- Vale of Rheidol Railway
-
Vale of Rheidol Railway
Rheilffordd Cwm RheidolLocale Ceredigion, Wales Terminus Aberystwyth and Devil's Bridge Commercial operations Name Vale of Rheidol Railway Built by Engineer: James Szlumper Original gauge 1 ft 11 3⁄4 in (603 mm) Preserved operations Operated by Vale of Rheidol Railway Ltd. Stations 9 Length 113⁄4 miles (18.91 km) Preserved gauge 1 ft 11 3⁄4 in (603 mm) Commercial history Opened August 1902
Opened for passengers: 22 December 1902
Cambrian Railways: 1 July 1913
GWR Grouping: 1923
British Railways: 1948
Last BR Steam railway: from 1968Preservation history 1989 Privatised The Vale of Rheidol Railway (Welsh: Rheilffordd Cwm Rheidol) is a narrow-gauge 1 ft 11 3⁄4 in (603 mm) gauge heritage railway that runs for 113⁄4 miles (18.91 km) between Aberystwyth and Devil's Bridge in the county of Ceredigion, Wales. It was the last line to be operated by steam as part of the nationalised British Railways network, until it was privatised in 1989.
Contents
History
A narrow gauge railway in the area of Aberystwyth was first proposed after the initial route planned for the Manchester and Milford Railway, from Llanidloes to Aberystwyth via Devil's Bridge, was altered, and then abandoned, before construction started.
The original primary purpose of the line was to carry timber and ore from the Rheidol valley to the sea and the main line railway at Aberystwyth. Many lead mines in the valley were producing ore at the end of the 19th century. Construction was begun in 1901 following an Act of Parliament in 1897. Rock was hand-hewn instead of being blasted, in order to save money.
By the time the railway was ready to open in 1902, lead mining in Ceredigion was in steep decline. However a significant growth in tourism was under way, and the carriage of passengers soon became the principal traffic of the railway. It opened for mineral traffic in August 1902 and for passengers on 22 December 1902.
On 1 July 1913, the line was absorbed by the Cambrian Railways. During World War I, the establishment of military camps in the valley, and the need for timber for the war effort, meant that freight became the principal revenue source for a short while.
It was subsequently grouped into the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1923. The GWR turned it into a service solely for tourists, freight services being withdrawn, and from 1931 trains only operated during the summer months. The entire line was closed for the duration of World War II, though maintainance continued. In July 1945 it reopened and in 1948 the line passed into the hands of British Railways. In 1968 the line was rerouted in Aberystwyth to run adjacent to the BR line into the former standard gauge Carmarthen line platforms of the main station which had been abandoned in 1965. The former standard gauge locomotive shed was also refurbished and adapted into use for this railway. The former station site is now occupied by a supermarket and the former route of this alignment has been sold for redevelopment. The line was finally privatised in 1989 and sold to the Brecon Mountain Railway who, in 1996, sold it on to the Phyllis Rampton Trust.[1] Today, it still operates as a tourist railway, offering an hour-long journey through the Cambrian Mountains, much of it at a gradient of 1 in 50 (2%). The headquarters of the railway are at Aberystwyth where it shares a terminus with the standard gauge main line, trains leaving from the former Carmarthen bay platform. For many years, it was the sole steam-operated line on the British Rail network, steam traction having ceased in 1968 on all other parts of the system. In 2010 work started at Aberystwyth on construction of a new locomotive and carriage works. Future plans include construction of a new station platform and buildings at Aberystwyth close to the existing station.
- For details of the locomotives used on the line see: Vale of Rheidol Railway locomotives
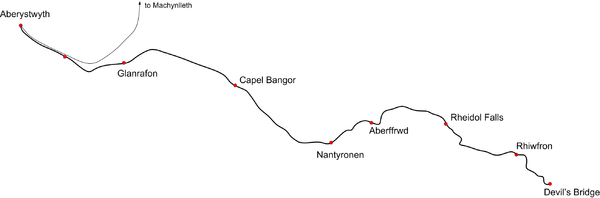
The route
There are nine stations. Whilst all trains generally stop at block stations, for operational reasons, the other (smaller) stations are request stops.
- Aberystwyth
- Llanbadarn
- Glanrafon
- Capel Bangor Passing Loop.
- Nantyronen Water Tower
- Aberffrwd Passing Loop.
- Rheidol Falls
- Rhiwfron
- Devil's Bridge
When the lead mines were being worked there was an aerial cableway linking them with Rhiwfron.
The railway had a branch line which ran to Aberystwyth harbour, principally for freight services. The Harbour Branch became redundant with the predominance of tourist passenger operations and was closed and lifted. Little evidence of it remains today.[2]
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ Boyd-Hope, Gary (January 2009). "Rheidol revival: 20 years of private enterprise". Steam Railway 358: 91–5.
- ^ Parts of the route may be traced via the Geograph Project as here, for example.
External links
Vale of Rheidol Railway Rolling stock Locomotives of the Vale of Rheidol Railway
Stations Aberystwyth • Llanbadarn • Glanrafon • Capel Bangor • Nantyronen • Aberffrwd • Rheidol Falls • Rhiwfron • Devil's Bridge
Miscellaneous  Railway museums and heritage railways in Wales
Railway museums and heritage railways in WalesNarrow gauge Great Little Trains of Wales · Bala Lake Railway · Brecon Mountain Railway · Corris Railway · Fairbourne Railway · Ffestiniog Railway · Llanberis Lake Railway · Rhyl Miniature Railway · Snowdon Mountain Railway · Talyllyn Railway · Teifi Valley Railway · Vale of Rheidol Railway · Welsh Highland Railway · Welsh Highland Heritage Railway · Welshpool and Llanfair Light Railway
Standard gauge Centres and museums Categories:- Vale of Rheidol Railway
- Cambrian Railways
- Heritage railways in Ceredigion
- Pre-grouping British railway companies
- 2ft gauge railways
- Great Western Railway constituents
- Narrow gauge railways in Wales
- Aberystwyth
- Railway companies established in 1897
- Railway lines opened in 1902
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.