- McDonnell Douglas T-45 Goshawk
-
T-45 Goshawk The T-45A in flight Role Naval trainer aircraft Manufacturer McDonnell Douglas
Boeing
BAE SystemsFirst flight 16 April 1988[1] Introduction 1991 Primary user United States Navy Number built 214 as of 31 December 2008[2] Developed from BAE Hawk The T-45 Goshawk is a highly modified version of the BAE Hawk land-based training jet aircraft. Manufactured by McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) and British Aerospace (now BAE Systems), the T-45 is used by the United States Navy as an aircraft carrier-capable trainer.
Contents
Design and development
The T-45 Goshawk is a fully carrier-capable version of the British Aerospace Hawk Mk.60.[1][3] It was developed as a jet flight trainer for the United States Navy (USN) and United States Marine Corps (USMC).
The Goshawk's origins began in the mid-1970s, when the US Navy began looking for replacement for its T-2 and TA-4 trainers.[4][5] The US Navy started the VTXTS advanced trainer program in 1978. British Aerospace and McDonnell Douglas proposed a version of the Hawk and were awarded the T-45 contract in 1981.[6]
The Hawk had not been designed for carrier operations and numerous modifications were required to make it carrier-suitable. These included improvements to the low-speed handling characteristics and a reduction in the approach speed.[4] Other changes were strengthened airframe,[7] more robust and wider landing gear with catapult tow bar attachment and an arresting hook.[4] It features a two-wheel nose landing gear.[8]
The Goshawk first flew in 1988 and became operational in 1991.[8] BAE Systems manufactures the fuselage aft of the cockpit, the air inlets, the vertical stabilizer of the T-45 at Samlesbury, and the wings at Brough, England. Boeing, which merged with McDonnell Douglas in 1997, manufactures the remainder of the aircraft and assembles them in St. Louis, Missouri.
On 16 March 2007 the 200th airframe was delivered to the US Navy. Their requirements call for 223 aircraft.[9] All T-45A aircraft will eventually be converted to a T-45C configuration under the T-45 Required Avionics Modernization Program (T-45 RAMP).
Operational history
The T-45 has been used for intermediate and advanced portions of the Navy/Marine Corps Student Naval Aviator strike pilot training program with Training Air Wing One at Naval Air Station Meridian, Mississippi and Training Air Wing Two at Naval Air Station Kingsville, Texas. The T-45 replaced the T-2C Buckeye intermediate jet trainer and the TA-4J Skyhawk II advanced jet trainer with an integrated training system that includes the T-45 Goshawk aircraft, operational and instrument flight simulators (OFT/IFT), academics, and training integration system support. In 2008, the T-45C also began operation in the advanced portion of Navy/Marine Corps Student Naval Flight Officer (NFO) training with Training Air Wing Six at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
The T-45A, which became operational in 1991, contains an analog cockpit design while the newer T-45C, which was first delivered in December 1997, features a new digital "glass cockpit" design. The T-45A and C models are currently in operational use. The T-45 is to be in service until 2035 or later.[9]
Variants
- T-45A
- Two-seat basic and advanced jet trainer for the US Navy.
- T-45B
- Proposed land-based version for the US Navy, which would have been basically a conventional Hawk with a USN cockpit and no carrier capability. The USN had wanted the T-45B to get an earlier training capability, but abandoned the idea in 1984 in favor of less-costly updates to the TA-4J and T-2C.
- T-45C
- Improved T-45A with glass cockpit, inertial navigation, and other improvements. Existing T-45As are being upgraded to the T-45C standard.[10]
Operators
- United States Navy operates the T-45C variant (glass cockpit, HUD).
Specifications (T-45A)
Data from The International Directory of Military Aircraft, 2002-2003,[3] Navy fact file[8]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 (student, instructor)
- Length: 39 ft 4 in (11.99 m)
- Wingspan: 30 ft 10 in (9.39 m)
- Height: 13 ft 5 in (4.08 m)
- Wing area: 190.1 ft² (17.7 m²)
- Empty weight: 10,403 lb (4,460 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 14,081 lb (6,387 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce Turbomeca F405-RR-401 (Adour) turbofan, 5,527 lbf (26 kN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 560 knots, (645 mph, 1,038 km/h) at 8,000 ft
- Range: 700 nmi (805 mi, 1288 km)
- Service ceiling: 42,500 ft (12,950 m)
- Rate of climb: 8,000 ft/min (40.6 m/s)
Armament
- Usually none. One hardpoint under each wing can be used to carry practice bomb racks, rocket pods, or fuel tanks. A centerline hardpoint can carry a cargo pod for crew baggage.
Avionics
Data from naval-technology.com [1]
- Smiths Industries, Ltd. AN/USN-2(V) Standard Attitude Heading and Reference System (SAHRS). Later replaced by the BAE/Marconi AN/ASN-180 Navigation Guidance System (NGS).
- Rockwell Collins AN/ARN-144 VHF Omnidirectional Radio Range / Instrument Landing System (VOR/ILS).
- Honeywell AN/APN-194 Radar Altimeter.
- Northrop Grumman AN/ASN-166 Inertial Guidance Set (IGS). [2] Incorporates a Northrop Grumman (formerly Litton) LN-100G Ring Laser Gyroscope, a Rockwell Collins Global Positioning System (GPS), and a Kalman filter.[3]
Communications Suite
Data from naval-technology.com [4]
- Rockwell Collins AN/ARN-182 UHF/VHF radio.
- Honeywell AN/APX-100 Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) system.
See also
 External images
External imagesHi-res cutaway of T-45 Goshawk 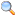
Hi-res cutaway of T-45 Goshawk by Flight Global. - Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
- ^ a b Donald, David: Warplanes of the Fleet, p. 175. AIRtime Publishing Inc, 2004. ISBN 1-880588-81-1
- ^ "T-45 Training System". Boeing Defense, Space & Security. http://www.boeing.com/defense-space/military/t45/index.htm. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ a b Frawley, Gerard: The International Directory of Military Aircraft, p. 48. Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd, 2002. ISBN 1-875671-55-2
- ^ a b c Goebel, Greg, "T-45 Goshawk". VectorSite.net, 1 March 2006.
- ^ T-45 history page. US Navy, 16 November 2000.
- ^ T-45 history on GlobalSecurity.org
- ^ Frawley, Gerard: The International Directory of Military Aircraft, Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd, 2002. ISBN 1-875671-55-2
- ^ a b c T-45A US Navy fact file
- ^ a b "Boeing Delivers 200th T-45 Trainer to U.S. Navy". Boeing, 16 March 2007.
- ^ http://www.defenseindustrydaily.com/us-carrier-pilots-t45-training-system-updated-03022/
External links
- T-45 Goshawk US Navy fact file and T-45 US Navy history page
- T-45 Goshawk page and T-45 Goshawk history page on Boeing.com
- BAE Hawk at Greg Goebel's AIR VECTORS
- T-45 Goshawk page on GlobalSecurity.org
- Boeing/BAE SYSTEMS T-45 Goshawk page on Aeroflight.co.uk
- T-45A/C Goshawk page on Naval-Technology.com
- US Navy to add synthetic radar to Goshawk, eyes T-45D, Flightglobal.com
- FAS Page on the T-45
- Boeing Page on the T-45TS - the T-45 Training System
McDonnell and McDonnell Douglas military aircraft and spacecraft Fighters USAAF/US Air ForceUS Navy/USMCExportLicensedAttack US Navy/USMCTrainers US NavyT-45
Transports US Air ForceUS NavyLicensedHelicopters US Army/US Air ForceUS NavyXHJH · XHCH · XHRH
ExportDrones (UAVs) US NavyKDH
Experimental US Army/US Air ForceXV-1 · X-36 · F-15 STOL/MTD · Bird of Prey
Spacecraft NASAUS Air ForceUSAAC/USAAF/USAF/Tri-service trainer aircraft Advanced Trainer Basic Combat Basic Trainer Primary Trainer (1924-1948) Trainer (1948-1990) "T-1", "T-2", "T-3" and "T-6" have also been assigned since 1962 in a separate sequence.Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Boeing aircraft
- British Aerospace aircraft
- Carrier-based aircraft
- McDonnell Douglas aircraft
- United States military trainer aircraft 1980–1989
- Single-engined jets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




