- Corris Railway
-
Corris Railway
Rheilffordd Corris
Locale Mid-Wales Terminus (Original) Machynlleth & Aberllefenni
(Current) Maespoeth & CorrisCommercial operations Name Corris Railway Company Built by Corris, Machynlleth & River Dovey Tramroad Original gauge 2 ft 3 in (686 mm) Preserved operations Operated by Corris Railway Company Ltd, supported by Corris Railway Society Stations 2 Length 1.6 km Preserved gauge 2 ft 3 in (686 mm) Commercial history 1859 Opened (horse-drawn) 1879 Converted to steam operation 1883 Commencement of steam-hauled passenger service 1930 Cessation of passenger service 1948 Closed Preservation history 1966 Foundation of what became The Corris Railway Society 1970 Opening of Corris Railway Museum 1971 Building of demonstration line 1981 Purchase of Maespoeth shed 2002 Passenger services resumed 2005 Steam trains re-introduced The Corris Railway (Welsh: Rheilffordd Corris) is a narrow gauge preserved railway based in Corris on the border between Merionethshire (now Gwynedd) and Montgomeryshire (now Powys) in Mid-Wales.
The line opened in 1859, and originally ran from Machynlleth north to Corris and on to Aberllefenni. Branches served the slate quarries at Corris Uchaf, Aberllefenni, the isolated quarries around Ratgoed and quarries along the length of the Dulas Valley.
The railway closed in 1948, but a preservation society was formed in 1966, initially opening a museum; a short section of line between Corris and Maespoeth was re-opened to passengers in 2002. The railway now operates as a tourist attraction. A new steam locomotive was built for the railway, which was delivered in 2005. The two surviving locomotives, plus some of the original rolling stock, are preserved on the nearby Talyllyn Railway.
The gauge of the railway is 2 ft 3 in (686 mm).
Contents
History
Tramroad era: 1850 to 1878
Proposals to construct a line to connect the slate quarries in the district around Corris, Corris Uchaf and Aberllefenni with wharves on the estuary of the Afon Dyfi at Derwenlas and Morben, south-west of Machynlleth, first appeared around 1850 with Arthur Causton as engineer. At this time slate from the quarries was hauled by horse-drawn carts and sledges to transport their output to the river. The proposed Corris, Machynlleth & River Dovey Railway would have run along Dulas Valley to the north shore of the Dyfi at Pant Eidal. This scheme was not constructed, and was followed by two further proposals during 1850. Following the plans for a standard gauge railway along the Dyfi valley, these early proposals were shelved.[1]
On 12 July 1858 the Corris Machynlleth & River Dovey Tramroad (CM&RDT) was formed, and immediately began construction on a 2 ft 3 in (686 mm) gauge railway. The first train ran on 1 April 1859.[2] Locomotives were forbidden from use, so the railway was worked using horses and gravity.[1]
On 3 January 1863 the standard gauge Newtown and Machynlleth Railway opened, followed on 1 July of the same year by the line from Machynlleth to Borth of the Aberystwyth and Welsh Coast Railway. These two lines had become part of the Cambrian Railways by August 1865. The opening of the standard gauge line to Borth made the section of the CM&RDT from Machynlleth to Morben obsolete. It was much easier to transship slates to the main line at Machynlleth, so the lower section of the tramway was abandoned.[3]
With the arrival of the standard gauge, the CM&RDT saw the chance to greatly expand their operation. They applied, on 13 November 1863 to convert the tramroad to a railway, adopt steam locomotives and formally close the section between Machynlleth and Derwenlas.[4] On 25 July 1864 an Act of Parliament was passed changing the name to the Corris Railway Company and permitting the use of locomotives on the line. It appears that around this time the line was under the control of Thomas Savin, the contractor who built the standard gauge lines in the area.[5]
It took until the 1870s for work to begin to upgrade the Corris Railway to a standard where locomotives could be used. The original tramroad was laid with light bridge rail suitable for waggons to traverse as they were pulled by horses. These rails would not support the weight of much heavier steam locomotives. In 1878 control of the railway passed to the Imperial Tramways Company of London. The new owners saw the potential for passenger traffic on the Corris Railway and ordered the first passenger carriages for the railway, even though the Act of 1864 did not permit passengers to be carried.[6] They also appointed Joseph R. Dix, son of the main-line stationmaster at Machynlleth, as Manager in successor to David Owen.
The Dix Years: 1879 to 1906
 Horse-drawn charabancs owned by the Corris Railway pass Tal-y-llyn Lake on the "Grand Tour"
Horse-drawn charabancs owned by the Corris Railway pass Tal-y-llyn Lake on the "Grand Tour"
In 1880 and 1883, two new Acts were obtained which adjusted the tolls on the railway and permitted the carriage of passengers. The second of these Acts was necessary because the owners of the quarries served by the railway objected that passenger trains would interfere with their mineral traffic. Initially the railway ran a test passenger service on the local roads; this proved to be so popular that they were able to pass the parliamentary act over the opposition of the quarry owners. It was also the first instance of a long history of the Corris Railway operating passenger road services in the area.[7]
In February 1879 three new steam locomotives purchased from the Hughes Locomotive Company arrived and began work. Although the carriages arrived in 1878 it was not until 1883 that the Act of Parliament was secured to allow the formal commencement of passenger services.[7] A semi-official passenger service had been running since the early 1870s using adapted waggons to convey quarry workers and visitors.
The line was now in its settled form and began to operate a full service under Dix's energetic management. The railway was widely promoted to visitors as the best route to Tal-y-llyn Lake and Cader Idris (ignoring the claims of the rival Talyllyn Railway). The initial passenger service ran from Machynlleth to Corris, with new stations at Esgairgeiliog and Llwyngwern opening in 1884. The track was upgraded beyond Corris so that passenger services could reach the line's northern terminus at Aberllefenni, with services starting on 25 August 1887, and in the same year stations were also opened at Ffridd Gate and Garneddwen.[7]
The railway developed a network of horse-hauled road services, including providing a link between Corris station and Abergynolwyn station on the Talyllyn Railway. This was promoted as part of a circular "Grand Tour" which took in the two narrow gauge railways and the Cambrian service between Tywyn and Machynlleth.
In 1892 control of Imperial Tramways moved to Bristol and George White of Bristol Tramways became chairman and Clifton Robinson became managing director.[8] In the 1900s Bristol motor buses were sent by the parent company to run the road services.
Decline: 1907 to 1930
Following a dispute with the directors Dix was dismissed and replaced by John J O'Sullivan (formerly of the Cork, Blackrock and Passage Railway). The closure of Braichgoch Quarry in 1906 brought the railway its first loss, and although the line continued on through subsequent decades, serving the quarries around Corris and Aberllefenni, it never again showed a profit. As well as slate and passengers, the line hauled timber extracted from the Dyfi forest in the 1910s through 1930s. There was also a constant traffic in coal and general goods to the quarries and communities served by the railway.
After World War I, the decline in slate traffic continued as cheaper foreign slate and alternative roofing materials became popular. O'Sullivan had died in office in 1917 and the new manager, Daniel J McCourt, took over after the war and was responsible for developing and extending the connecting bus services as partial compensation for the decline in rail traffic.
Takeover and nationalisation: 1931 to 1948
In 1930 Imperial Tramways sold the Corris to the Great Western Railway (who by that time were the owners of the main line serving Machynlleth) whose primary interest was taking control of the railway's bus routes. After running a bus in direct competition with the railway in 1930, the railway's passenger service was withdrawn at the beginning of 1931. In 1948 the line was nationalised along with its parent company as part of British Railways. Serious erosion to the railway formation caused by the Afon Dyfi led to closure later that year, the last train running on 20 August 1948. The track was lifted by the end of 1949.
The two remaining locomotives and several goods waggons were purchased in 1951 by the newly preserved Talyllyn Railway which shares the unusual 2 ft 3 in (686 mm) gauge. This stock is still in operation just over the mountain at Tywyn.
Preservation
In December 1966 a group of dedicated enthusiasts led by Alan Meaden, formed the Corris Railway Society with the aim of preserving what was left of the railway, opening a dedicated museum, and to explore the possibility of reviving some or all of the line. Many of the founding members of the Society were volunteers on the nearby Talyllyn Railway.
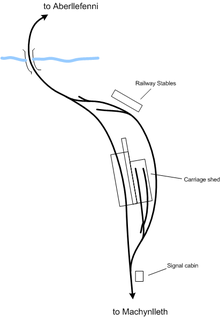
Other than at Aberllefenni and Braichgoch quarries, no rails remained in situ along the Corris route. Initially the Society sought to purchase Machynlleth station for its museum, but when this proved impossible it turned its sights elsewhere. The main buildings of Corris station were demolished in 1968 leaving only the adjacent railway stable block standing, and these buildings - badly in need of maintenance - were acquired, along with a short section of trackbed leading southwards. In 1970 the first part of the building was opened as the Corris Railway Museum. A short length of "demonstration" track was laid in 1971.
During the 1970s the Society undertook lengthy negotiations with the relevant authorities to establish the requirements for re-opening the line for passengers, while steadily building up funds and equipment. A new Corris Railway Company, reviving the original name, was incorporated to act as the Society's trading and operating arm, while the Society achieved charitable status. The Museum was extended as more of the building was returned to satisfactory condition.
In 1981 the line's original locomotive shed at Maespoeth was acquired and became the railway's operational base. During the 1980s light track was laid between Maespoeth and Corris, a distance of just under a mile (1.6 km). The formal "first train" back to Corris ran in 1985. In the following years the track was upgraded to passenger standards while negotiations with the authorities continued.
In the summer of 2002 passenger services resumed after a break of seventy-two years, initially diesel-hauled. The society has also built a new steam locomotive, to a design based on the Kerr Stuart No.4. This loco arrived on the railway on 17 May 2005 and runs as No.7 (the Corris Railway never officially named its locomotives). No.7 went into service on 20 August 2005, fifty-seven years to the day since the last train on the original railway, and now hauls the regular passenger service between Corris and Maespoeth.
The railway is also actively pursuing a southwards extension towards Machynlleth, with the initial aim of extending the line to Tan-y-Coed, midway between Esgairgeiliog and Llwyngwern and some two and a half miles south of Corris. As always, this is involving lengthy negotiations with the authorities, not least due to the line south of Maespoeth running immediately adjacent to the A487 trunk road. While these are continuing the railway has consolidated its facilities at Maespoeth with the construction of a new two-road carriage shed in the adjacent field (the original carriage sheds at Corris and Machynlleth having been demolished).
During 2009 the railway marked the 150th anniversary of the first train on the Corris with a series of events, including demonstration horse-worked freight trains and gravity runs of rakes of waggons.
The revived Corris Railway has maintained friendly links with the Talyllyn Railway, which resulted in both of the original Corris locos and rolling stock returning to the railway. In 1996 ex-Corris loco No. 4 returned to celebrate its 75th anniversary. In 2003 ex-Corris loco No. 3 returned on the occasion of its 125th anniversary with a heritage train of coach No 17, brake van No 6 and two trucks. Corris No. 5 visited the Talyllyn Railway in 1983 and 1990,[9] and No. 7 in October 2011.[10] It hauled a few charter trains and played a vital part in the TR's Corris Weekend, when it ran with the two surviving ex Corris engines; No 4 Edward Thomas and No 3 Sir Haydn.
About the railway
The Corris Railway had several unusual features:
- The 2 ft 3 in (686 mm) gauge is rare, shared by only three other public lines in the UK: the nearby Talyllyn Railway and Plynlimon and Hafan Tramway and the Campbeltown and Machrihanish Light Railway in Scotland.
- Its origins as a horse tramroad and ascent through the narrow and winding Dulas valley meant it had exceptionally tight curves. Its original passenger carriages were simple 4-wheelers derived from urban horse-drawn tramway designs with end balconies; they rode poorly and were quickly rebuilt into longer bogie carriages by placing two of the original bodies end-to-end on a longer underframe.
- The stations were exceptionally narrow, again because of the geography of the line, and all were on the east side of the rails, so the carriages and locomotives had doors on that side only, as on the neighbouring Talyllyn Railway.
- The vertical trestle waggons for carrying large slabs of slate from the quarries were also rarely found on other railways, notable exceptions being the Ffestiniog Railway and the nearby Hendre-Ddu Tramway.
- Corris Station and the original Machynlleth Station had overall roofs, features which were rare on a British narrow gauge railway
Route
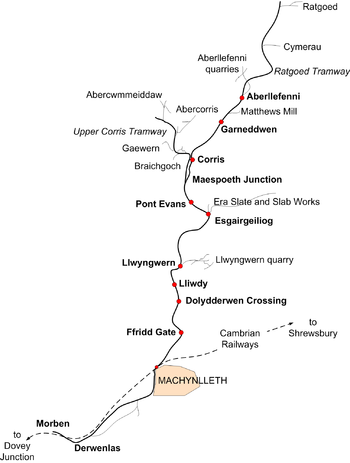
Stations and halts
- Cei (or Quay) Ward a wharf on the Afon Dyfi at Morben, the main trans-shipment point for the original tramroad. Closed in the 1860s.
- Cei Tafarn Isa and Cei Ellis, wharves on the Afon Dyfi at Derwenlas where slates were off-loaded onto shipping. Closed in the 1860s when the bend of the river was cut off by the construction of the Aberystwyth and Welsh Coast Railway.
- Machynlleth the main slate transshipment point and interchange station with the Cambrian Railways (later GWR and BR)
- Ffridd Gate for Llanwrin
- Doldderwen Crossing
- Lliwdy
- Llwyngwern for Pantperthog
- Esgairgeiliog for Ceinws
- Maespoeth Junction locomotive and carriage shed, no passenger station
- Corris
- Garneddwen
- Aberllefenni
Branch lines and tramways
The Corris Railway had numerous branch lines, mainly built to serve the slate quarries along its route. The principal branches were:
- Llwyngwern quarry tramway, at Llwyngwern
- Era Slate quarry tramway at Esgairgeiliog
- the Upper Corris Tramway from Maespoeth Junction to quarries surrounding Corris Uchaf
- Matthew's Mill Siding near Aberllefenni serving Y Magnus slate enamelling works
- Aberllefenni Quarry tramway serving the slate mills and quarry adits
- the Ratgoed Tramway north of Aberllefenni serving Cymerau Quarry and Ratgoed Quarry
None of these branches were locomotive worked, instead being powered by gravity and horses.
Quarries served
The principal reason for the existence of the Corris Railway was to serve the slate quarries of this district. Although usually referred to as quarries, those on the Narrow Vein were usually underground mine workings, following the course of the vein, while those on the Broad Vein were more usually opencast quarries. This list shows the main quarries that the railway served:
- Llwyngwern quarry - connected by its own tramway
- Era Quarry and Slab Works at Esgairgeiliog - connected by its own tramway
- Abercorris quarry - connected to the Upper Corris tramway
- Gaewern quarry - connected to the Upper Corris tramway, subsequently worked together with Braichgoch.
- Braichgoch Quarry - connected to the Upper Corris tramway
- Abercwmmeiddaw quarry - connected to the Upper Corris tramway and the main Broad Vein quarry in the Corris area.
- Aberllefenni Slate Quarry - connected via internal tramway at Aberllefenni
- Cymerau quarry - connected to the Ratgoed tramway
- Ratgoed Quarry - connected to the Ratgoed tramway
The railway also served Y Magnus (Matthew's Mill), a slate enamelling works situated between Aberllefenni and Garneddwen.
Locomotives
Original railway
The locomotives that ran on the original Corris Railway between 1878 and 1948 (none carried names on the Corris) :
Number Image Builder Type Works Number Built Notes 1 Hughes Falcon Works 0-4-2 ST 324 1878 Originally built as an 0-4-0 ST, scrapped 1930 2 Hughes Falcon Works 0-4-2 ST 322 1878 Originally built as an 0-4-0 ST, scrapped 1930 3 
Hughes Falcon Works 0-4-2 ST 323 1878 Originally built as an 0-4-0 ST, now running on the Talyllyn Railway. 4 
Kerr Stuart 0-4-2 ST 4047 1921 Tattoo class locomotive, now running on the Talyllyn Railway. Preserved railway
Locomotives brought to the restored Corris Railway since 1967:
Number Image Name Builder Type Works Number Built Notes 5 Alan Meaden Motor Rail Simplex 4wDM 22258 1965 Ex-Staveley Lime Products, Hindlow, Derbys. Formerly 2 ft (610 mm) gauge. Named in honour of the Society's founder. 6 Ruston and Hornsby 4wDH 518493 1966 Ex-BICC Prescot, Merseyside. Formerly 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge. 7 
Winson Engineering
and Drayton Designs0-4-2 ST 17 2005 Built for the railway, based on the Kerr Stuart "Tattoo" class design of No. 4 8 Hunslet 4wDM 7274 1973 Ex-Houghton Main Colliery, Barnsley. On long term loan from the National Coal Mining Museum 9 Aberllefenni[11] Clayton 4wBE B0457 1974 Ex-Aberllefenni Slate Quarry. Donated and named by Wincilate Ltd 10 Corris Railway 0-4-2 ST Under construction Based on the first three locomotives which first ran the line. Carriages
The original railway had ten four-wheel, tramcar-like carriages, built at the Falcon Works, Loughborough, and numbered from 1 to 10, with a brake van from the same source taking the number 11. The first bogie carriage, which looked like two four-wheel bodies mounted on a single chassis, received number 12, and the four-wheelers were rebuilt over a five-year period on new chassis to form five bogie vehicles. A re-numbering had the rebuilds as 1 to 5 and the former 12 becoming 6. Two all-new carriages to a similar design were built by Metropolitan and numbered 7 & 8. Nos. 1 to 6 disappeared, presumed scrapped, after 1930, but 8 was rebuilt for use on the Talyllyn Railway as their No.17 while 7 is on display in the Corris Railway Museum. The brake van was also preserved on the Talyllyn but has been substantially rebuilt after being damaged in a fire.
So with eleven four-wheel vehicles and eight bogie vehicles having run on the railway, the Society has numbered its new carriages from 20 onwards.
Carriage 20 is similar in appearance to the bogie vehicles, but on a shorter, ex-National Coal Board four-wheel chassis. Carriage 21 and the partially built carriage 22 have been designed to appear as similar as possible to the original 19th Century bogie vehicles, but constructed to 21st Century safety standards. There are two more carriages planned which will be numbered 23 and 24.
When carriage 22 is completed the railway will be able to run an authentic-looking "1920s" train with the "Tattoo" loco and two bogie carriages.
See also
- List of 2 ft 3 in gauge railways
- List of British heritage and private railways
- British narrow gauge railways
References
- ^ a b Boyd 1965, pages 20-21
- ^ Railway Through Talerddig
- ^ Boyd 1965, page 22
- ^ Boyd 1965, page 23
- ^ Corris Railway Society 1988
- ^ Boyd 1965, page 24
- ^ a b c Boyd 1965, pages 24-25
- ^ Corris Railway Society Journal 1992 & 1993
- ^ Bate, John (2001). The Chronicles of Pendre Sidings. RailRomances. p. 205. ISBN 1-900622-05-X.
- ^ "Corris No 7 Visit - 7th and 8th October 2011". Talyllyn Railway. 8 October 2011. http://www.talyllyn.co.uk/news/corris-no-7-visit-7th-and-8th-october-2011. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ "Photo of battery loco no. 9". http://www.corris.co.uk/images/261008dkc/pages/2971.htm. Retrieved 11 April 2010.
Bibliography
- Boyd, James I.C. (1965). Narrow Gauge Railways in Mid Wales. The Oakwood Press.
- Cozens, Lewis (1949). The Corris Railway.
- The Corris Railway Society (1988). A Return to Corris. Avon-Anglia Publications. ISBN 0905466896.
- Briwnant Jones, Gwyn. Railway Through Talerddig.
- Briwnant Jones, Gwyn. Great Western Corris.
- Briwnant Jones, Gwyn. Last Days of the Old Corris.
- Briwnant Jones, Gwyn. Tales of the Old Corris.
External links
- Corris Railway Society
- Corris Discussion Group
- Map sources for Corris Railway
Coordinates: 52°38′50″N 3°50′35″W / 52.64728°N 3.84313°W
Corris Railway Locomotives № 3 • № 4Locations Morben • Derwenlas • Machynlleth • Ffridd Gate • Llwyngwern • Esgairgeiliog • Maespoeth Junction • Corris • Corris Uchaf • Garneddwen • Aberllefenni
Quarries and mines People George Vane-Tempest, 5th Marquess of Londonderry • Clifton Robinson • George White • Edward Temperley Gourley • Sydney Ernest Smith •
Miscellaneous  Railway museums and heritage railways in Wales
Railway museums and heritage railways in WalesNarrow gauge Great Little Trains of Wales · Bala Lake Railway · Brecon Mountain Railway · Corris Railway · Fairbourne Railway · Ffestiniog Railway · Llanberis Lake Railway · Rhyl Miniature Railway · Snowdon Mountain Railway · Talyllyn Railway · Teifi Valley Railway · Vale of Rheidol Railway · Welsh Highland Railway · Welsh Highland Heritage Railway · Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway
Standard gauge Centres and museums Categories:- Heritage railways in Gwynedd
- Corris Railway
- Great Western Railway constituents
- Narrow gauge railways in Wales
- Slate industry in Wales
- Railway companies established in 1858
- Railway lines opened in 1859
- Railway lines closed in 1948
- 2ft 3in gauge railways
- Horse-drawn railways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.