- Calcium sulfide
-
Calcium sulfide 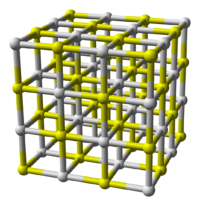 Calcium sulfideOther namesCalcium monosulfide,
Calcium sulfideOther namesCalcium monosulfide,
Hepar calcies,
Sulfurated lime
OldhamiteIdentifiers CAS number 20548-54-3 
PubChem 10197613 ChemSpider 8373113 
UNII 1MBW07J51Q 
EC number 243-873-5 Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- [Ca]=S
[Ca+2].[S-2]
Properties Molecular formula CaS Molar mass 72.143 g/mol Appearance white crystals
hygroscopicDensity 2.59 g/cm3 Melting point 2525 °C
Solubility in water slightly soluble Solubility insoluble in alcohol
reacts with acidRefractive index (nD) 2.137 Structure Crystal structure Halite (cubic), cF8 Space group Fm3m, No. 225 Coordination
geometryOctahedral (Ca2+); octahedral (S2–) Hazards EU Index 016-004-00-0 EU classification Irritant (Xi)
Dangerous for the environment (N)R-phrases R31, R36/37/38, R50 S-phrases (S2), S28, S61 Main hazards H2S source NFPA 704 Related compounds Other anions Calcium oxide Other cations Magnesium sulfide
Strontium sulfide
Barium sulfideRelated sulfides Sodium sulfide  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Calcium sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula CaS. This white material crystallizes in cubes like rock salt. CaS has been studied as a component in a process that would recycle gypsum, a product of flue gas desulfurization. Like many salts containing sulfide ions, CaS typically has an odour of H2S, which results from small amount of this gas formed by hydrolysis of the salt.
In terms of its atomic structure, CaS crystallizes in the same motif as sodium chloride indicating that the bonding in this material is highly ionic. The high melting point is also consistent with its description as an ionic solid. In the crystal, each S2− ion is surrounded by an octahedron of six Ca2+ ions, and complementarily, each Ca2+ ion surrounded by six S2− ions.
Contents
Production
CaS is produced by "carbothermic reduction" of calcium sulfate, which entails the conversion of carbon, usually as charcoal, to carbon dioxide:
- CaSO4 + 2 C → CaS + 2 CO2
and can react further:
- 3 CaSO4 + CaS → 4 CaO + 4 SO2
In the second reaction the sulfate (+6 oxidation state) oxidizes the sulfide (-2 oxidation state) to sulfur dioxide (+4 oxidation state), while it is being reduced to sulfur dioxide itself (+4 oxidation state).
CaS is also a byproduct in the Leblanc process.
Reactivity and uses
Calcium sulfide decomposes upon contact with water, including moist air, giving a mixture of Ca(SH)2, Ca(OH)2, and Ca(SH)(OH).
- CaS + H2O → Ca(SH)(OH)
- Ca(SH)(OH) + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2S
Milk of lime, Ca(OH)2, reacts with elemental sulfur to give a "lime-sulfur", which has been used as an insecticide. The active ingredient is probably a calcium polysulfide, not CaS.[1]
It reacts with acids such as hydrochloric acid to release toxic hydrogen sulfide gas.
- CaS + 2 HCl → CaCl2 + H2S
Natural occurrence
Oldhamite is the name for mineralogical form of CaS. It is a rare component of some meteorites and has scientific importance in solar nebula research. Burning of the coal dumps can also produce such compound.
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
Calcium compounds CaB6 · CaBr2 · CaC2 · CaCN2 · CaCO3 · CaC2O4 · CaCl · CaCl2 · Ca(ClO)2 · Ca(ClO3)2 · CaCrO4 · CaF2 · CaH2 · Ca(HCO3)2 · CaH2S2O6 · CaI2 · Ca(IO3)2 · Ca(MnO4)2 · Ca(NO3)2 · CaO · CaO2 · Ca(OH)2 · CaS · CaSO3 · CaSO4 · CaSi2 · CaTiO3 · Ca2P2O7 · Ca2SiO4 · Ca3(AsO4)2 · Ca3(BO3)2 · Ca3(C6H5O7)2 · Ca3N2 · Ca3P2 · Ca3(PO4)2 · Ca(H2PO4)2 · CaHPO4 · C36H70CaO4
Categories:- Sulfides
- Calcium compounds
- Meteorite minerals
- [Ca]=S
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

