- Cichoric acid
-
Cichoric acid 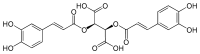 (2R,3R)-2,3-bis{[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy}butanedioic acid
(2R,3R)-2,3-bis{[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy}butanedioic acidIdentifiers CAS number 6537-80-0 
PubChem 5281764 KEGG C10437 
ChEMBL CHEMBL282731 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)[C@H](OC(=O)\C=C\c1ccc(O)c(O)c1)[C@@H](OC(=O)\C=C\c2cc(O)c(O)cc2)C(=O)O
- InChI=InChI=1/C22H18O12/c23-13-5-1-11(9-15(13)25)3-7-17(27)33-19(21(29) 30)20(22(31)32)34-18(28)8-4-12-2-6-14(24)16(26)10-12/h1-10,19-20, 23-26H,(H,29,30)(H,31,32)/b7-3+,8-4+/t19-,20-/m1/s1
Properties Molecular formula C22H18O12 Molar mass 474.371 g/mol  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cichoric acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound of the phenylpropanoid class and occurs in a variety of plant species. It is a derivative of both caffeic acid and tartaric acid.[1] As a suitable marker for the distinction of Echinacea species, it is often assayed using RP-HPLC and Thin layer chromatography (TLC) methods.[2] It has the chemical formula C22H18O12.
Sources
Cichoric acid has first been isolated from Cichorium intybus (chicory) but also occurs in significant amounts in Echinacea, particularly E. purpurea, dandelion leaves, basil, lemon balm and in aquatic plants, including algae and sea grasses.[3][4]
Biological functions
Cichoric acid has been shown to stimulate phagocytosis in both in vitro and in vivo studies, to inhibit the function of hyaluronidase (an enzyme which breaks down hyaluronic acid in the human body), protect collagen from damage due to free radicals, and inhibit the function of HIV-1 integrase.[5][6]
References
- ^ Hall III, Clifford; Jurgen G. Schwarz (2002) John Shi, G. Mazza, Marc Le Maguer ed. Functional Foods: Biochemical & Processing Aspects 2 CRC Press p. 241 ISBN 1566769027 http://books.google.com/?id=rEr8g-phGHAC. Retrieved 2008-12-09
- ^ Bauer R, Khan IA, Wagner H. Echinacea-Drogen, Standardisierung mittels HPLC und DC. Deutsche Apotheker Zeitung, 1986, 126:1065–1070. Citation in WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants - Volume 1
- ^ I.D. Chkhikvishvili and G.I. Kahrebava (2001). “Cichoric and Chlorogenic Acids in Plant Species from Georgia”. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 37 (2): 188-191. doi: 10.1023/a:1002888016985
- ^ Jungmin Lee (2010). Short communication “Caffeic acid derivatives in dried Lamiaceae and Echinacea purpurea products”. Journal of Functional Foods 2, 158-162. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2010.02.003
- ^ Mazza, G.; Oomah, B. Dave (2000), Herbs, Botanicals & Teas, CRC Press, pp. 51, ISBN 1566768519, http://books.google.com/?id=Au1HLD7eyZQC, retrieved 2008-12-09
- ^ Miller, Sandra Carol; Yu, He-Ci (2004), Echinacea, CRC Press, pp. 140, ISBN 0415288282, http://books.google.com/?id=WMGlDuGhKq8, retrieved 2008-12-09
Hydroxycinnamic acids Caffeic acid | Cichoric acid | Cinnamic acid | Coumaric acid | Diferulic acid | Ferulic acid | Plicatins A and B | Sinapinic acidGlycosides Tartaric acid esters Caftaric acid | Coutaric acid | Fertaric acidOthers Grape reaction productCategories:- Dicarboxylic acids
- Tartrates
- Cinnamates
- Catechols
- Hydroxycinnamic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
