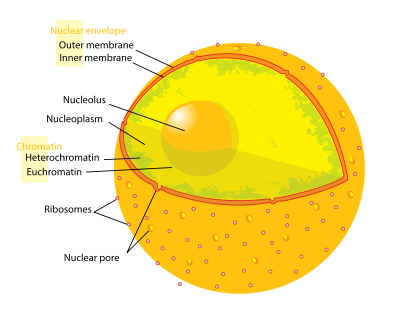
- Nuclear envelope
-
A nuclear envelope (NE) (also known as the perinuclear envelope, nuclear membrane, nucleolemma or karyotheca) is a double lipid bilayer that encloses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. The nuclear envelope also serves as the physical barrier, separating the contents of the nucleus (DNA in particular) from the cytosol (cytoplasm). Many nuclear pores are inserted in the nuclear envelope, which facilitate and regulate the exchange of materials (proteins such as transcription factors, and RNA) between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Each of the two membranes is composed of a lipid bilayer. The outer membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum while the inner nuclear membrane is the primary residence of several inner nuclear membrane proteins. The outer and inner nuclear membrane are fused at the site of nuclear pore complexes. The structure of the membrane also consists of ribosomes.
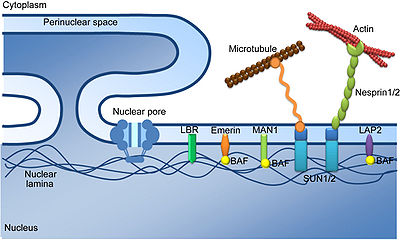 The three layers of NE proteins. The nuclear pore complex (NPC) transverses the inner and outer nuclear membranes. Perinuclear space is clearly visible. INM proteins, including SUN1, LAP2, Emerin, MAN1 and LBR, are mostly associated with the nuclear lamina. Emerin, LAP2 and MAN1 harbor a LEM domain which interacts with BAF (barrier-to-autointegration factor), a chromatin-binding protein. The nuclear lamina forms a meshwork underlying the inner nuclear membrane. Chi et al. Journal of Biomedical Science 2009.[1]
The three layers of NE proteins. The nuclear pore complex (NPC) transverses the inner and outer nuclear membranes. Perinuclear space is clearly visible. INM proteins, including SUN1, LAP2, Emerin, MAN1 and LBR, are mostly associated with the nuclear lamina. Emerin, LAP2 and MAN1 harbor a LEM domain which interacts with BAF (barrier-to-autointegration factor), a chromatin-binding protein. The nuclear lamina forms a meshwork underlying the inner nuclear membrane. Chi et al. Journal of Biomedical Science 2009.[1]
The inner nuclear membrane is connected to the nuclear lamina, a network of intermediate filaments composed of various lamins (A, B1, B2, & C). The lamina acts as a site of attachment for chromosomes and provides structural stability to the nucleus. The lamins have been associated with various genetic disorders collectively termed laminopathies.
The space between the two membranes that make up the nuclear envelope is called the perinuclear space (also called the perinuclear cisterna, NE Lumen), and is usually about 20 - 40 nm wide.
The nuclear envelope has been postulated to play a role in the organization and transcriptional activity of chromatin.
References
- ^ Chi YH, Chen ZJ, Jeang KT (2009). "The nuclear envelopathies and human diseases". J. Biomed. Sci. 16: 96. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-16-96. PMC 2770040. PMID 19849840. http://www.jbiomedsci.com/content/16//96.
External links
- Histology at BU 20102loa
- Animations of nuclear pores and transport through the nuclear envelope
- Illustrations of nuclear pores and transport through the nuclear envelope
- MeSH Nuclear+envelope
Structures of the cell membrane Membrane lipids Membrane protein locations Membrane glycoproteins, Integral membrane proteins/transmembrane protein, Peripheral membrane protein/Lipid-anchored proteinOther Caveolae/Coated pits - Cell junctions - Glycocalyx - Lipid raft/microdomains - Membrane contact sites - Membrane nanotubes - Myelin sheath - Nodes of Ranvier - Nuclear envelope - Phycobilisomes - PorosomesStructures of the cell nucleus / nuclear protein Envelope (membrane)/
nuclear laminaNucleolus Other Chromatin · Dot (PML body) · Paraspeckle
SMC protein: Cohesin (SMC1A, SMC1B, SMC3) · Condensin (NCAPD2, NCAPD3, NCAPG, NCAPG2, NCAPH, NCAPH2, SMC2, SMC4) · DNA repair (SMC5, SMC6)
Transition nuclear protein: TNP1, TNP2
Nuclear matrix · Nucleoplasm · Nucleoskeleton · Nucleosol
see also transcription factors and intracellular receptorsCategories:- Cell anatomy
- Nuclear substructures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.