- Newport, Abergavenny and Hereford Railway
-
Newport, Abergavenny and Hereford Railway
Including Taff Vale ExtensionLegend




To Shrewsbury 




To Worcester To Hay-on-Wye 



Hereford Barton 




Hereford (Barrs Court) 



River Wye Redhill Junction 



To Grange Court Tram Inn 




St Devereux 




To Three Cocks Junction 




Pontrilas 




Pandy 




Llanvihangel 




Abergavenny Junction 



To Merthyr 









Abergavenny Penpergwm 




(Monmouth Road) Nantyderry 









To Monmouth (Troy) Little Mill Junction 




Pontypool Road 









To Newport 




GWR to Newport Pontypool Clarence Street 




GWR to Blaenavon 



Crumlin Valley Colliery 




Hafodyrynys 








Glyn Tunnel (280 yards) 








Ebbw Valley Line 







Ebbw River Crumlin Viaduct 



Crumlin High Level 




Treowen 




Pennar Junction 



Pennar Branch to Risca Pennar Branch to 




Markham Colliery 




Pentwynmawr 




Pontllanfraith Low Level L&NWR Sirhowy 




Valley Branch 









Bryn Tunnel (398 yards) Maesycymmer Junction 









B&MJR to Bargoed 


B&MJR to Maesycymmer 




Rhymney River 




Hengoed Viaduct Hengoed High Level 














RVR to Bargoed 



RVR to Ystrad Mynach Penallta Colliery Branch 









Penallta Junction Nelson Branch to Pontypridd 









Nelson and Llancaiach RVR to Taff Bargoed 




Treharris 




TVR extension to Pontypridd 



Quakers Yard Branch Junctionn Quakers Yard High Level 




Quakers Yard Low Level 

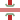


Quakers Yard Viaduct Quakers Yard No.2 Viaduct 




TVR to Merthyr Tydfil 




Cefn Glas Tunnel (703 yards) RVR Taff Branch to Merthyr 



Vale of Neath Railway The Newport, Abergavenny and Hereford Railway was a railway line connecting the Welsh port city of Newport via Abergavenny, to the major English market town of Hereford.
Sponsored by the LNWR, it opened on 6 December 1853. For a great deal of its length it ran through joint stations, allowing various railway companies based in the South Wales Valleys to access the industrial Midlands and Northwest England.
On post-World War I amalgamation, it was taken over by the Great Western Railway, and then on nationalisation post-World War II became part of the Western Region of British Railways. Surviving the Beeching Axe, it now forms the southern section of Network Rails Welsh Marches Line.
History
Incorporated on 3 August 1846, in 1847, the Act was passed for the Taff Vale Extension, from Coedygric North Junction, Pontypool westwards to the Taff Vale Railway at Quakers Yard. The railway company was formed by the amalgamation of the Hereford Railway, the Llanfihangel Railway and the Grosmont Railway.
Surveyed and designed by Chief Engineer Charles Liddell, he noted that at its northern end, the terminus at Hereford Barton was not big enough to take the five railways converging on the major market town. So it was agreed by the joint GWR/LNWR Shrewsbury and Hereford Railway and the broad gauge GWR sponsored Hereford, Ross and Gloucester Railway, the construction of Hereford Barrs Court. A joint opening of both stations took place on 6 December 1853.
Liddell faced the problem of bridging two key natural geographic barriers to connect with the Taff Vale Railway at Quakers Yard, the Ebbw Valley and the Rhymney Valley. After agreeing a tendering process with the board, the winner was agreed to be Thomas W. Kennard. While Liddell was the key architect of both the Crumlin Viaduct (built from wrought iron due to its projected height), and the Hengoed Viaduct (built from stone, on a curve), Kennard acted as designer and engineer for both projects, and supplier for the Crumlin, where his father Robert Kennard's company Falkirk Iron Co supplied the innovative Warren trusses.
On 2 January 1854, the line opened from Hereford to Coedygric, Pontypool on the Monmouthshire Railway and Canal Company line. The station at Abergavenny was opened.
In 1860, the Newport, Abergavenny and Hereford Railway merged with the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway and Worcester and Hereford Railway to form the West Midland Railway.
On 1 October 1862, Abergavenny Junction was opened to the Merthyr, Tredegar and Abergavenny Railway. Abergavenny Junction closed in 1958.
On 9 June 1958, the majority of stations on the line were closed to goods traffic.
Chronology
- 1846 - Tramroads the Llanvihangel Railway, Grosmont Railway and Hereford Railway purchased.
- 1847 - Act for Taff Vale Extension passed from Coedygric North Junction to the Taff Vale Railway at Quakers Yard.
- 1852 - Construction work commences on Crumlin Viaduct.
- 1853 - Construction on Hengoed Viaduct (Maesycwmmer Viaduct) begins.
- 1854 - Line to Abergavenny opened.
- 1854 - Section opened from Hereford (Barton) to Coedygric on the Monmouthshire Railway and Canal Company. Line is operated by the London and North Western Railway.
- 1854 - Railway becomes fully independent.
- 1860 - Newport Abergavenny and Hereford Railway, Oxford Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway and Worcester and Hereford Railway merged to form the West Midland Railway.
- 1862 - Abergavenny Junction station opened.
- 1863 - West Midland Railway builds platforms north of the south facing junction with the Merthyr, Tredegar and Abergavenny Railway.
- 1864 - Traffic serves the newer Abergavenny railway station.
- 1870 - Abergavenny Junction station re-built further north from original site.
- 1871 - Abergavenny Junction station re-built at London and North Western Railway expense.
- 1884 - Private coal and stores siding laid to Abergavenny from south junction at triangle. London and North Western Railway acquire running powers.
- 1928 - Double-track across Crumlin Viaduct downscaled to a single track.
- 1950 - Abergavenny renamed "Abergavenny Monmouth Road".
- 1958 - Abergavenny Junction station closes, and all stations between Pontypool Road and Hereford (excluding Abergavenny Monmouth Road) all close to goods traffic.
- 1964 - Passenger services between Pontypool Road and Neath withdrawn and the line over Crumlin viaduct closes to all traffic.
- 1965 - Pontypool Road engine shed closes.
- 1965 - Crumlin Viaduct demolished.
- 1967 - Pontypool Road engine shed is demolished. Sidings in Pontypool and at Coedygric are largely removed during Beeching Axe.
- 1968 - "Abergavenny Monmouth Road" station is renamed Abergavenny again.
- 1972 - With the closures of Crane Street and Pontypool Clarence Street, Pontypool Road station is renamed "Pontypool".
- 2000 - The disused Hengoed Viaduct is opened for public access.
- 2004 - The Heritage Lottery Fund provides refurbishment grant for Hengoed Viaduct and remains of Hengoed High Level railway station which becomes part of the Celtic cycle trail.
External links
Categories:- Railway lines in Wales
- Early British railway companies
- Railway companies established in 1846
- Railway lines opened in 1853
- Railway companies disestablished in 1860
- Standard gauge railways in Wales
- Standard gauge railways in England
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
