- Oxygen difluoride
-
Oxygen difluoride 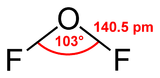
 Other namesdifluorine monoxide
Other namesdifluorine monoxide
fluorine monoxide
oxygen fluoride
hypofluorous anhydrideIdentifiers CAS number 7783-41-7 
PubChem 24547 ChemSpider 22953 
ChEBI CHEBI:30494 
RTECS number RS2100000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - FOF
Properties Molecular formula OF2 Molar mass 53.9962 g/mol Appearance colorless gas, pale yellow liquid when condensed Density 1.9 g/cm3 as liquid at -145°C Melting point −223.8 °C
Boiling point −144.8 °C
Solubility in other solvents 68 mL gaseous OF2 in 1 L (0 °C)[1] Thermochemistry Std enthalpy of
formation ΔfHo29824.5 kJ mol−1 Related compounds Related compounds HFO
O2F2
difluoride (verify) (what is: /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Oxygen difluoride is the chemical compound with the formula F2O. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a "V" shaped structure like H2O, but it has very different properties, being a strong oxidizer.
Contents
Preparation
Oxygen difluoride was first reported in 1929; it was obtained by the electrolysis of molten potassium fluoride and hydrofluoric acid containing small quantities of water.[2][3] The modern preparation entails the reaction of fluorine with a dilute aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, with sodium fluoride as a side-product:
- 2 F2 + 2 NaOH → OF2 + 2 NaF + H2O
Reactions
Its powerful oxidizing properties are suggested by the oxidation number of +2 for the oxygen atom, which is unusual. Above 200 °C, OF2 decomposes to oxygen and fluorine via a radical mechanism.
OF2 reacts with many metals to yield oxides and fluorides. Nonmetals also react: phosphorus reacts with OF2 to form PF5 and POF3; sulfur gives SO2 and SF4; and unusually for a noble gas, xenon reacts, at elevated temperatures, yielding XeF4 and xenon oxyfluorides.
Oxygen difluoride reacts very slowly with water to form hydrofluoric acid:
- OF2 (aq) + H2O (aq) → 2 HF (aq) + O2 (g)
Oxygen difluoride oxidizes sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide:
- OF2 + SO2 → SO3 + F2
However, in the presence of UV radiation the products are sulfuryl fluoride, SO2F2, and pyrosulfuryl fluoride, S2O5F2:
- OF2 + 2 SO2 → S2O5F2
Popular culture
In Robert L. Forward's science fiction novel Camelot 30K, oxygen difluoride was used as a biochemical solvent by fictional life forms living in the solar system's Kuiper belt.
Safety
OF2 is a dangerous chemical, as is the case for any strongly oxidizing gas.
References
- ^ Yost, D. M. "Oxygen Fluoride" Inorganic Syntheses, 1939 volume, 1, pages 109-111.
- ^ Paul Lebeau; Damiens, A. "A New Method for the Preparation of the Fluorine Oxide”Compt. rend. 1929, volume 188, 1253-5.
- ^ Lebeau, P.; Damiens, A. "The Existence of an Oxygen Compound of Fluorine"Compt. rend. 1927, volume 185, pages 652-4.
External links
Categories:- Oxygen compounds
- Fluorides
- Nonmetal halides
- Rocket oxidizers
- Oxidizing agents
- Chalcohalides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
