- Isothiocyanate
-
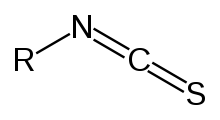
Isothiocyanate is the chemical group –N=C=S, formed by substituting sulfur for oxygen in the isocyanate group. Many natural isothiocyanates from plants are produced by enzymatic conversion of metabolites called glucosinolates. These natural isothiocyanates, such as allyl isothiocyanate, are also known as mustard oils. An artificial isothiocyanate, phenyl isothiocyanate, is used for amino acid sequencing in the Edman degradation.
Contents
Synthesis
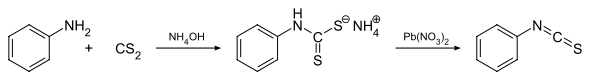
General method for synthesis of isothiocyanates by reacting primary amine (e.g. aniline) with carbon disulphide in aqueous ammonia resulting in precipitation of ammonium dithiocarbamate derivative, which then treated with lead nitrate to yield corresponding isothiocyanate derivative.[1] Another method relies on a tosyl chloride mediated decomposition of a dithiocarbamate salts that are generated in first step.[2] Isothiocyanates may also be accessed via the thermally-induced fragmentation reactions of 1,4,2-oxathiazoles.[3] This synthetic methodology has been appplied to a polymer-supported synthesis of isothiocyanates.[4]
Reactions
In general, isothiocyanates act as electrophiles with the carbon atom as the electrophilic center.
![The reaction of acetophenone enolate with phenyl isothiocyanate. In this one-pot synthesis [5] the ultimate reaction product is a Thiazolidine. This reaction is stereoselective with the formation of the Z-isomer only.](ThiazolidineSynthesis.gif)
Biological activity
Isothiocyanates, such as phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) and sulforaphane, have been shown to inhibit carcinogenesis and tumorigenesis and as such are useful chemopreventive agents against the development and proliferation of cancers. They work on a variety of levels, the most notable one being the inhibition of carcinogenesis through inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which oxidize compounds such as benzo[a]pyrene and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) into more polar epoxy-diols, which can then cause mutation and induce cancer development.[6] Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) has been shown to induce apoptosis in certain cancer cell lines, and, in some cases, is even able to induce apoptosis in cells that are resistant to some currently used chemotherapeutic drugs, for example, in drug-resistant leukemia cells that produce the powerful apoptosis inhibitor protein Bcl-2.[citation needed] Furthermore, isothiocyanates have been the basis of a drug in development that replaces the sulfur bonds with selenium, with far stronger potency against melanoma.[7] Certain isothiocyanates have also been shown to bind to the mutated p53 proteins found in many types of tumors, causing an increase in the rate of cell death.[8]
In foods
Vegetable foods with characteristic flavors due to isothiocyanates include wasabi, horseradish, mustard, radish, Brussels sprouts, watercress, nasturtiums and capers. These various species generate different isothiocyanates in different proportions, and so have different, but recognisably related, flavors. All these species are members of the Brassicales, an order which is characterised by the production of glucosinolates, and of the enzyme myrosinase, which acts on glucosinolates resulting in the creation of isothiocyanates.
See also
- methylisothiocyanate
- Wasabi
References
- ^ F. B. Dains, R. Q. Brewster, and C. P. Olander, "Phenyl isothiocyanate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV1P0447; Coll. Vol. 1: 447
- ^ R. Wong, S. J. Dolman, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 3969-3971 Online article
- ^ "Ab-initio investigation of the fragmentation of 5,5-diamino-substituted 1,4,2-oxathiazoles" O'Reilly, R. J.; Radom, L. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1325-1328. Online article
- ^ "Polymer-supported thiobenzophenone: a self-indicating traceless 'catch and release' linker for the synthesis of isothiocyanates" Burkett, B. A.; Kane-Barber, J. M.; O'Reilly, R. J.; Shi, L. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5355-5358. Online article
- ^ Improved approaches in the synthesis of new 2-(1, 3-thiazolidin-2Z-ylidene)acetophenones M. Carmen Ortega-Alfaro, José G. López-Cortés, Hiram Rangel Sánchez, Rubén A. Toscano, Guillermo Penieres Carrillo, and Cecilio Álvarez-Toledano Arkivoc (EJ-1528C) pp 356-365 2005 Online article
- ^ Zhang Y, Kensler TW, Cho CG, et al. Anticarcinogenic activities of sulforaphane and structurally related synthetic norbornyl isothiocyanates. (1994) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3147-3150. PMID 8159717. online article
- ^ Physorg:Vegetable-based drug could inhibit melanoma
- ^ Wall, Tim (March 10, 2011). "How Brocolli Fights Cancer". Discovery News. http://news.discovery.com/human/how-broccoli-fights-cancer-110310.html.
Functional groups Acetyl · Acetoxy · Acryloyl · Acyl · Alcohol · Aldehyde · Alkane · Alkene · Alkyne · Alkoxy group · Amide · Amine · Azo compound · Benzene derivative · Carboxylic acid · Cyanate · Disulfide · Ester · Ether · Epoxide · Haloalkane · Hydrazone · Hydroxyl · Imine · Isocyanate · Isonitrile · Isothiocyanate · Ketone · Methine · Nitrile · Nitro compound · Nitroso compound · Organophosphorus · Oxime · Peroxide · Phosphonous and Phosphonic acid · Pyridine derivative · Sulfone · Sulfonic acid · Sulfoxide · Thiocyanate · Thioester · Thioether · Thiol · Urea
See also Chemical classification Categories:- Isothiocyanates
- Antioxidants
- Phytochemicals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.