- Tampa Bay
-
This article is about the body of water. For the demographic region, see Tampa Bay Area. For the city, see Tampa, Florida. For other possible uses, see Tampa (disambiguation).
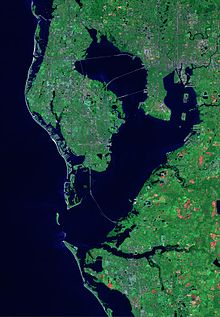
Tampa Bay is a large natural harbor and estuary along the Gulf of Mexico on the west central coast of Florida, comprising Hillsborough Bay, Old Tampa Bay, Middle Tampa Bay, and Lower Tampa Bay.[1]
"Tampa Bay" is not the name of any municipality. This misconception probably stems from the naming of several professional sports franchises (including the Tampa Bay Buccaneers, Tampa Bay Lightning, Tampa Bay Rays, and FC Tampa Bay) whose names represent the collective Tampa Bay Area, the hub of which is the city of Tampa, Florida.[2]
Contents
Geography
Origin
Approximately 6,000 years ago, Tampa Bay formed as a brackish drowned river valley type[3] estuary with a wide mouth connecting it to the Gulf of Mexico. Prior to that time, it was a large fresh water lake, possibly fed by the Floridan Aquifer through natural springs.[4] Though the exact process of the lake-to-bay transformation is not completely understood, the leading theory is that rising seas levels following the last ice age coupled with the formation of a massive sink hole near the current mouth of the bay created a connection between the lake and the gulf.[5]
Ecology
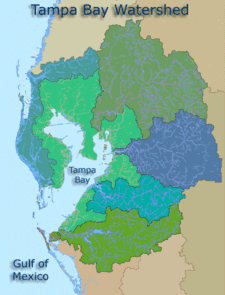
Tampa Bay is Florida's largest open-water estuary, extending over 400 square miles (1,000 km2) and forming coastlines of Hillsborough, Manatee and Pinellas counties. The freshwater sources of the bay are distributed among over a hundred small tributaries, rather than a single river.[6] The Hillsborough River is the largest such freshwater source, with the Alafia, Manatee, and Little Manatee rivers the next largest sources. Because of these many flows into the bay, its large watershed covers portions of five Florida counties[7] and approximately 2,200 square miles (5,700 km2). The bay bottom is silty and sandy, with an average water depth of only about 12 feet (3.7 m).[8]
Tampa Bay's shallow waters, sea grass beds, mud flats, and surrounding mangrove-dominated wetlands provide habitat for a wide variety of wildlife. More than 200 species of fish are found in the waters of the bay, along with bottlenose dolphins and manatees, plus many types of marine invertebrates including oysters, scallops, clams, shrimp and crab. More than two dozen species of birds, including brown pelicans, several types of heron and egret, Roseate spoonbills, cormorants, and laughing gulls make their year-round home along its shores and small islands, with several other migratory species joining them in the winter. The cooler months is when warm-water outfalls from power plants bordering the bay draw one out of every six manatees, an endangered species, to the area.[9]
Tampa Bay has been designated an "Estuary of National Significance" by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. Two National Wildlife Refuges are located in Tampa Bay: Pinellas National Wildlife Refuge and the refuge on Egmont Key. Most of the islands (including several man-made islands built from dredge spoil[8][10]) and sandbars are off-limits to the public, due to their fragile ecology and their use as nesting sites by many species of birds. The Tampa Bay Estuary Program keeps watch over the Bay's health.[8]
Human habitation
Humans have lived in the area for millennia, possibly as long as 12,000 to 14,000 years. The first local people to fully adapt to a sea-side lifestyle were the Manasota culture, who lived on the shores of Tampa Bay beginning around 5,000 - 6,000 years ago. They were ancestors to the Weeden Island culture.[11] Approximately 1,100 years ago, the Tocobaga developed near present-day Safety Harbor along Old Tampa Bay. These were the people living in the area at the time of first contact with Europeans.[12]
Spanish maps dated as early as 1584 identifies Tampa Bay as Baya de Spirito Santo ("Bay of the Holy Spirit").[13] A map dated 1695 identifies the area as Bahia Tampa.[14] Later maps dated 1794[15] and 1800[16] show the bay divided with three different names, Tampa Bay, Hillsboro Bay and the overall name of Bay of Spiritu(o) Santo.
The United States acquired Florida from Spain in 1819. The name Spirito Santo seems to have disappeared from maps of the region in favor of "Tampa Bay" (sometimes divided into Tampa and Hillsboro Bays) soon after the US established Fort Brooke at the mouth of the Hillsborough River in 1824.[17]
For the next 100 years, many new communities were founded around the bay. Fort Brooke begat Tampa on the northeast shores, Fort Harrison begat Clearwater on the west, the trading post of "Braden's Town" developed into Bradenton on the south, and St. Petersburg grew quickly after its founding in the late 19th century. By 2000, the region surrounding Tampa Bay had more than 2.5 million residents.
Environmental decline and recovery
Tampa Bay was once teeming with fish and wildlife. The Tocobaga lived almost entirely from mullet, shellfish, sea turtles, manatees, crabs, and other bounties harvested form the sea. After Tampa had been incorporated for several decades, visitors still reported schools of mullet swimming in such numbers that they "impeded the passage of boats."[18]
The growth of the surrounding communities slowly caused deterioration of the natural environment. Heavy fishing, dredging to deepen shipping channels, and the clearing of mangroves for shoreline development were important factors.[19] Most damaging was the discharge of waste water and other pollutants into the bay, which destroyed water quality and grasses.[20] By the 1970s, sea grass coverage (which is vital to marine life) had decreased by more than 80%, the water was so murky that sunlight could not reach the shallow bottom, and bay beaches were regularly closed due to unsafe levels of pollutants.[20]
Beginning in the early 1980s after federal and state legislation to improve water quality, authorities installed improved water treatment plants and tightened regulation of industrial discharge. Gradually the bay was being cleaned.[21] By 2010, measures of sea grass coverage, water clarity, and biodiversity had improved to levels last seen in the 1950s.[22]
Transportation
In Tampa's early days, the easiest way to get to Fort Brooke was by boat. But, by the late 19th century, the deeper drafts of newer vessels meant that much of naturally shallow Tampa Bay was not navigable by commercial shipping. When Henry B. Plant's railroad reached the area in 1885, he continued the line past Tampa and across the Interbay Peninsula, where he built the town of Port Tampa on Old Tampa Bay. He wanted to create a new port for his fleet of steamships.
To alleviate the problem of the shallow bay, the US Army Corps of Engineers began dredging operations in the early 20th century. The Corp currently maintains more than 80 miles of deep-water channels in Tampa Bay; these must be continuously re-dredged and deepened due to the sandy nature of the bay bottom. Dredging has enabled seaborne commerce to become an important part of the Tampa Bay area's economy but sharply threatened the bay and region's ecology. From its small beginnings, the Port of Tampa has grown into the largest port in Florida and the 10th largest in the nation. It accommodates half of Florida's cargo in the form of bulk, break bulk, roll-on/roll-off, refrigerated and container cargo. It is the site of a ship repair and building industry, along with recently expanded cruise facilities.
The Port of Manatee, with more refrigerated dockside space than any other Gulf of Mexico port, is the closest of the three Tampa Bay deepwater ports to the Panama Canal. It is also one of the state's busiest, ranking fifth among Florida's fourteen seaports in total annual cargo tonnage. The Port of St. Petersburg is home to a U.S. Coast Guard station. The smallest of Florida's ports, it operates as a landlord port managed by the city of St. Petersburg.
Bridges that cross Tampa Bay
- Sunshine Skyway Bridge: spans the mouth of Tampa Bay from Bradenton on the south to St. Petersburg on the north. Part of I-275
- Gandy Bridge: spans Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to St. Petersburg on the west. 1st bridge to link Hillsborough and Pinellas
- Howard Frankland Bridge: spans middle of Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to St. Pete on the west. Part of I-275
- Courtney Campbell Causeway: spans northern Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to Clearwater on the west.
- Bayside Bridge: runs roughly parallel to the western shore of Old Tampa Bay from Largo on the south to Clearwater on the north
See also
- Climate of the Tampa Bay Area
- Battle of Tampa, an American Civil War naval battle in Tampa Bay.
- St. Petersburg Pier, a tourist attraction that juts into the bay from downtown Saint Petersburg, Florida
- Bayshore Boulevard, street near Downtown Tampa that runs along the bay, world's longest sidewalk
References
- ^ "Tampa Bay Watershed - Hillsborough River, Alafia River, Manatee River - Florida's Water: Ours to Protect". Protectingourwater.org. http://www.protectingourwater.org/watersheds/map/tampa_bay/. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ Craig Pittman. "Media found the Rays, lost the 'Bay' - St. Petersburg Times". Tampabay.com. http://www.tampabay.com/news/humaninterest/article675482.ece?comments=legacy. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ Kunneke, J.T., and T.F. Palik, 1984. "Tampa Bay environmental atlas", U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Biol. Rep. 85(15), page 3. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ^ Holocene and Pleistocene Marine and Non-marine Sediment from Tampa Bay, Florida
- ^ St. Petersburg Times Depths detail bay's beginnings
- ^ GulfBase: Tampa Bay and Keys
- ^ Map of the Tampa Bay Watershed
- ^ a b c "Tampa Bay Estuary Program", Official Website
- ^ "Can manatees survive without warm waters from power plants?", Tampa Tribune (tbo.com), Jan. 7, 2011.
- ^ "Dredging and Dredged Material Management", Tampa Bay Estuary Program
- ^ "Manasota". Co.pinellas.fl.us. http://www.co.pinellas.fl.us/BCC/yatki/manasota.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ "Tocobaga Indians of Tampa Bay". Fcit.usf.edu. http://fcit.usf.edu/Florida/lessons/tocobag/tocobag1.htm. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ^ "University of Georgia Libraries, Hargrett Rare Books and Manuscript Library: 1584 map of La Florida". http://www.libs.uga.edu/darchive/hargrett/maps/1584o6.jpg. Retrieved April 27, 2009.
- ^ "University of Georgia Libraries, Hargrett Rare Books and Manuscript Library: 1695 Spanish Map". http://www.libs.uga.edu/darchive/hargrett/maps/1695c6.jpg. Retrieved April 27, 2009.
- ^ "Historical Map Archive: The Peninsula and Gulf of Florida, or New Bahama Channel, with the Bahama Islands". http://cartweb.geography.ua.edu:9001/StyleServer/calcrgn?cat=North%20America%20and%20United%20States&item=States/Florida/Florid1794a.sid&wid=500&hei=400&props=item(Name,Description),cat(Name,Description)&style=simple/view-dhtml.xsl. Retrieved April 27, 2009.
- ^ "University of Georgia Libraries, Hargrett Rare Books and Manuscript Library: An exact map of North and South Carolina & Georgia, with East and West Florida". http://www.libs.uga.edu/darchive/hargrett/maps/1800e8.jpg. Retrieved April 27, 2009.
- ^ "Historical Map Archive: 1933 Map of Florida by A. Finley, Philadelphia". http://cartweb.geography.ua.edu:9001/StyleServer/calcrgn?cat=North%20America%20and%20United%20States&item=States/Florida/Florid1833a.sid&wid=500&hei=400&props=item(Name,Description),cat(Name,Description)&style=simple/view-dhtml.xsl. Retrieved April 27, 2009.
- ^ http://www.tampabay.wateratlas.usf.edu/upload/documents/OldTampaBaylit.pdf
- ^ http://www.epa.gov/owow/estuaries/ccmp/documents/tampabay_ccmp_pt6.pdf
- ^ a b http://www.tampabay.wateratlas.usf.edu/upload/documents/Seagrass%20Meadows%20of%20Tampa%20Bay%20-%20A%20Review.pdf
- ^ Ten Communities: Profiles in Environmental Progress
- ^ "Tampa Bay sea grasses, a leading indicator of water health, hit 60-year high", St. Petersburg Times
External links
Tampa Bay Area Topics Tampa Bay · Climate · History · Media · Sports · Tampa International Airport · Hillsborough County Schools · Pinellas County Schools · University of South Florida
Central cities Smaller communities Pinellas Park · Temple Terrace · Brandon · Zeyphrhills · Plant City · Largo · Dunedin · Tarpon Springs · Lutz · Greater Sun CenterCities in wider region Counties in MSA Counties in wider region Region Outlying regions Southwest Florida · Florida Heartland · Big Bend ·
Fun CoastCoastal Waters of Florida Bays: Apalachicola · Biscayne · Choctawhatchee · East · Escambia · Estero · Florida · Palm · Pensacola · Ponce de Leon · Sarasota · St. Andrews · Tampa · Whitewater
Inlets: Baker's Haulover · Blind Pass · Captiva Pass · Caxambus Pass · Gasparilla Pass · Hillsboro · Lake Worth · Matanzas · Ponce de León · Redfish Pass · Sebastian · St. Lucie
Lagoons: Banana River · Guana River · Halifax River · Indian River · Lake Worth · Marquesas Keys · Matanzas River · Mosquito Lagoon
See Also: Florida Everglades · Intracoastal Waterway · List of Florida rivers
Categories:- Bays of Florida
- Estuaries of Florida
- Geography of the Tampa Bay Area
- Geography of Hillsborough County, Florida
- Geography of Manatee County, Florida
- Geography of Pinellas County, Florida
- Bays of the Gulf of Mexico
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.