- Dioxygen difluoride
-
Dioxygen difluoride 
 Dioxygen difluorideSystematic nameFluorooxy hypofluoriteOther namesDifluorine dioxide
Dioxygen difluorideSystematic nameFluorooxy hypofluoriteOther namesDifluorine dioxide
Fluorine dioxide
PerfluoroperoxideIdentifiers Abbreviations FOOF CAS number 7783-44-0 PubChem 123257 
ChemSpider 109870 
ChEBI CHEBI:47866 
Gmelin Reference 1570 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - FOOF
Properties Molecular formula O2F2 Molar mass 69.996 g·mol−1 Melting point −154 °C, 119 K, -245 °F
Boiling point −57 °C, 216 K, -71 °F (extrapolated)
Solubility in other solvents decomp. Related compounds Related compounds H2O2
OF2
FClO2
S2Cl2 difluoride (verify) (what is:
difluoride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dioxygen difluoride is a compound with the formula O2F2. It exists as an orange solid that melts into a red liquid at −163 °C[1] It is a strong oxidant and decomposes into OF2 and oxygen even at −160 °C (4% per day).[2]
Contents
Preparation
Dioxygen difluoride can be obtained by subjecting a 1:1 mixture of gaseous fluorine and oxygen at low pressure (7–17 mmHg is optimal) to an electric discharge of 25–30 mA at 2.1–2.4 kV. This is basically the reaction used for the first synthesis by Otto Ruff in 1933.[3] Another synthesis involves mixing O2 and F2 in a stainless steel vessel cooled to −196 °C, followed by exposing the elements to 3 MeV bremsstrahlung for several hours.
Structure and electronic description
In O2F2, oxygen is assigned the unusual oxidation state of +1. In most of its other compounds, oxygen has an oxidation state of −2.
The structure of dioxygen difluoride resembles that of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, in its large dihedral angle, which approaches 90°. This geometry conforms with the predictions of VSEPR theory. The O−O bond length is within 2 pm of the 120.7 pm distance for the O=O double bond in dioxygen, O2.
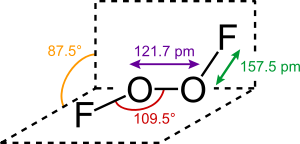
The bonding within dioxygen difluoride has been the subject of considerable speculation over the years, particularly because of the very short O–O distance and the long O–F distances. Bridgeman has proposed a scheme which essentially has an O–O triple bond and an O–F single bond that is destabilised and lengthened by repulsion between the lone pairs on the fluorine atoms and the π-orbitals of the O–O bond.[4] Repulsion involving the fluorine lone pairs is also responsible for the long and weak covalent bonding in the fluorine molecule.
Reactivity
The overarching property of this unstable compound is its oxidizing power, despite the fact that all reactions must be conducted near −100 °C.[5] With BF3 and PF5, it gives the corresponding dioxygenyl salts:[2][6]
- 2 O2F2 + 2 PF5 → 2 [O2]+[PF6]− + F2
It converts uranium and plutonium oxides into the corresponding hexafluorides.[7]
References
- ^ Kirshenbaum, A. D.; Grosse, A. V. (1959). "Ozone Fluoride or Trioxygen Difluoride, O3F2". Journal of the American Chemical Society 81 (6): 1277. doi:10.1021/ja01515a003.
- ^ a b Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Ruff, O.; Mensel, W. (1933). "Neue Sauerstofffluoride: O2F2 und OF". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 211 (1–2): 204–208. doi:10.1002/zaac.19332110122.
- ^ Bridgeman, A. J.; Rothery, J. (1999). "Bonding in mixed halogen and hydrogen peroxides". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions 1999 (22): 4077–4082. doi:10.1039/a904968a.
- ^ Streng, A. G. (1963). "The Chemical Properties of Dioxygen Difluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society 85 (10): 1380–1385. doi:10.1021/ja00893a004.
- ^ Solomon, I. J.; et al. (1964). "New Dioxygenyl Compounds". Inorganic Chemistry 3 (3): 457. doi:10.1021/ic50013a036.
- ^ Atwood, D. A. (2006). "Fluorine: Inorganic Chemistry". Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/0470862106.ia076.
External links
Categories:- Fluorides
- Oxygen compounds
- Oxidizing agents
- Chalcohalides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
