- Methine
-
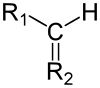
In chemistry, methine (also known as methylidyne or methyne) is a trivalent functional group CH, derived formally from methane. The methine group consists of a carbon atom bound by two single bonds and one double bond, where one of the single bonds is to a hydrogen. This can also encompass subunits of an aromatic compound, although these do not have discrete single and double bonds.
It is sometimes used non-systematically for a carbon with four single bonds, where one bond is to a hydrogen.
Systematically it should be named methylylidene.
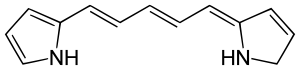
Example
Every carbon in this molecule is a methine carbon, except the two that are attached to the two nitrogens and not to any hydrogens, and the one attached to the nitrogen, which is attached to two hydrogens (far right). There is a five-carbon poly-methine chain in the center of this molecule.
See also
- Methyl
- Methylene
Functional groups Acetyl · Acetoxy · Acryloyl · Acyl · Alcohol · Aldehyde · Alkane · Alkene · Alkyne · Alkoxy group · Amide · Amine · Azo compound · Benzene derivative · Carboxylic acid · Cyanate · Disulfide · Ester · Ether · Epoxide · Haloalkane · Hydrazone · Hydroxyl · Imine · Isocyanate · Isonitrile · Isothiocyanate · Ketone · Methine · Nitrile · Nitro compound · Nitroso compound · Organophosphorus · Oxime · Peroxide · Phosphonous and Phosphonic acid · Pyridine derivative · Sulfone · Sulfonic acid · Sulfoxide · Thiocyanate · Thioester · Thioether · Thiol · Urea
Categories:- Functional groups
- Substituents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.