- Duchy of Modena and Reggio
-
Duchy of
Ducato di Modena e Reggio
Ducatus Mutinae et RegiiState of the Holy Roman Empire (until 1806) ← 
←
1452–1796
1814–1859 →
→
 →
→Flag
Motto
Dextera Domini exaltavit me
"The right hand of the Lord is exalted"Anthem
Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser
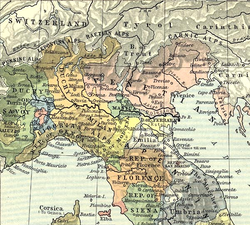
"God Save Emperor Francis"Northern Italy in 1494:
Este territories (Modena, Reggio and Ferrara) in yellowCapital Modena Language(s) Latin, Italian Religion Catholicism Government Principality Duke - 1450-1471 Borso d'Este - 1471-1505 Ercole I d'Este - 1505-1534 Alfonso I d'Este - 1534-1559 Ercole II d'Este - 1559-1597 Alfonso II d'Este Historical era Early modern era - Created 1452 - Conquered by France 1796 - Re-established 1814 - Popular revolution 1859 Today part of  Italy
ItalyThe Duchy of Modena and Reggio (Italian: Ducato di Modena e Reggio, Latin: Ducatus Mutinae et Regii was a small Italian state that existed from 1452 to 1859, with a break between 1796 and 1814.[1] It was ruled by the noble House of Este, from 1814 Austria-Este.
Contents
House of Este
In 1452 Emperor Frederick III enfeoffed the duchy to Borso d'Este, whose family had ruled the city of Modena and Reggio Emilia for centuries. Borso in 1450 had also succeeded his brother as margrave in the adjacent Papal Duchy of Ferrara, where he received the ducal title in 1471. The Este lands on the southern border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Papal States formed a stabilizing buffer state in the interest of both.
The first Este dukes ruled invulnerably and achieved an economic and cultural peak: Borso's successor Duke Ercole I had the city of Modena rebuilt according to plans designed by Biagio Rossetti, his successors were patrons of artists like Titian and Ludovico Ariosto. In the War of the League of Cambrai from 1508, troops from Modena fought in Papal service against the Republic of Venice. Upon the death of Duke Alfonso II in 1597, the ducal line became extinct. The Este lands were bequested to Alfonso's cousin Cesare d'Este, however, the succession was not acknowledged by Pope Clement VIII and Ferrara was finally seized by the Papacy. Cesare could retain Modena and Reggio as Imperial fiefs.
In the 1628 War of the Mantuan Succession, the dukes of Modena sided with Habsburg Spain and in turn received the town of Correggio from the hands of Emperor Ferdinand II. During the War of the Spanish Succession, Duke Rinaldo was ousted by French troops under Louis Joseph de Bourbon, he could not return until 1707. His successor Francesco III backed France in the 1740 War of the Austrian Succession, and was expelled by Habsburg forces, but his duchy was restored by the 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. In 1711 the small duchy of Mirandola was absorbed by the Este.
In 1796, Modena was again occupied by a French army under Napoleon Bonaparte, who deposed Duke Ercole III and created the Cispadane Republic out of his territory. By the 1801 Treaty of Lunéville the last Este Duke was compensated with the Breisgau region of the former Further Austrian territories in southwestern Germany, and died in 1803. Following his death, Mthe ducal title was inherited by his son-in-law, the Habsburg-Lorraine archduke Ferdinand of Austria, an uncle of Emperor Francis II.
House of Austria-Este
With the dissolution of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1814, Ferdinand's son, Francis IV, again assumed the rule as Duke of Modena. Soon after, he inherited the territories of Massa and Carrara from his mother. In the course of the Italian unification, the Austria-Este dukes were briefly ousted in 1831 and 1848, but soon returned.
During the Second Italian War of Independence, following the 1859 Battle of Magenta the last Duke Francis V was again forced to flee, this time permanently. In December, Modena joined with Tuscany and Parma to form the United Provinces of Central Italy, which were annexed to the Kingdom of Sardinia in March 1860.
Provinces of the Duchy before the dissolution
- Modena (Duchy of Modena)
- Reggio (Duchy of Reggio)
- Guastalla
- Frignano
- Garfagnana
- Lunigiana
- Massa and Carrara (Duchy of Massa and Carrara)
See also
References
- ^ Trudy Ring; Robert M. Salkin; Sharon La Boda (1 January 1996). International Dictionary of Historic Places: Southern Europe. Taylor & Francis. pp. 446–. ISBN 9781884964022. http://books.google.com/books?id=74JI2UlcU8AC&pg=PA446. Retrieved 21 February 2011.
1st Generation Alfonso I, Duke of Modena · Ippolito, Cardinal d'Este · Prince Ferrante · Prince Sigismondo · Prince Alberto · Ercole, Signore of San Martino2nd Generation Prince Alessandro · Ercole II, Duke of Modena · Prince Alessandro · Francesco, Marquis of Massalombarda · Prince Alfonso · Alfonsino, Marquis of Castelnuovo · Sigismondo, Signore of San Martino · Ippolito, Cardinal d'Este
3rd Generation Prince Alfonso · Alfonso II, Duke of Modena · Cesare, Duke of Modena · Luigi, Cardinal of Ferrera · Prince Alessandro · Filipo, Marchese of San Martino4th Generation Alfonso III, Duke of Modena · Prince Cesare · Prince Obizzo · Prince Cesare · Prince Rinaldo · Prince Borso · Prince Ippolito · Prince Foresto · Prince Bonofazio · Prince Rinaldo · Prince Filiberto · Luigi, Lord of Montecchio and Scandiano · Sigismondo, Marchese of Lanzo and Borgomanero5th Generation Francesco I, Duke of Modena · Filippo Francesco, Marquess of Lanzo · Carlo Emanuele, Marquess of Lanzo6th Generation Alfonso IV, Duke of Modena · Rinaldo, Duke of Modena · Prince Tedald · Prince Almerigo · Prince Tedald · Sigismondo, Marquess of San Martino · Carlo Filiberto, Marques of Borgomanero · Sigismondo, Marchese of San Martino7th Generation Francesco II, Duke of Modena · Francesco III, Duke of Modena · Prince Gian Federico · Prince Clemente · Carlo Emanuele, Marques of Borgomanero · Carlo Filiberto, Marchese of San Martino8th Generation Prince Alfonso · Prince Francesco Constantino · Ercole III, Duke of Modena · Benedetto Filippo, Abbot of Anchin9th Generation Prince Reinaldo10th Generation Prince Josef Franz* · Francis IV, Duke of Modena* · Prince Ferdinand Karl Joseph* · Prince Maximilian* · Prince Karl*11th Generation *also Archduke of Austria Princesses of Modena Generations start from Ercole I d'Este, first Duke of Modena 1st Generation Isabella, Marchioness of Mantua · Beatrice, Duchess of Milan · Princess Caterina · Princess Angela Caterina2nd Generation Princess Leonora · Princess Isabella Maria3rd Generation Anna, Duchess of Guise, Duchess of Nemours · Lucrezia, Duchess of Urbino · Princess Eleonora · Princess Angela Caterina4th Generation Princess Julia · Maria Laura, Duchess of Mirandola · Princess Caterina · Princess Angela Caterina5th Generation Princess Caterina Maria · Margarete, Duchess of Guastalla · Princess Beatrice · Princess Beatrice · Anna Beatrice, Duchess of Mirandola · Ippolita, Lady of Montecchio and Scandiano6th Generation Isabella, Duchess of Parma · Princess Leonore · Princess Eleonore · Maria, Duchess of Parma · Princess Vittoria · Matilde, Countess of Novellara · Maria Angela Caterina, Princess of Carignan · Princess Julia · Princess Julia7th Generation Maria Beatrice, Queen of England · Princess Benedetta · Amalia, Marchioness of Villeneuf · Enrichetta, Duchess of Parma8th Generation Maria Teresa Felicitas, Duchess of Penthièvre · Princess Mathilde · Maria Fortunata, Princess of Conti · Maria Anna, Princess of Paliano9th Generation 10th Generation Maria Theresa, Queen of Sardinia* · Princess Josepha* · Maria Leopoldine, Electress of Bavaria* · Princess Maria Antonia* · Maria Ludovika, Empress of Austria*11th Generation Maria Theresa, Duchess of Orléans* · Maria Beatrix, Countess of Montizón*12th Generation Princess Anna Beatrice* · Maria Theresa, Queen of Bavaria**also Archduchess of Austria 1st Generation Princess Eleanor of Naples ·2nd Generation 3rd Generation 4th Generation 5th Generation 6th Generation Maria Caterina Farnese · Vittoria Farnese · Lucrezia Barberini* · Princess Margherita of Savoy · Teresa Maria Grimaldi7th Generation 8th Generation 9th Generation 10th Generation none11th Generation 12th Generation *did not have a royal or noble title by birth
^also a princess of Modena in her own rightFormer monarchies of the Italian Peninsula, Sardinia and Sicily Amalfi • Apulia • Arborea • Benevento • Byzantine Empire • Cagliari • Capua • Carrara • Castro • Ceva • Etruria • Ferrara • Finale • Florence • Gaeta • Gallura • County of Guastalla • Duchy of Guastalla • Italy (Lombard) • Italy (modern) • Italy (Napoleonic) • Lombardy-Venetia • Principality of Lucca and Piombino • Duchy of Lucca • Mantua • Massa • Medieval Italy • Milan • Mirandola • Modena • Montferrat • Duchy of Naples • Kingdom of Naples • Ogliastra • Ostrogothic Kingdom • Papal States • Parma • Piombino • Presidi • Reggio • Roman Kingdom • Roman Empire • Salerno • Saluzzo • Sardinia • Savoy • Emirate of Sicily • County of Sicily • Kingdom of Sicily • Sora • Tavolara • Torres • Trent • Tuscany • Two Sicilies • Urbino • Western Roman Empire
Categories:- Former principalities
- Former countries on the Italian Peninsula
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1452
- States and territories disestablished in 1859
- Contemporary Italian history
- House of Habsburg-Lorraine
- House of Este
- House of Austria-Este
- 1859 disestablishments
- States and territories established in 1814
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.