- Aesculin
-
Aesculin 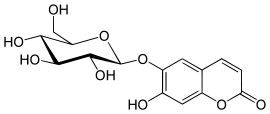 7-hydroxy-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy- 6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-tetrahydropyranyl]oxy}-2-chromenoneOther namesEsculetin 6-β-D-glucoside
7-hydroxy-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy- 6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-tetrahydropyranyl]oxy}-2-chromenoneOther namesEsculetin 6-β-D-glucosideIdentifiers CAS number 531-75-9 
PubChem 5281417 ChemSpider 4444765 
UNII 1Y1L18LQAF 
ChEMBL CHEMBL482581 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C/3Oc2c(cc(O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)CO)c(O)c2)\C=C\3
- InChI=1S/C15H16O9/c16-5-10-12(19)13(20)14(21)15(24-10)23-9-3-6-1-2-11(18)22-8(6)4-7(9)17/h1-4,10,12-17,19-21H,5H2/t10-,12-,13+,14-,15-/m1/s1

Key: XHCADAYNFIFUHF-TVKJYDDYSA-N
InChI=1/C15H16O9/c16-5-10-12(19)13(20)14(21)15(24-10)23-9-3-6-1-2-11(18)22-8(6)4-7(9)17/h1-4,10,12-17,19-21H,5H2/t10-,12-,13+,14-,15-/m1/s1
Key: XHCADAYNFIFUHF-TVKJYDDYBL
Properties Molecular formula C15H16O9 Molar mass 340.282 g/mol Exact mass 340.079432  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Aesculin, also rendered Æsculin or Esculin, is a glucoside that naturally occurs in the horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum),[1] California Buckeye (Aesculus californica)[2] and in daphnin (the dark green resin of Daphne mezereum).
Contents
Medical uses
Aesculin is used in a microbiology laboratory to aid in the identification of bacterial species (especially Enterococci and Listeria). In fact, all strains of Group D Streptococci hydrolyze æsculin in 40% bile.
Aesculin hydrolysis test
Aesculin is incorporated into agar with ferric citrate and bile salts (bile aesculin agar).[3] Hydrolysis of the aesculin forms aesculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) and glucose. The aesculetin forms dark brown or black complexes with ferric citrate, allowing the test to be read.
The bile aesculin agar is streaked and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. The presence of a dark brown or black halo indicates that the test is positive. A positive test can occur with Enterococcus, Aerococcus and Leuconostoc. Aesculin will fluoresce under long wave ultraviolet light (360 nm): hydrolysis of aesculin results in loss of this fluorescence.
Enterococcus will often flag positive within four hours of the agar being inoculated.
Line notes
References
- Plant poisons: Aesculin
- National Standard Methods MSOP 48 (Bile aesculin agar) and BSOPTP 2 (Aesculin hydrolysis test (UK)).
- C. Michael Hogan (2008) California Buckeye: Aesculus californica, GlobalTwitcher.com, N. Stromberg ed.
Bond Geometry Glycone Aglycone biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iAglycones glycosides Aesculin | Skimmin (7-O-β-D-glucopyranosylumbelliferone) | ScopolinFuran derivatives Furanocoumarins (Angelicin | Apterin | Bergamottin | Bergapten | Imperatorin | Marmesin | Methoxsalen | Psoralen | Trioxsalen) | FuranochromonesMonoterpene coumarin ether Synthetic or drugs Categories:- Coumarin glycosides
- Microbiological media ingredients
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
