- Cynarine
-
Cynarine 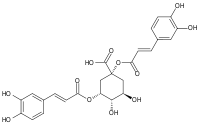
 (1R,3R,4S,5R)-1,3-bis[[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy]-4,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acidOther names1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid; Cynarin; Cinarin; Cinarine
(1R,3R,4S,5R)-1,3-bis[[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy]-4,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acidOther names1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid; Cynarin; Cinarin; CinarineIdentifiers CAS number 30964-13-7 
PubChem 5281769 ChEMBL CHEMBL487258 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C[C@]1(C(=O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O)O
Properties Molecular formula C25H25O12 Molar mass 517.46 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cynarine is a hydroxycinnamic acid and a biologically active chemical constituent of artichoke.[1] Chemically, it is an ester formed from quinic acid and two units of caffeic acid. It inhibits taste receptors, making water (and other foods and drinks) seem sweet.[2]
References
- ^ Panizzi, Luigi; Scarpati, Maria Luisa (1954). "Constitution of Cynarine, the Active Principle of the Artichoke". Nature 174 (4440): 1062. doi:10.1038/1741062a0. PMID 13214078.
- ^ Feifer, Jason (May 2011). "A Matter of Taste". Men's Health 26 (4): 140.
Hydroxycinnamic acids Caffeic acid | Cichoric acid | Cinnamic acid | Coumaric acid | Diferulic acid | Ferulic acid | Plicatins A and B | Sinapinic acidGlycosides Chlorogenic acid | CynarineTartaric acid esters Caftaric acid | Coutaric acid | Fertaric acidOthers Grape reaction productThis article about a natural phenol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
