- Hamate bone
-
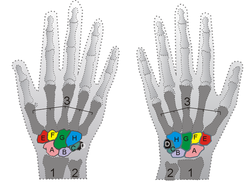
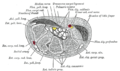
Bone: Hamate bone Shown is the right hand, palm down (left) and palm up (right).
Proximal: A=Scaphoid, B=Lunate, C=Triquetral, D=Pisiform
Distal: E=Trapezium, F=Trapezoid, G=Capitate, H=HamateThe left hamate bone Latin os hamatum Gray's subject #54 227 Articulations articulates with five bones:
the lunate proximally
the fourth and fifth metacarpals distally
the triangular medially
the capitate laterallyMeSH Hamate+Bone The hamate bone (unciform bone) is a bone in the human hand that may be readily distinguished by its wedge-shaped form, and the hook-like process which projects from its volar surface. It is situated at the medial and lower angle of the carpus, with its base downward, resting on the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, and its apex directed upward and lateralward. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "fourth distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
The etymology derives from the Latin hamatus "hooked," from hamus which means "hook."
Contents
Surfaces
The superior surface, the apex of the wedge, is narrow, convex, smooth, and articulates with the lunate.
The inferior surface articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, by concave facets which are separated by a ridge.
The dorsal surface is triangular and rough for ligamentous attachment.
The volar surface presents, at its lower and ulnar side, a curved, hook-like process, the hamulus, directed forward and lateralward.
The medial surface articulates with the triangular bone by an oblong facet, cut obliquely from above, downward and medialward.
The lateral surface articulates with the capitate by its upper and posterior part, the remaining portion being rough, for the attachment of ligaments.
Clinical significance
This is the bone most commonly fractured when an amateur golfer hits the ground hard with their golf club on the downswing. The fracture is usually a hairline fracture, commonly missed on normal X-Rays. Symptoms are pain aggravated by gripping, tenderness over the hamate and symptoms of irritation of the ulnar nerve. This is characterized by numbness and weakness of the pinky finger with partial involvement of the ring finger as well, the "ulnar 1½ fingers."
It is also a common injury in baseball players. A number of professional baseball players have had the bone removed during the course of their careers.[1][2][3][4][5][6]
The calcification of the hammate bone is seen on radiographs during puberty and is sometimes used in orthodontics to determine if the adolescent patient is suitable for orthognathic intervention (e.g. before or at their growth spurt).
Notable cases
- Jose Canseco, Oakland Athletics outfielder (1989)
- Ken Griffey, Jr., Seattle Mariners outfielder (1996)
- Jim Thome, Cleveland Indians first baseman (1996)
- Eric Hinske, Atlanta Braves first baseman (2003)
- Ryan Kalish, Boston Red Sox outfielder (2007)
- Dustin Pedroia, Boston Red Sox second baseman (2007)
- Troy Tulowitzki, Colorado Rockies shortstop (2010)
- Domonic Brown, Philadelphia Phillies outfielder (2011)
- Pablo Sandoval, San Francisco Giants third baseman (2011)
- Chase Woofter, Kansas City Royals second baseman (2011)
See also
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
Additional images
References
- ^ Snow, Chris (June 1, 2006). "Peña to have surgery". The Boston Globe. http://www.boston.com/sports/baseball/redsox/articles/2006/06/01/pea_to_have_surgery/. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
- ^ Manuel, John (March 31, 2004). "Wrist Troubles Drain Prospects' Power". Baseball America. http://www.baseballamerica.com/today/features/040331wrist.html. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
- ^ "Pedroia played final month, playoffs with cracked hamate bone". ESPN. November 10, 2007. http://sports.espn.go.com/mlb/news/story?id=3103634. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
- ^ Benjamin, Amalie (July 27, 2007). "He's gaining in arms race". The Boston Globe. http://www.boston.com/sports/baseball/redsox/articles/2007/07/27/hes_gaining_in_arms_race/. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
- ^ "Dickerson has hand, wrist surgery". Associated Press. ESPN. May 3, 2010. http://sports.espn.go.com/mlb/news/story?id=5160329. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
- ^ Carobine, Kieran (March 08, 2011). "Domonic Brown’s Surgery A Success". Phillies Nation. http://philliesnation.com/archives/2011/03/domonic-browns-surgery-a-success/. Retrieved 2011-09-02.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of upper limbs (TA A02.4, GA 2.200–230) Pectoral girdle,
clavicleScapula fossae (subscapular, supraspinatous, infraspinatous) · scapular notch · glenoid cavity
tubercles (infraglenoid, supraglenoid) · spine of scapula · acromion · coracoid process
borders (superior, lateral/axillary, medial/vertebral) · angles (superior, inferior, lateral)Humerus upper extremity: necks (anatomical, surgical) · tubercles (greater, lesser) · intertubercular sulcus
body: radial sulcus · deltoid tuberosity
lower extremity: capitulum · trochlea · epicondyles (lateral, medial) · supracondylar ridges (lateral, medial) · fossae (radial, coronoid, olecranon)Forearm Hand carpus: scaphoid · lunate · triquetral · pisiform · trapezium · trapezoid · capitate · hamate (hamulus)
metacarpus: 1st metacarpal · 2nd · 3rd · 4th · 5th
phalanges of the hand: proximal · intermediate · distalIf the hamate bone is broken, it immobilizes your ring finger, pinky finger, and wrist until it is healed.
Categories:- Bones of the upper limb
- Skeletal system
- Wrist
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.