- Cobalt(II,III) oxide
-
Cobalt(II,III) oxide[1] 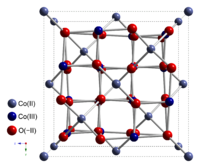 cobalt(II) dicobalt(III) oxideOther namescobalt oxide, cobalt(II,III) oxide, cobaltosic oxide, tricobalt tetroxide
cobalt(II) dicobalt(III) oxideOther namescobalt oxide, cobalt(II,III) oxide, cobaltosic oxide, tricobalt tetroxideIdentifiers CAS number 1308-06-1 
ChemSpider 9826389 
RTECS number GG2500000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Co]=O.O=[Co]O[Co]=O
Properties Molecular formula Co3O4
CoO.Co2O3
Molar mass 240.80 g mol−1 Appearance black solid Density 6.11 g/cm3 Melting point 895 °C
Boiling point 900 °C (decomposes)
Solubility in water Insoluble Solubility soluble in acids and alkalis Hazards R-phrases R40 R41 R42 R43 S-phrases S36/37 NFPA 704  oxide (verify) (what is:
oxide (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cobalt(II,III) oxide is inorganic compound with the formula Co3O4. It is one of two well characterized cobalt oxides. It is a black antiferromagnetic solid. As a mixed valence compound, its formula is sometimes written as CoIICoIII2O4 and sometimes as CoO.Co2O3.[2]
Contents
Structure
Co3O4 adopts the normal spinel structure, with Co2+ ions in tetrahedral interstices and Co3+ ions in the octahedral interstices of the cubic close-packed lattice of oxide anions[2].
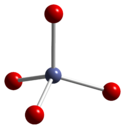
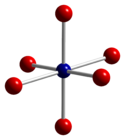
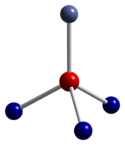
tetrahedral coordination geometry of Co(II) distorted octahedral coordination geometry of Co(III) distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry of O Synthesis
Cobalt(II) oxide, CoO, converts to Co3O4 if heated to around 1000 °C in air. Above 900 °C, CoO is stable.[3] These reaction are described by the following equilibrium:
- Co3O4
 3 CoO + 1/2 O2
3 CoO + 1/2 O2
Research
This inorganic compound is currently utilized in the process of artificial photosynthesis. Artificial photosynthesis is being used to create an alternative liquid fuel.
Safety
Cobalt compounds are potentially poisonous in large amounts.[4]
References
Cobalt compounds Categories:- Cobalt compounds
- Oxides
- Mixed valence compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


