- Ibandronic acid
-
Ibandronic acid 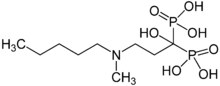
Systematic (IUPAC) name {1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]propane-1,1-diyl}bis(phosphonic acid) Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Licence data EMA:Link, US FDA:link Pregnancy cat. C(US) Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes Oral, intravenous Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 0.6% Protein binding 90.9 to 99.5%
(concentration-dependent)Metabolism Nil Half-life 10 to 60 hours Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 114084-78-5 ATC code M05BA06 PubChem CID 60852 DrugBank APRD00231 ChemSpider 54839 
UNII UMD7G2653W 
KEGG D08056 
ChEMBL CHEMBL997 
Chemical data Formula C9H23NO7P2 Mol. mass 319.229 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) acid (verify)
(what is this?) acid (verify)Ibandronic acid (INN) or ibandronate sodium (USAN), marketed under the trade names Boniva, Bondronat and Bonviva, is a potent bisphosphonate drug used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.[1]
It may also be used to treat hypercalcemia (elevated blood calcium levels). It is Marketed and Manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline and Roche Laboratories. Global sales in 2008 were 1.1B CHF ($1.0B USD at 01/01/2009 exchange rates).[2]
Contents
Medical uses
Ibandronate is indicated for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. Men should not take ibandronate unless they are participating in clinical trials[3]. In May 2003, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Ibandronate as a daily treatment for post-menopausal osteoporosis. The basis for this approval was a three-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial women with post-menopausal osteoporosis. Every participant also received daily oral doses of calcium and 400IUs [international units] of vitamin D. At the study's conclusion, both doses significantly reduced the occurrence risk of new vertebral fractures by 50–52 percent when compared to the effects of the placebo drug.
Adverse effects
In 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a communication warning of the possibility of severe and sometimes incapacitating bone, joint and/or muscle pain.[4] A study conducted by the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research concluded that long term use of bisphosphonates, including Boniva, may increase the risk of a rare but serious fracture of the thigh bone. [5]
References
- ^ Bauss F, Schimmer RC (March 2006). "Ibandronate: the first once-monthly oral bisphosphonate for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis". Therapeutics and clinical risk management 2 (1): 3–18. PMC 1661644. PMID 18360577. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1661644.
- ^ "Roche 2008 Annual Report". Roche. http://www.roche.com/gb08e04.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-13.
- ^ "boniva". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. http://www.drugs.com/monograph/boniva.html. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ "Information for Healthcare Professionals: Bisphosphonates (marketed as Actonel, Actonel+Ca, Aredia, Boniva, Didronel, Fosamax, Fosamax+D, Reclast, Skelid, and Zometa)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm124165.htm. Retrieved 27 October 2010.
- ^ "Drugs Commonly Prescribed for Osteoporosis Patients are Effective at Reducing Risk of Hip and Spine Fractures, But Panel Says May be Related to Unusual Thigh Bone Fractures When Used Long Term". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research=27 October 2010. http://www.asbmr.org/about/pressreleases/detail.aspx?cid=a68f2b70-a117-4094-9f6f-b5993c6a6149.
External links
- Boniva Osteoporosis Treatment by GlaxoSmithKline and Roche Laboratories
- Boniva Side Effects Reported by Users
- Boniva adverse events reported to the FDA
Drugs for treatment of bone diseases (M05) Bisphosphonates Nitrogenous (Alendronic acid, ibandronic acid, incadronic acid, pamidronic acid, risedronic acid, zoledronic acid)
Non-nitrogenous (Etidronic acid, clodronic acid, tiludronic acid)Bone morphogenetic proteins Dibotermin alfa • Eptotermin alfaOther Resorption inhibitor (Ipriflavone) • Aluminium chlorohydrate • Dual action bone agent (Strontium ranelate) •
RANKL inhibitor (Denosumab) • Cathepsin K inhibitor (Odanacatib)Categories:- Bisphosphonates
- GlaxoSmithKline
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
