- Crystal Palace (High Level) railway station
-
This article is about the disused High Level station. For the open Low Level station, see Crystal Palace railway station.
Crystal Palace (High Level) Location Place Crystal Palace Area Southwark Coordinates 51°25′17″N 0°04′43″W / 51.4214°N 0.0785°WCoordinates: 51°25′17″N 0°04′43″W / 51.4214°N 0.0785°W Grid reference TQ337709 Operations Original company Crystal Palace and South London Junction Railway Pre-grouping London, Chatham and Dover Railway
South Eastern and Chatham RailwayPost-grouping Southern Railway
British RailwaysPlatforms 6 History 1 August 1865 Opened as Crystal Palace (High Level) 1 November 1898 Renamed Crystal Palace High Level and Upper Norwood 1 January 1917 Temporarily closed 1 March 1919 Reopened 9 July 1923 Renamed Crystal Palace High Level July 1925 electrified 22 May 1944 Temporarily closed 4 March 1946 Reopened 20 September 1954 Station closed to passengers Disused railway stations in the United Kingdom Closed railway stations in Britain
A B C D–F G H–J K–L M–O P–R S T–V W–ZCrystal Palace (High Level) railway station was a station in the London Borough of Southwark in south London. It was one of two stations built to serve the site of the 1851 exhibition building, the so-called Crystal Palace, when it was moved from Hyde Park to Sydenham Hill after 1851.
Contents
History
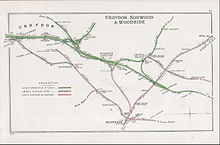 A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of lines in South London, including (right) part of the Crystal Palace and South London Junction Railway and Crystal Palace (High Level) station (shown here as Crystal Palace & Upper Norwood)
A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of lines in South London, including (right) part of the Crystal Palace and South London Junction Railway and Crystal Palace (High Level) station (shown here as Crystal Palace & Upper Norwood)
The Crystal Palace and South London Junction Railway was promoted by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR); by 1860 the LCDR had a line running to Beckenham Junction via Loughborough Junction, some three miles to the north-west of the Crystal Palace site. In order to capture traffic from the LBSCR, the LCDR constructed a branch line from the latter station, with a junction at Nunhead to run directly to the Crystal Palace site. The line opened on 1 August 1865. The station was designed by Edward Middleton Barry as a lavish red brick and buff terra cotta building. The station was excavated into the ridge below Crystal Palace Parade requiring major engineering works. The line was one of the first of the former South Eastern and Chatham Railway to be electrified by Southern Railway, under "South Eastern Electrification – Stage 1" in July 1925[1].
After the Crystal Palace was destroyed by fire in 1936 traffic on the branch declined. During World War 2 the line was temporarily closed after bomb damage. Although temporary repairs were made and the line subsequently reopened the decline in traffic and a requirement for heavy reconstruction work led to the decision to close the station and branch on 20 September 1954, although it was not demolished until 1961.
Although the site of the station was developed for housing in the 1970s, the retaining walls below Crystal Palace Parade and the ornamental portal of Paxton Tunnel to the north are still readily visible.
The High Level Station was connected to the Palace by a fan-vaulted pedestrian subway in finely detailed red and cream brickwork. This subway and an adjacent courtyard survived the 1936 fire, and was used as an air raid shelter during World War II. It is now a Grade II listed building [2]. Although the subway is now sealed off, it is sometimes opened to allow organised visits.
Preceding station Disused railways Following station Upper Sydenham
Line and station closedBritish Rail
Southern Region
Crystal Palace and South London Junction RailwayTerminus The train entombed in the tunnel myth
There is a rumor that in one of the sealed tunnels in the area, an engine or carriage remains hidden collecting dust. Another version of the story, popular amongst local schoolchildren, claims that the High Level station was closed because a commuter train was trapped by a tunnel collapse, entombing the passengers who remain there to this day.[3]
These stories are an example of the extraordinary persistence of local urban legend. The story of the entombed train was apparently current in the 1930s. Back then it referred to the abandoned 1860s pneumatic railway on the north side of the grounds of Crystal Palace Park. See Crystal Palace pneumatic railway for more information.[3]
Most traces of this had almost certainly been destroyed by the building works for the 1911 Festival of Empire, but there was an unsuccessful archaeological dig for the train sponsored by the BBC's Nationwide current affairs programme in the 1970s.[3]
References
- ^ "Electric Railways". 'Stendec Systems'. 2007. http://www.electric-railways.co.uk/L2_DC_750_CR/1_general/g3_proj/prj-0d75-sr.html. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ SEMG
- ^ a b c Crystal Palace High Level & Upper Norwood Station at Subterranea Britannica
Further reading
- Crystal Palace (High Level) and Catford Loop by V Mitchell & K Smith, Middleton Press, 1991
- The Railway through Sydenham Hill Wood, From the Nun's Head to the Screaming Alice by Mathew Frith, The Friends of the Great North Wood and London Wildlife Trust leaflet 1995
- London's Local Railways by A A Jackson, David & Charles, 1978
- The Crystal Palace (High Level) Branch by W Smith, British Railway Journal 28, 1989
External links
- London's Abandoned Stations – Crystal Palace branch
- Crystal Palace High Level & Upper Norwood Station at Subterranea Britannica
Categories:- Disused railway stations in Southwark
- Former London, Chatham and Dover Railway stations
- Railway stations opened in 1865
- Railway stations closed in 1917
- Railway stations opened in 1919
- Railway stations closed in 1944
- Railway stations opened in 1946
- Railway stations closed in 1954
- Urban legends
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


