- Cinnamic acid
-
Cinnamic acid 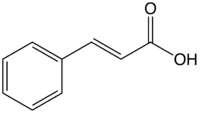
 Other namesCinnamic Acid
Other namesCinnamic Acid
trans-Cinnamic Acid
Phenylacrylic acid
Cinnamylic acid
3-Phenylacrylic acid
(E)-Cinnamic acid
Benzenepropenoic acid
Isocinnamic acidIdentifiers CAS number 140-10-3 
PubChem 444539 ChemSpider 392447 
KEGG C00423 
ChEBI CHEBI:35697 
ChEMBL CHEMBL27246 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)\C=C\c1ccccc1
Properties Molecular formula C9H8O2 Molar mass 148.16 g mol−1 Exact mass 148.05243 Appearance White monoclinic crystals Density 1.2475 g/cm3[1] Melting point 133 °C, 406 K, 271 °F ([1])
Boiling point 300 °C, 573 K, 572 °F ([1])
Solubility in water 500 mg/L[1] Acidity (pKa) 4.44 Hazards EU classification Irritant (Xi) R-phrases R36 S-phrases S25 Flash point >100 °C (212 °F)[1]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cinnamic acid is a white crystalline hydroxycinnamic acid, which is slightly soluble in water.
It is obtained from oil of cinnamon, or from balsams such as storax.[2] It is also found in shea butter and is the best indication of its environmental history and post-extraction conditions. It can also be made synthetically.
Cinnamic acid is used in flavors, synthetic indigo, and certain pharmaceuticals, though its primary use is in the manufacturing of the methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters for the perfume industry.[2] Cinnamic acid has a honey-like odor;[3] it and its more volatile ethyl ester (ethyl cinnamate) are flavor components in the essential oil of cinnamon, in which related cinnamaldehyde is the major constituent. Cinnamic acid is also part of the biosynthetic shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways. Its biosynthesis is performed by action of the enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) on phenylalanine.
Cinnamic acid is freely soluble in benzene, diethyl ether, acetone, and acetic acid;[2] it is insoluble in hexane.
Cinnamic acid is also a kind of self-inhibitor produced by fungal spore to prevent germination.
Chemical synthesis
Rainer Ludwig Claisen (1851–1930), German chemist, described for the first time in 1890 the synthesis of cinnamates by reacting aromatic aldehydes with esters. The reaction is known as the Claisen reaction.
References
Hydroxycinnamic acids Caffeic acid | Cichoric acid | Cinnamic acid | Coumaric acid | Diferulic acid | Ferulic acid | Plicatins A and B | Sinapinic acidGlycosides Tartaric acid esters Others Grape reaction productCategories:- Flavors
- Aromatic compounds
- Hydroxycinnamic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
