- Lunate bone
-
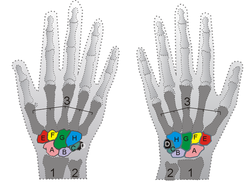
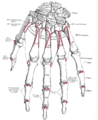
Bone: Lunate bone "Cow chin Bone" Shown is the right hand, palm down (left) and palm up (right).
Proximal: A=Scaphoid, B=Lunate, C=Triquetral, D=Pisiform
Distal: E=Trapezium, F=Trapezoid, G=Capitate, H=HamateThe left lunate bone Latin os lunatum Gray's subject #54 224 Articulations radius proximally
capitate and hamate distally
scaphoid laterally
triangular mediallyMeSH Lunate+Bone The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone (wrist bone) in the human hand that may be distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row of the carpus (wrist) region between the fore arm and hand (manus). In standard medical posture, the lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral Scaphoid bone and medial Triquetral bone. The lunate carpal bone straddles distally the bordering ulna and radius bones and proximally to distal carpus (wrist) Trapezium bone and Trapezoid bone.
The etymology of the Lunate bone derives from the Latin luna which means "moon", the lunate bone looks semi-similar to a crescent moon. In amphibians and reptiles, the bone is instead referred to as the intermedium, because of its position between the other two proximal carpals.
Contents
Surfaces
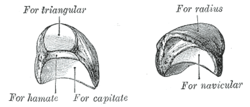
The superior surface, convex and smooth, articulates with the radius.
The inferior surface is deeply concave, and of greater extent from before backward than transversely: it articulates with the head of the capitate, and, by a long, narrow facet (separated by a ridge from the general surface), with the hamate.
The dorsal and palmar surfaces are rough, for the attachment of ligaments, the former being the broader, and of a somewhat rounded form.
The lateral surface presents a narrow, flattened, semilunar facet for articulation with the scaphoid.
The medial surface is marked by a smooth, quadrilateral facet, for articulation with the triangular bone.
Clinical relevance
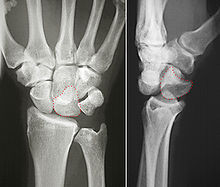
The lunate bone is the most frequently dislocated carpal bone.
See also
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
Additional images
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of upper limbs (TA A02.4, GA 2.200–230) Pectoral girdle,
clavicleScapula fossae (subscapular, supraspinatous, infraspinatous) · scapular notch · glenoid cavity
tubercles (infraglenoid, supraglenoid) · spine of scapula · acromion · coracoid process
borders (superior, lateral/axillary, medial/vertebral) · angles (superior, inferior, lateral)Humerus upper extremity: necks (anatomical, surgical) · tubercles (greater, lesser) · intertubercular sulcus
body: radial sulcus · deltoid tuberosity
lower extremity: capitulum · trochlea · epicondyles (lateral, medial) · supracondylar ridges (lateral, medial) · fossae (radial, coronoid, olecranon)Forearm Hand carpus: scaphoid · lunate · triquetral · pisiform · trapezium · trapezoid · capitate · hamate (hamulus)
metacarpus: 1st metacarpal · 2nd · 3rd · 4th · 5th
phalanges of the hand: proximal · intermediate · distalCategories:- Bones of the upper limb
- Wrist
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.