- Potassium ferrate
-
Potassium ferrate 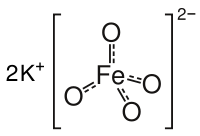
 Potassium ferrate(VI)Other namesPotassium ferrate
Potassium ferrate(VI)Other namesPotassium ferrate
Dipotassium ferrateProperties Molecular formula K2FeO4 Molar mass 198.0392 g/mol Appearance Dark purple solid Density 2.829 g/cm3, solid Melting point >198 °C (decomposition temp)
Solubility in water soluble in 1M KOH Solubility in other solvents reacts with most solvents Structure Crystal structure K2SO4 motif Coordination
geometryTetrahedral Dipole moment 0 D Hazards R-phrases 8 S-phrases 17-36 Main hazards oxidizer Flash point non-combustible Related compounds Other anions K2MnO4
K2CrO4
K2RuO4Other cations BaFeO4
Na2FeO4 ferrate (verify) (what is:
ferrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Potassium ferrate is the chemical compound with the formula K2FeO4. This purple salt is paramagnetic, and is a rare example of an iron(VI) compound. In most of its compounds, iron has the oxidation state +2 or +3 (Fe2+ or Fe3+). Reflecting its high oxidation state, FeO42− is a powerful oxidizing agent.
K2FeO4 has attracted interest for applications in "green chemistry" because the by-products of its use, iron oxides, are environmentally innocuous. In contrast, some related oxidants such as chromate are considered environmentally hazardous. However, the main difficulty with the use of K2FeO4 is that it is often too reactive, as indicated by the fact that it decomposes in contact with water.[1]
- 4 K2FeO4 + 4 H2O → 3 O2 + 2 Fe2O3 + 8 KOH
Synthesis and structure
Georg Ernst Stahl (1660 – 1734) first discovered that the residue formed by igniting a mixture of potassium nitrate (saltpetre) and iron powder dissolved in water to give a purple solution. Edmond Frémy (1814 – 1894) later discovered that fusion of potassium hydroxide and iron(III) oxide in air produced a compound that was soluble in water. The composition corresponded to that of potassium manganate. In the laboratory, K2FeO4 is prepared by oxidizing an alkaline solution of an iron(III) salt with concentrated chlorine bleach.[2]
The salt is isostructural with K2MnO4, K2SO4, and K2CrO4. The solid consists of K+ and the tetrahedral FeO42− anion, with Fe-O distances of 1.66 Å.[3] The poorly soluble barium salt, BaFeO4, is also known.
Properties and applications
As a dry solid, K2FeO4 is stable. It decomposes with evolution of O2 in neutral water, and especially rapidly in acidic water. At high pH, aqueous solutions are stable. The deep purple solutions are similar in appearance to potassium permanganate (KMnO4). It is stronger oxidizing agent than the latter.
Because the side products of its redox reactions are rust-like iron oxides, K2FeO4 has been described as a "green oxidant." It has been employed in waste-water treatment as an oxidant for organic contaminants and as a biocide. Conveniently, the resulting reaction product is iron(III) oxyhydroxide, an excellent flocculant.
In organic synthesis, K2FeO4 oxidizes primary alcohols.[4]
K2FeO4 has also attracted attention as a potential cathode material in a "super iron battery."
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Schreyer, J. M.; Thompson, G. W.; Ockerman, L. T. "Potassium Ferrate(VI)" Inorganic Syntheses, 1953 volume IV, pages 164-168.
- ^ Hoppe, M. L.; Schlemper, E. O.; Murmann, R. K. "Structure of Dipotassium Ferrate(VI)" Acta Crystallographica 1982, volume B38, pp. 2237-2239. doi:10.1107/S0567740882008395.
- ^ Green, J. R. “Potassium Ferrate” Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001, John Wiley. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp212.
Potassium compounds KBr · KBrO3 · KCN · KCNO · KCl · KClO3 · KClO4 · KF · KH · KHCO2 · KHCO3 · KHF2 · KHSO3 · KHSO4 · KH2AsO4 · KI · KIO3 · KIO4 · KMnO4 · KN3 · KNO2 · KNO3 · KOCN · KOH · KO2 · KPF6 · KSCN · K2CO3 · K2CrO4 · K2Cr2O7 · K2FeO4 · K2MnO4 · K2O · K2O2 · K2PtCl4 · K2PtCl6 · K2S · K2SO3 · K2SO4 · K2SO5 · K2S2O5 · K2S2O7 · K2S2O8 · K2SiO3 · K3[Fe(CN)6] · K3[Fe(C2O4)3] · K4[Fe(CN)6] · K3PO4 · Categories:
- Ferrates
- Potassium compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Ferrate — A ferrate is the anion FeO42 in which iron is in a +6 formal oxidation state (iron VI). A ferrate can be formed by oxidizing iron with strong oxidizing agents under alkaline conditions or in the solid state by heating a mixture of iron filings… … Wikipedia
Potassium ferrocyanide — chembox Name = Potassium ferrocyanide ImageFile = Potassium ferrocyanide trihydrate sample.jpg ImageSize = 250px ImageName = Potassium ferrocyanide trihydrate IUPACName = Potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) OtherNames = Tetrapotassium ferrocyanide,… … Wikipedia
Barium ferrate — Chembox new ImageFile = ImageSize = IUPACName = barium ferrate(VI) OtherNames = Section1 = Chembox Identifiers CASNo = 13773 23 4 PubChem = SMILES = Section2 = Chembox Properties Formula = MolarMass = 257.17 g/mol Appearance = maroon Density =… … Wikipedia
Iron — Fe redirects here. For other uses, see Fe (disambiguation). This article is about the chemical element. For other uses, see Iron (disambiguation). manganese … Wikipedia
Super iron battery — The Super iron battery is a new class of rechargeable electric battery. Super iron is a moniker for a special kind of ferrate salt (iron(VI)), this is, potassium ferrate (K2FeO4) or barium ferrate (BaFeO4), used in this new class of batteries. [… … Wikipedia
Kaliumferrat — Strukturformel … Deutsch Wikipedia
Химические свойства спиртов — Химические свойства спиртов это химические реакции спиртов во взаимодействии с другими веществами. Они определяются в основном наличием гидроксильной группы и строением углеводородной цепи, а также их взаимным влиянием: Чем больше… … Википедия
Ферраты — Раствор феррата натрия (слева) в сравнении с перманганатом калия (справа) Ферраты соли, содержащие феррат анион FeO42 . Соответствуют железной кислоте H2FeO4, которая в свободном виде не существует. Как правило, имеют фиолетовый цвет.… … Википедия
Liste de composés inorganiques K — Sommaire 1 Potassium 2 Krypton A B C D E F G H I K L … Wikipédia en Français
Liste des composés inorganiques K — Liste de composés inorganiques K Sommaire 1 Potassium 2 Krypton // A B C D … Wikipédia en Français
