- Smith–Fineman–Myers syndrome
-
Smith–Fineman–Myers syndrome Classification and external resources 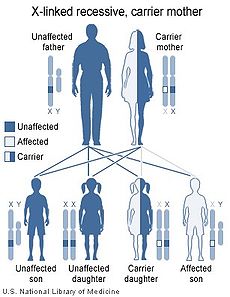
X-linked recessive inheritanceOMIM 309580 DiseasesDB 32665 Smith–Fineman–Myers syndrome (SFMS1), also called X-linked mental retardation-hypotonic facies syndrome 1 (MRXHF1), Carpenter–Waziri syndrome, Chudley–Lowry syndrome, Holmes–Gang syndrome and Juberg–Marsidi syndrome (JMS),[1] is a rare X-linked recessive[2] congenital disorder that causes birth defects, including mental retardation. The head is small, narrow, and elongated. Those affected by this illness exhibit dwarfism (are shorter than would be expected) and have deformed chests,[3] as well as hypogonadism and mild obesity.[4] It is named for Robert M. Fineman, Gart G. Myers, and Richard D. Smith.[3]
It is associated with ATRX.
References
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 309580
- ^ Saugier-Veber, P.; Abadie, V.; Moncla, A.; Mathieu, M.; Piussan, C.; Turleau, C.; Mattei, J.; Munnich, A. et al. (Jun 1993). "The Juberg-Marsidi syndrome maps to the proximal long arm of the X chromosome (Xq12-q21)". American Journal of Human Genetics 52 (6): 1040–1045. PMC 1682258. PMID 8503439. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1682258.
- ^ a b synd/2227 at Who Named It?
- ^ "Smith–Fineman–Myers syndrom." on Wrong Diagnosis. Online. November 24, 2009.
Categories:- Genetic disorder stubs
- Rare diseases
- X-linked recessive disorders
- Syndromes
- Congenital disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
