- Lower extremity of radius
-
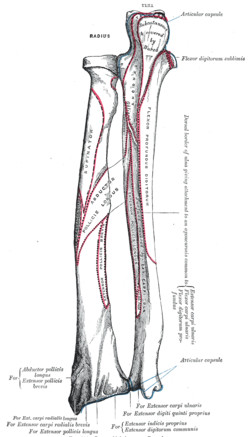
Bone: Distal radius The radius and ulna of the left forearm, posterior surface. The top is proximal (elbow) and bottom is distal (wrist). Gray's subject #52 220 The distal end of the radius is large and of quadrilateral form.
Articular surfaces
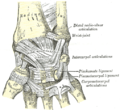
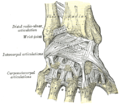
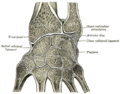
It is provided with two articular surfaces - one below, for the carpus, and another at the medial side, for the ulna.
- The carpal articular surface is triangular, concave, smooth, and divided by a slight antero-posterior ridge into two parts. Of these, the lateral, triangular, articulates with the scaphoid bone; the medial, quadrilateral, with the lunate bone.
- The articular surface for the ulna is called the ulnar notch (sigmoid cavity) of the radius; it is narrow, concave, smooth, and articulates with the head of the ulna.
These two articular surfaces are separated by a prominent ridge, to which the base of the triangular articular disk is attached; this disk separates the wrist-joint from the distal radioulnar articulation.
Non-articular surfaces
This end of the bone has three non-articular surfaces - volar, dorsal, and lateral.
- The volar surface, rough and irregular, affords attachment to the volar radiocarpal ligament.
- The dorsal surface is convex, affords attachment to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament, and is marked by three grooves. Enumerated from the lateral side:
- The first groove is broad, but shallow, and subdivided into two by a slight ridge; the lateral of these two transmits the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle, the medial the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.
- The second is deep but narrow, and bounded laterally by a sharply defined ridge; it is directed obliquely from above downward and lateralward, and transmits the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle.
- The third is broad, for the passage of the tendons of the Extensor indicis proprius and Extensor digitorum communis.
- The lateral surface is prolonged obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection, the styloid process, which gives attachment by its base to the tendon of the brachioradialis, and by its apex to the radial collateral ligament of the wrist-joint. The lateral surface of this process is marked by a flat groove, for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus muscle and extensor pollicis brevis muscle.
Additional images
-
X-Ray of a closed fracture of the distal radius with 10o of lateral angulation, subject is the left arm of 11 year old male
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Categories:- Bones of the upper limb
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.