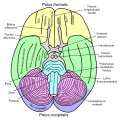
- Fusiform gyrus
-
Brain: Fusiform gyrus 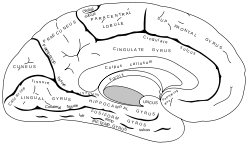
Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere. (Fusiform gyrus visible near bottom) 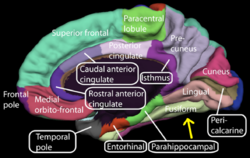
Medial surface of right cerebral hemisphere. (Fusiform gyrus visible near bottom) Latin gyrus fusiformis Gray's subject #189 824 NeuroNames hier-121 NeuroLex ID birnlex_1641 The fusiform gyrus is part of the temporal lobe in Brodmann Area 37. It is also known as the (discontinuous) occipitotemporal gyrus. [1] Other sources have the fusiform gyrus above the occipitotemporal gyrus and underneath the parahippocampal gyrus.[2]
Contents
Function
There is still some dispute over the functionalities of this area, but there is relative consensus on the following:
- processing of color information
- face and body recognition (see Fusiform face area)
- word recognition
- number recognition [questionable: may only be as a result of a global response of any generic recognition tasks, further statistical evidence needed]
- within-category identification
Some researchers think that the fusiform gyrus may be related to the disorder known as prosopagnosia, or face blindness. Research has also shown that the fusiform face area, the area within the fusiform gyrus, is heavily involved in face perception but only to any generic within-category identification which is shown to be one of the functions of the fusiform gyrus.[3] Fusiform gyrus has also been involved in the perception of emotions in facial stimuli.[4]
Increased neurophysiological activity in the fusiform face area may produce hallucinations of faces, whether realistic or cartoonesque, as seen in Charles Bonnet syndrome, hypnagogic hallucinations, peduncular hallucinations, or drug-induced hallucinations.[5]
Recent research has seen activation of the fusiform gyrus during subjective grapheme-color perception in people with synaesthesia.[6]
References
- ^ Nature Neuroscience, vol7, 2004
- ^ nervsystemet.se - Hjärnatlas
- ^ McCarthy, G et al. Face-specific processing in the fuman fusform gyrus.J. Cognitive Neuroscicence. 9, 605-610(1997).
- ^ Radua, Joaquim; Phillips, Mary L.; Russell, Tamara; Lawrence, Natalia; Marshall, Nicolette; Kalidindi, Sridevi; El-Hage, Wissam; McDonald, Colm et al. (2010). "Neural response to specific components of fearful faces in healthy and schizophrenic adults". NeuroImage 49 (1): 939–946. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.030. PMID 19699306.
- ^ Jan Dirk Blom. A Dictionary of Hallucinations. Springer, 2010, p. 187. ISBN 978-1-4419-1222-0
- ^ Imaging of connectivity in the synaesthetic brain « Neurophilosophy
Additional images
External links
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich n1a2p13 - "Cerebral Hemisphere, Inferior View"
- Location at mattababy.org
- "VS Ramachandran on your mind" at ted.com
- "Oliver Sacks: What hallucination reveals about our minds" at ted.com
- NIF Search - Fusiform Gyrus via the Neuroscience Information Framework
Categories:- Neuroanatomy stubs
- Cerebrum
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.