 July 2006 at http://assembly.coe.int/Main.asp?link=/Documents/WorkingDocs/Doc06/EDOC11007.htm
- ^ a b http://assembly.coe.int/ASP/NewsManager/EMB_NewsManagerView.asp?ID=5361&L=2
- ^ http://www.kazembassy.org.uk/path_to_europe_state_programme.html
- ^ "Europarådet kan frånta USA observatörsstatus". Yelah. 2004. http://www.yelah.net/articles/20020226183029. Retrieved 22 February 2008.
- ^ http://www.dailystar.com.lb/News/Middle-East/2011/Oct-05/150490-council-of-europe-body-gives-palestinians-partner-status.ashx#axzz1a5JmHE9k
- ^ http://www.jpost.com/MiddleEast/Article.aspx?id=240529
- ^ Libya is observer of the Union for the Mediterranean.[citation needed]
Categories:- Member states of the Council of Europe
- Member states by organization
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.