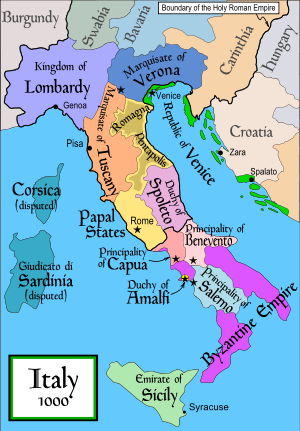
- Principality of Capua
-
The Principality of Capua (Latin: Principatus Capuae or Capue, Italian Principato di Capua) was a Lombard state in Southern Italy, usually de facto independent, but under the varying suzerainty of Western and Eastern Roman Empires. It was originally a gastaldate, then a county, within the principality of Salerno.
Contents
Origins
Old Capua was an ancient Italian city, the greatest Roman city of the south. It was the centre of Lombard gastaldate in the duchy of Benevento, although little is known of this part of its history. It first enters history as a Lombard state under Landulf the Old with the death of the Beneventan duke Sicard in 839. Landulf and his sons were partisans of Siconulf of Salerno. In 841, Capua was sacked and completely destroyed by Saracens in the pay of Radelchis I of Benevento. Landulf and his eldest son, Lando I, took the initiative in fortifying the nearby hill of Triflisco on which was built "New Capua": the Capua of today.
Pando the Rapacious declared Capua independent of Salerno in 862. On his death in the same year, the succession to the county was thrown into dispute. His son was deposed by Bishop Landulf who thus united the ecclesiastical and secular rule of the region as Athanasius was to do near-contemporaneously in Naples. Disputes over the bishopric and the countship befell Capua on Landulf's death and a civil war enveloped the principality between Pandenulf, the earlier deposed son of Pando, and Lando III, another grandson of Landulf I. Salerno allied with Lando and Benevento with Pandenulf. A succession crisis followed in 887 and Atenulf established himself and his princely status with the aid of the aforementioned Athanasius of Naples. Atenulf would try to avert future succession crises and to vindicate the independent pretensions of Capua à la those of Benevento and Salerno.
Union with Benevento
In 899, Atenulf I defeated Radelchis II and conquered Benevento. He declared Capua and Benevento inseparable and introduced the principle of co-rule, whereby sons would be associated with their fathers and brothers with each other, a principle soon borrowed by Salerno. Atenulf associated his son, Landulf, as co-prince and built up alliances with the local Greek states, like Naples and Gaeta, which alliances were continued under his successor. He also began planning the eventual reconquest of Moslem-occupied territory in the region, but died before his plans, which culminated in the victorious Battle of the Garigliano in 915, could come to fruition. Landulf mostly continued the policies of his father and spent most of his career after Garigliano trying to weaken the Byzantine authority in Apulia and the Campania. In this, he was only moderately successful. His son, Landulf II, allied against the Lombard principality of Salerno, but failed to oust Gisulf I. Like his father, he attacked Byzantine possessions, but was defeated and forced to submit to nominal Byzantine suzerainty.
Under Landulf's sons, the union of Capua and Benevento broke down and they remained legally bound, but with Pandulf ruling separately in Capua and Landulf III in Benevento. However, all Langobardia minor was unified one last time by when Pandulf, called Ironhead, usurped his brother's share from his nephew on Landulf's death in 969 and then became Prince of Salerno in 978. Before his death (March 981), he had gained from Emperor Otto I the title of Duke of Spoleto also. He split his great dominion between his sons: Landulf IV received Benevento-Capua and Pandulf II, Salerno.
11th century
Soon, Benevento and Capua split legally, with Landulf IV keeping a Capua much reduced in power. In the 990s, Capua experienced debilitating turmoil as one prince was assassinated, another deposed by the Emperor Otto III, and a third deposed by the citizens. The old dynasty was reinstalled in 1000 under Landulf VII, who made his brother, Pandulf II of Benevento, regent for his heir, Pandulf II of Capua. Thus, Capua and Benevento were briefly united for the last time.
The chief interest of Lombard Capua in this, its declining period, was the control of a seaport, especially a large and important one, such as Gaeta or Naples. Capua experienced a new zenith under Pandulf IV, who was deposed twice between his succession in 1016 and his death in 1050. He was originally an ally of the Byzantines and remained allied with them against all his neighbours until the end. His reign was occupied by constant disputes with the church, whose bishops and abbots he treated with disdain, and with the coastal duchies of Naples, Gaeta, and Amalfi. He desired to give Capua a seaport and deposed both Sergius IV of Naples and John V of Gaeta. His personal character, however, soon involved him in a war with Guaimar IV of Salerno, who had him deposed by the Holy Roman Emperor, and took his principalities. Despite the importance of Capua in the region, the city declined under Pandulf's successors until it was eventually taken by the Norman allies of Guaimar.
Norman rule
In 1058, a year after the death of Pandulf's weak successor, the Norman count Richard of Aversa conquered Capua, but left the city itself in the control of Landulf VIII for another four years. Richard immediately increased his prestige with the princely title and his power by the territory which came under his authority. He became a neighbour of the popes and was both their protector and supporter and also an enemy who spent his last years in excommunication, as did his son and successor, Jordan I, who carved out a chunk of papal territory for the principality. At Richard's death, his family, the Drengot, had a prestige and power to match that of the Hauteville family, but they acted in a different sphere of influence: the Papal States and central Italy primarily.
With the death of Jordan I, the principality declined fast. From 1090 to 1098, the city of Capua itself was in the hands of Lando, a Lombard count who was raised by the citizens in opposition to the young Richard II. The latter was only reinstalled with the aid of his fellow Normans and thus Capua became dependent on the Hautevilles and their duchy, though the princes continued to try and influence papal elections and act as papal protectors. With the death of the religious Jordan II in 1127, the principality became the object of desire of Roger II, who had united the Sicilian and peninsular domains of his family. For twenty years from 1135 to 1155, the Hautevilles warred with Robert II of Capua until his clan was finally removed permanently from power.
See also
Sources
- Chalandon, Ferdinand. Histoire de la domination normande en Italie et en Sicile. Paris, 1907.
- Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani. Rome, 1960–Present.
- Oman, Charles. The Dark Ages 476-918. Rivingtons: London, 1914.
- Gwatkin, H.M., Whitney, J.P. (ed) et al. The Cambridge Medieval History: Volume III. Cambridge University Press, 1926.
- Norwich, John Julius. The Normans in the South 1016-1130. Longmans: London, 1967.
Former monarchies of the Italian Peninsula, Sardinia and Sicily Amalfi • Apulia • Arborea • Benevento • Byzantine Empire • Cagliari • Capua • Carrara • Castro • Ceva • Etruria • Ferrara • Finale • Florence • Gaeta • Gallura • County of Guastalla • Duchy of Guastalla • Italy (Lombard) • Italy (modern) • Italy (Napoleonic) • Lombardy-Venetia • Principality of Lucca and Piombino • Duchy of Lucca • Mantua • Massa • Medieval Italy • Milan • Mirandola • Modena • Montferrat • Duchy of Naples • Kingdom of Naples • Ogliastra • Ostrogothic Kingdom • Papal States • Parma • Piombino • Presidi • Reggio • Roman Kingdom • Roman Empire • Salerno • Saluzzo • Sardinia • Savoy • Emirate of Sicily • County of Sicily • Kingdom of Sicily • Sora • Tavolara • Torres • Trent • Tuscany • Two Sicilies • Urbino • Western Roman Empire
Categories:- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- Former countries on the Italian Peninsula
- Former principalities
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.