- Cobalt(II) nitrate
-
Cobalt(II) nitrate  Other namesCobaltous nitrate
Other namesCobaltous nitrate
Nitric acid, cobalt(2+) saltIdentifiers CAS number 10141-05-6  ,
,
10026-22-9 (hexahydrate)PubChem 25000 ChemSpider 23369 
UNII 65W79BFD5V 
EC number 233-402-1 RTECS number GG1109000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Co+2].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
Properties Molecular formula Co(NO3)2 Molar mass 182.943 g/mol (anhydrous)
291.03 g/mol (hexahydrate)Appearance pale red powder (anhydrous)
red crystalline (hexahydrate)Density 2.49 g/cm3 (anhydrous)
1.87 g/cm3 (hexahydrate)Melting point 100 °C, decomp (anhydrous)
55 °C (hexahydrate)Boiling point 100–105 °C, decomp (hexahydrate)
Solubility in water 134 g/100 ml, 0 °C (hexahydrate)
soluble (anhydrous)Solubility soluble in alcohol, acetone (hexahydrate) Structure Coordination
geometrymonoclinic (hexahydrate) Hazards MSDS Cobalt (II) Nitrate MSDS EU Index 027-009-00-2 EU classification Carc. Cat. 2
Muta. Cat. 3
Repr. Cat. 2
Toxic (T)
Dangerous for the environment (N)R-phrases R49, R60, R42/43, R68, R50/53 NFPA 704 Related compounds Other anions Cobalt(II) sulfate
Cobalt(II) chloride
Cobalt oxalateOther cations Iron(III) nitrate
Nickel(II) nitrate (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cobalt nitrate is the inorganic cobalt(II) salt of nitric acid, often with various amounts of water. It is more commonly found as a hexahydrate, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a red-brown deliquescent salt that is soluble in water and other polar solvents.
Contents
Composition and structures
As well as the anhydrous compound Co(NO3)2, there are several hydrates of cobalt(II) nitrate. The various degrees of hydration can be summarised by the general chemical formula Co(NO3)2·nH2O, where n = 0, 2, 4, 6.
Anhydrous cobalt(II) nitrate adopts a three-dimensional polymeric network structure, with each cobalt(II) atom approximately octahedrally coordinated by six oxygen atoms, each from a different nitrate ion. Each nitrate ion coordinates to three cobalts.[1] The dihydrate is a two-dimensional polymer, with nitrate bridges between Co(II) centres and hydrogen bonding holding the layers together. The tetrahydrate consists of discrete, octahedral [(H2O)4Co(NO3)2] molecules. The hexahydrate is better described as hexaaquacobalt(II) nitrate, [Co(OH2)6][NO3]2, as it consists of discrete [Co(OH2)6]2+ and [NO3]− ions.[2]
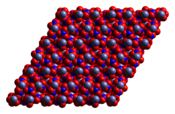
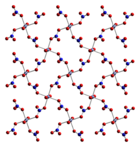
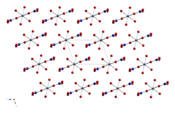
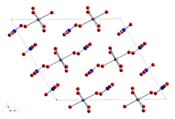
Co(NO3)2 Co(NO3)2·2H2O Co(NO3)2·4H2O Co(NO3)2·6H2O Uses
The high solubility of cobalt nitrate makes it a common source of cobalt in metal-organic frameworks and coordination chemistry. It is also reduced to metallic cobalt or precipitated on various substrates for Fischer-Tropsch catalysis.[3]
Production
It is derived from reacting metallic cobalt or one of its oxides, hydroxides, or carbonate with nitric acid. It is commonly used in dyes and inks.[4]
- CoCO3 + 2 HNO3 + 5 H2O → Co(NO3)2(H2O)6 + CO2
Above 55 °C, it dehydrates to the trihydrate and at higher temperatures to the monohydrate.
References
- ^ Tikhomirov, G. A.; Znamenkov, K. O.; Morozov, I. V.; Kemnitz, E.; Troyanov, S. I. (2002). "Anhydrous Nitrates and Nitrosonium Nitratometallates of Manganese and Cobalt, M(NO3)2, NO[Mn(NO3)3], and (NO)2[Co(NO3)4]: Synthesis and Crystal Structure". Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 628 (1): 269–273. doi:10.1002/1521-3749(200201)628:1<269::AID-ZAAC269>3.0.CO;2-P.
- ^ Prelesnik, P. V.; Gabela, F.; Ribar, B.; Krstanovic, I. (1973). Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2: 581–583.
- ^ Ernst B, Libs S, Chaumette P, Kiennemann A. Appl. Catal. A 186 (1-2): 145-168 1999
- ^ Lewis, Richard J., Sr. (2002). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary (14th Edition). John Wiley & Sons. http://www.knovel.com/knovel2/Toc.jsp?BookID=704&VerticalID=0
Cobalt compounds Categories:- Cobalt compounds
- Nitrates
- Oxidizing agents
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

