- Cycloguanil
-
Cycloguanil 
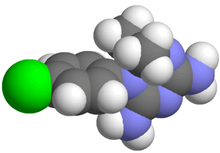
Systematic (IUPAC) name 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6,6-dimethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 516-21-2 ATC code P01BB02 PubChem CID 9049 ChemSpider 8697 
UNII 26RM326WVN 
ChEMBL CHEMBL747 
Chemical data Formula C11H14ClN5 Mol. mass 251.715 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Cycloguanil is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor,[1] and is a metabolite of the antimalarial drug proguanil; its formation in vivo has been thought to be primarily responsible for the antimalarial activity of proguanil[2]. However, more recent work has indicated that, while proguanil is synergistic with the drug atovaquone (as in the combination Malarone), cycloguanil is in fact antagonistic to the effects of atovaquone, suggesting that, unlike cycloguanil, proguanil may have an alternative mechanism of antimalarial action besides dihydrofolate reductase inhibition.[3]
Although cycloguanil is not currently in general use as an antimalarial, the continuing development of resistance to current antimalarial drugs has led to renewed interest in studying the use of cycloguanil in combination with other drugs.[4]
References
- ^ Srivastava IK, Vaidya AB (June 1999). "A mechanism for the synergistic antimalarial action of atovaquone and proguanil". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43 (6): 1334–9. PMC 89274. PMID 10348748. http://aac.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10348748.
- ^ Watkins, W. ; S. (Jun 1984). "The activity of proguanil and its metabolites, cycloguanil and p-chlorophenylbiguanide, against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro" (Free full text). Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 78 (3): 273–278. ISSN 0003-4983. PMID 6385887. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/r?dbs+hsdb:@term+@rn+54-05-7.
- ^ Thapar, M. ; G. (May 2003). "Pharmacodynamic interactions among atovaquone, proguanil and cycloguanil against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 97 (3): 331–337. doi:10.1016/S0035-9203(03)90162-3. ISSN 0035-9203. PMID 15228254.
- ^ Walzer, P. ; F. (Jul 1993). "Synergistic combinations of Ro 11-8958 and other dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors with sulfamethoxazole and dapsone for therapy of experimental pneumocystosis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 37 (7): 1436–1443. ISSN 0066-4804. PMC 187990. PMID 8363372. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=187990.
Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – Chromalveolate antiparasitics (P01) Alveo-
lateIndividual
agentsOtherDHFR inhibitors
(antifols)Sulfadoxine • sulfamethoxypyrazineCoformulationFansidar# (sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine)OtherCombi-
nationsFixed-dose (coformulated) ACTsartemether-lumefantrine#
artesunate-amodiaquine (ASAQ)
artesunate-mefloquine (ASMQ)
dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine
artesunate-pyronaridineOther combinations
(not co-formulated)artesunate/SP • artesunate/mefloquine •
quinine/tetracycline • quinine/doxycycline • quinine/clindamycinHetero-
kont#WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III 
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
