- Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link Hong Kong Section
-
"Choi Yuen Tsuen" redirects here. For public housing estate, see Choi Yuen Estate.
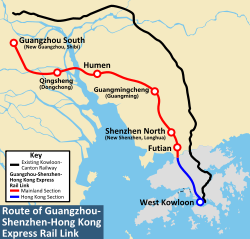
Route of Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong XRL Hong Kong SectionInfo Locale Hong Kong Transit type Passenger high-speed rail Number of stations 1 Daily ridership 99,000 Operation will start 2016 Technical Track gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) Standard gauge Electrification 50Hz 25,000V (AC) Top speed 200 km/h (120 mph) System map LegendItalic font indicates station or line under construction or planning. 


km Wu-Guang Railway to Wuhan 


0 New Guangzhou 



Pearl River 

Humen (Guang-Shen Intercity Railway) 





New Shenzhen (SZ Metro L4, Huan Zhong Line & SZ Metro L6) 


Futian (She Kou Line, Long Gang Line & 
Hong Kong-Shenzhen border Shenzhen River 

142 West Kowloon 
(Airport Express, Tung Chung Line & West Rail Line) This route map:
The Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link Hong Kong Section (XRL HK Section) is a proposed high speed railway connecting Kowloon with the high-speed rail network of China at Shenzhen. As its name suggests, it is part of the rail link between Hong Kong and Guangzhou, the capital city of Guangdong province.
Contents
Current plan
In April 2007, the Executive Council assigned the task of planning and design of the Hong Kong section of the Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link (XRL) to the MTR Corporation Limited (MTRCL). The government projected that the XRL will carry about 100,000 passengers daily in 2020 and 120,000 passengers in 2030, generating an economic benefit of $83 billion over the next 50 years in terms of travelling time saved. Construction cost were estimated at $39.5 billion (US$5 billion), giving an economic internal rate of return of about 9%.[1] The government stated the objectives were to "reinforce Hong Kong's position as the transport hub in southern China and integrate Hong Kong into the country's rapidly growing express rail network", and promoting cultural tourism. It also argued that shortening the travelling time between Hong Kong and Guangzhou to just under 50 minutes — half the current journey time — would save "$83 billion over the next 50 years in terms of travelling time", and the creation of 5,000 jobs during construction, and 10,000 operational jobs.[1]
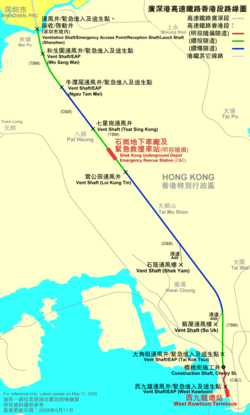
The XRL HK Section will only serve the West Kowloon Terminus. Trains will run to Guangzhou South Station in the Shibi Township of the Panyu District in southern Guangzhou through three intermediate stations, namely, Futian, Longhua (Shenzhen North) and Humen.[2][3] The expected travel time between Guangzhou South and West Kowloon stations is estimated to be 48 minutes, with a total distance of 142 kilometers.
It is expected that Shenzhen North Station will be open in 2010, and Futian Station in 2014. Trains departed from Hong Kong may have destinations beyond Guangzhou, through the Wuguang High-Speed Railway and the Shiwu High-Speed Railway, or via Shenzhen North to Hangzhou and Shanghai through the Xiashen Railway, Huhangyong Railway, etc.
Under the current plan the total distance of the Hong Kong section is 26 kilometres, most of which through underground tunnels.[4] The dedicated track will enable a top speed of 200 km/h;[4] the expected travel time from Kowloon, scheduled to open in 2016, to Shenzhen's Futian Station is 12 minutes.[citation needed]
The construction cost in Hong Kong will be covered by the Hong Kong taxpayer[1][5] (whereas the construction cost in the Mainland section will be covered by the Guangdong Provincial Government and PRC's Ministry of Railways).
Hoping to be able to start construction of the Hong Kong section of the Express Rail Link (XRL) project before the end of 2009, the Executive Council approved the implementation on 20 October, paving the way for funding approval from the Finance Committee of the Legislative Council.[4]
Appropriations for the project secured approval of the Hong Kong Legislative Council on 16 January 2010.[6]
Construction of the Guangshen Section is in progress, and service between Guangzhou South and New Shenzhen stations is expected to commence in mid-2010 (Futian Station will be opened in 2012)[7]; construction of the Hong Kong Section is expected to start as late as 2010[8] and be completed in 2015.[9]
Opposition to the project
Main article: Opposition to the Guangzhou-Hong Kong Express Rail LinkOn 29 November 2009, a demonstration of more than 1,000 people protesting against the construction of the Express Rail link gained the attention of the local media when a group of 100 people engaged in a sit-in protest in front of the government headquarters in Central.[10] On 18 December 2009, when the funding application was debated in the Finance Committee of the Legislative Council, a demonstration of an estimated 1,000 to 2,000 people was staged around the Legislative Council Building. The debate did not end at the time when the meeting was scheduled to be ended, and the funding application was not yet voted on.[8] A major protest followed in January 2010.
See also
References
- ^ a b c "Green light for local section of Express Rail Link" (in English). Hong Kong Government. http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200804/22/P200804220141.htm. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ^ Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link
- ^ HONG KONG SECTION OF GUANGZHOU-SHENZHEN-HONG KONG EXPRESS RAIL LINK PROJECT PROFILE
- ^ a b c ExCo approves implementation of high-speed rail link, Hong Kong Government, 20 October 2009
- ^ "廣深港高速鐵路香港段工程項目簡介" (in Chinese). Environmental Protection Department and MTR Corporation. http://www.epd.gov.hk/eia/chi/register/profile/latest/cesb189/cesb_189.pdf. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ^ Song, Shengxia (18 January 2010), Hongkongers protest vote on high-speed rail, People's Daily, Global Times, retrieved 28 January 2010
- ^ hkcd.com.hk
- ^ a b Opponents of high-speed rail link claim victory as pan-democrats delay funding, South China Morning Post, 19 December 2009
- ^ Hong Kong Government
- ^ Angry rail-link protesters clash with police, The Standard, 30 November 2009
External links
- Express Rail Link(Hong Kong), MTR official site
- XRL Project, MTR official site
- expressrailtruth.com, Opposition site (Chinese)
High-speed rail in the People's Republic of China Maglev Shanghai Maglev Train · Shanghai–Hangzhou Maglev LineConventional High
Speed RailwaysBeijing–Harbin PDLBeijing–Shenyang Passenger Railway · Harbin–Dalian Passenger Railway · Panjin–Yingkou Passenger RailwayBeijing–Shanghai PDL(Branch line: Hefei–Bengbu Passenger Railway)Links between Beijing–Harbin
PDL and Beijing–Shanghai PDLTianjin–Qinhuangdao Passenger Railway · Qinhuangdao–Shenyang Passenger RailwayBeijing–Hong Kong PDLBeijing–Shijiazhuang Passenger Railway · Shijiazhuang–Wuhan Passenger Railway · Wuhan–Guangzhou Passenger Railway · Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong XRL (HK Section)*Hangzhou–Fuzhou–Shenzhen PDLHangzhou–Ningbo Passenger Railway · Ningbo–Taizhou–Wenzhou Railway · Wenzhou–Fuzhou Railway · Fuzhou–Xiamen Railway · Xiamen–Shenzhen RailwayQingdao–Taiyuan PDLJiaozhou–Jinan Passenger Railway · Shijiazhuang–Jinan Passenger Railway · Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan Passenger RailwayXuzhou–Lanzhou PDLZhengzhou–Xuzhou Passenger Railway · Zhengzhou–Xi'an Passenger Railway · Xi'an–Baoji Passenger Railway · Baoji–Lanzhou Passenger RailwayShanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu PDLShanghai–Nanjing Intercity High-Speed Railway · Jinghu High-Speed Railway (Shanghai–Nanjing) · Hefei–Nanjing Passenger Railway · Hefei–Wuhan Passenger Railway · Wuhan–Yichang Railway · Yichang–Wanzhou Railway (Yichang-Lichuan) · Chongqing–Lichuan Railway · Suining–Chongqing Railway · Dazhou–Chengdu Railway (Suining-Chengdu)Shanghai–Kunming PDLShanghai–Hangzhou Passenger Railway · Hangzhou–Changsha Passenger Railway · Changsha–Kunming Passenger RailwayOtherGuizhou–Guangzhou Passenger Railway · Lanzhou–Xinjiang Passenger Railway · Hefei–Fuzhou Passenger RailwayIntercity
(200-250km/h)Chengdu-Dujiangyan Intercity Railway · Nanchang-Jiujiang Intercity Railway · Guangzhou–Zhuhai Intercity Mass Rapid Transit · Hainan East Ring Intercity Rail · Changchun-Jilin Intercity Rail · Guangzhou–Zhaoqing Intercity Railway · Nanjing-Anqing Intercity Railway · Dongguan–Huizhou Intercity Railway · Chengdu-Leshan Intercity Railway · Zhengzhou–Kaifeng Intercity RailwayIntercity
(300-350km/h)Beijing–Tianjin Intercity Railway · Shanghai–Nanjing Intercity High-Speed Railway · Jinbin Intercity Railway · Nanjing-Hangzhou Intercity Railway · Harbin-Qiqihar Intercity Railway · Chengdu-Chongqing Intercity Railway · Shenyang-Dandong Intercity RailwayUpgraded linesGuangzhou–Shenzhen Railway · Jiaozhou–Jinan Railway · Beijing–Shanghai Railway · Beijing–Harbin Railway · Beijing–Guangzhou Railway · Longhai Railway · Shanghai–Kunming Railway · Wuhan–Jiujiang Railway · Xiangfan–Chongqing Railway · Xiaoshan–Ningbo RailwayRolling StockCRH1 · CRH2 · CRH3 · CRH5 · CRH6 · China Star · X 2000 · Blue Arrow · Zefiro 380 · CRH380A · CIT TrainsNote: italics - under construction or currently not operational * in/related to the special administrative regionsPublic transport in the Pearl River Delta Note: Facilities that are either under construction, under planning or pending for approval are shown in italic.Guangdong, China  Foshan FMetro linesLine 1 · Guangzhou BRT linesGuangzhou Metro linesShenzhen Metro linesShenzhen monorail
Foshan FMetro linesLine 1 · Guangzhou BRT linesGuangzhou Metro linesShenzhen Metro linesShenzhen monorailHong Kong  Hong Kong MTR linesHong Kong LRT lines505 · 507 · 610 · 614 · 614P · 615 · 615P · 705 · 706 · 751 · 751P · 761PTrams and Cable Car
Hong Kong MTR linesHong Kong LRT lines505 · 507 · 610 · 614 · 614P · 615 · 615P · 705 · 706 · 751 · 751P · 761PTrams and Cable CarMacau  Macau LRT lines
Macau LRT linesInter-city lines PRD Rapid Transit linesOther linesAutomated people mover systems Major terminals Rail transportCentral (Hong Kong) · Dongguan · Foshan · Futian · Guangzhou · Guangzhou East · Guangzhou South · Jiangmen · Hengqin · Hong Kong · Hung Hom · Humen · Shenzhen · Shenzhen North · Tiyu Xilu · West Kowloon · Zhongshan · ZhuhaiAirportsPortsFerry services Cotai Jet · New World First Ferry · TurboJET · Star Ferry · Hong Kong & Kowloon Ferry · Discovery Bay Transportation Services · Park Island Transport · Fortune Ferry · Macao Dragon Company · Coral Sea Ferry · Chuen Kee Ferry · Tsui Wah FerryGuangshengang XRL: Mainland Section · Hong Kong Section — Jinggang PDL[citation needed] (under construction) Mainland Section: Guangzhou South · Dongchong · Humen · Guangming · Shenzhen North · Futian
Hong Kong Section: West KowloonCategories:- Stations of Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link
- High-speed railway lines in the People's Republic of China
- Proposed public transport in Hong Kong
- Standard gauge railways in Hong Kong
- Railway tunnels in Hong Kong
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.