- Antimony pentachloride
-
Antimony pentachloride 
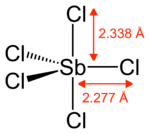 Antimony pentachloride
Antimony pentachloride
Antimony(V) chlorideOther namesAntimonic chloride
Antimony quintachloride
Antimony perchlorideIdentifiers CAS number 7647-18-9 
ChemSpider 10613049 
EC number 231-601-8 RTECS number CC5075000 Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- [Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[SbH3+3]
[SbH3+3].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-]
Properties Molecular formula SbCl5 Molar mass 299.02 g/mol Appearance Colourless or yellow (fuming) liquid Density 2.336 g/cm3 Melting point 2.8 °C, 276 K, 37 °F
Boiling point 140 °C, 413 K, 284 °F
Solubility in water decomposes Solubility soluble in HCl, chloroform and CCl4 Refractive index (nD) 1.59255 Viscosity 0.00191 Pa s Structure Molecular shape Trigonal bipyramidal Dipole moment 0 D Hazards EU Index 051-002-00-3 EU classification Corrosive (C)
Dangerous for the environment (N)R-phrases R34, R51/53 S-phrases (S1/2), S26, S45, S61 NFPA 704 Flash point 77 °C LD50 1115 mg/kg, oral (rat) Related compounds Other anions Antimony pentafluoride Other cations Phosphorus pentachloride Related compounds Antimony trichloride  pentachloride (verify) (what is:
pentachloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Antimony pentachloride is a the chemical compound with the formula SbCl5. It is a colourless oil, but typical samples are yellowish due to impurities. Owing to its tendency to hydrolyse to hydrochloric acid, SbCl5 is highly corrosive substance.
Contents
Preparation and structure
Antimony pentachloride is prepared by passing chlorine gas into molten antimony trichloride:
- SbCl3 + Cl2 → SbCl5
Gaseous SbCl5 has a trigonal prismatic structure.[1]
Reactions
Antimony pentachloride hydrolyses readily to give hydrochloric acid:
- 2 SbCl5 + 5 H2O → Sb2O5 + 10 HCl
This reaction is suppressed in the presence of large excess of chloride owing to formation of the hexachloroantimonate complex ion:
- SbCl5 + Cl− → [SbCl6]−
The mono- and tetrahydrates are known, SbCl5.H2O SbCl5.4H2O.
This compound forms adducts with many Lewis bases. It is used as the standard Lewis acid in the Gutmann scale of Lewis basicity.[2]
It is also a strong oxidizing agent.[3]
Applications
Antimony pentachloride is used as a polymerization catalyst and for the chlorination of organic compounds.
References
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.
- ^ V. Gutmann (1976). "Solvent effects on the reactivities of organometallic compounds". Coord. Chem. Rev. 18 (2): 225. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(00)82045-7.
- ^ Connelly, N. G. and Geiger, W. E. (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry". Chem. Rev. 96: 877–922. doi:10.1021/cr940053x. PMID 11848774.
Antimony compounds Categories:- Antimony compounds
- Chlorides
- Inorganic compounds
- Oxidizing agents
- Inorganic compound stubs
- [Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[SbH3+3]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

