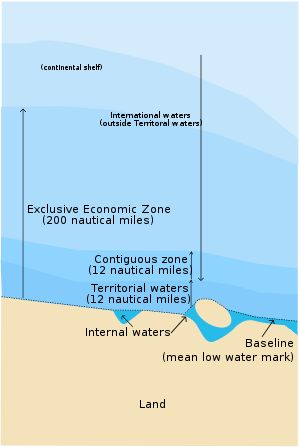
- International waters
-
International Ownership Treaties Antarctic Treaty System Law of the Sea Outer Space Treaty Moon Treaty International waters Extraterrestrial real estate The terms international waters or trans-boundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.[1]
Oceans, seas, and waters outside of national jurisdiction are also referred to as the high seas or, in Latin, mare liberum (meaning free seas).
Ships sailing the high seas are generally under the jurisdiction of the flag state;[2] (if there is one) however, when a ship is involved in certain criminal acts, such as piracy,[3] any nation can exercise jurisdiction under the doctrine of universal jurisdiction.
Contents
International waterways
Several international treaties have established freedom of navigation on semi-enclosed seas.
- The Copenhagen Convention of 1857 opened access to the Baltic by abolishing the Sound Dues and making the Danish Straits an international waterway free to all military and commercial shipping.
- Several conventions have opened the Bosporus and Dardanelles to shipping. The latest, the Montreux Convention Regarding the Regime of the Turkish Straits, maintains the straits' status as an international waterway.
Other international treaties have opened up rivers, which are not traditionally international waterways.
- The Danube River is an international waterway so that landlocked Austria, Hungary, Serbia and Slovakia (and the southern parts of Germany, itself not landlocked) can have secure access to the Black Sea.
Disputes over International waters
See also: Australian Antarctic territorial watersCurrent unresolved disputes over whether particular waters are "International waters" include:
- The Arctic Ocean: While Canada, Denmark, Russia and Norway all regard parts of the Arctic seas as national waters or internal waters, most European Union countries and the United States officially regard the whole region as international waters.[citation needed]
- The Southern Ocean: Australia claims EEZ around its antarctic territorial claim. Since this claim is only recognised by four other countries, the EEZ claim is also disputed.
In addition to formal disputes, the government of Somalia exercises little control de facto over Somali territorial waters. Consequently, much piracy, illegal dumping of waste and fishing without permit has occurred.
International waters agreements
Global agreements
- International Freshwater Treaties Database (freshwater only).[4]
- The Yearbook of International Cooperation on Environment and Development profiles agreements regarding the Marine Environment, Marine Living Resources and Freshwater Resources.[5]
- 1972 London Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter (London Convention 1972).[6]
- 1973 London International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973 MARPOL
- 1982 United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea (United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea, United Nations - especially parts XII-XIV).[7]
- 1997 United Nations Convention on the Law of Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses (CIW) - not ratified.[8]
- Transboundary Groundwater Treaty, Bellagio Draft - proposed, but not signed.[9]
- Other global conventions and treaties with implications for International Waters:
- 1971 Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.[10]
- 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity.[11]
Regional agreements
At least ten conventions are included within the Regional Seas Program of UNEP,[12] including:
- the Atlantic Coast of West and Central Africa[13]
- the North-East Pacific (Antigua Convention);
- the Mediterranean (Barcelona Convention);
- the wider Caribbean (Cartagena Convention);
- the South-East Pacific;[14]
- the South Pacific (Nouméa Convention);
- the East African seaboard[15]
- the Kuwait region (Kuwait Convention);
- the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden (Jeddah Convention).
Addressing regional freshwater issues is the 1992 Helsinki Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (UNECE/Helsinki Water Convention)[16]
Water body-specific agreements
- Baltic Sea (Helsinki Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area, 1992)[17]
- Black Sea (Bucharest Convention)[18]
- Caspian Sea (Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea)[19]
- Lake Tanganyika (Convention for the Sustainable Management of Lake Tanganyika)[20]
International waters institutions
Freshwater institutions
- The UNESCO International Hydrological Programme (IHP)
- The International Joint Commission between Canada and USA (IJC-CMI)
- The International Network of Basin Organizations (INBO)
- The International Shared Aquifer Resource Management project
- The International Water Boundary Commission (US Section) between Mexico and USA
- The International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
- The World Conservation Union Water and Nature Initiative (WANI)
Marine institutions
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- The International Seabed Authority
- The International Whaling Commission
- The UNEP Regional Seas Programme
- The UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC)
- The International Ocean Institute
- The World Conservation Union Global Marine Program (GMP)
See also
- Baseline
- Birth aboard aircraft and ships
- Continental shelf
- Exclusive economic zone
- Freedom of the seas
- Hugo Grotius
- Internal waters
- Ocean colonization
- Territorial waters
References
- ^ International Waters, United Nations Development Programme
- ^ UNCLOS article 92(1)
- ^ UNCLOS article 105
- ^ "International Freshwater Treaties Database". Transboundarywaters.orst.edu. http://www.transboundarywaters.orst.edu/database/interfreshtreatdata.html. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Yearbook of International Cooperation on Environment and Development
Marine Environment[dead link]
Marine Living Resources[dead link]
Freshwater Resources[dead link] - ^ London Convention 1972[dead link]
- ^ "United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea". Un.org. http://www.un.org/Depts/los/convention_agreements/texts/unclos/closindx.htm. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "CIW" (PDF). http://untreaty.un.org/ilc/texts/instruments/english/conventions/8_3_1997.pdf. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Bellagio Draft" (PDF). http://www.ana.gov.br/guarani/gestao/tratados/The%20Bellagio%20Draft%20Treaty%20(ingles).pdf. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Text of Ramsar Convention and other key original documents". Ramsar.org. http://www.ramsar.org/cda/en/ramsar-documents-texts/main/ramsar/1-31-38_4000_0__. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Text of the Convention on Biological Diversity especially Articles 12-13, as related to transboundary aquatic ecosystems
- ^ "Regional Seas Program". Unep.org. http://www.unep.org/regionalseas/. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Convention for Co-operation in the Protection and Development of the Marine and Coastal Environment of the West and Central African Region; and Protocol (1981)". Sedac.ciesin.org. http://sedac.ciesin.org/entri/texts/marine.coastal.west.central.africa.1981.html. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Lima Convention, 1986)
- ^ Nairobi Convention, 1985);
- ^ "Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes". Unece.org. http://www.unece.org/env/water. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area". Helcom.fi. http://www.helcom.fi/Convention. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Bucharest Convention, 1992), see also the Black Sea Commission
- ^ Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea, 2003
- ^ Convention for the Sustainable Management of Lake Tanganyika, 2003
External links
- Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law Peace Palace Library
- The GEF International Waters Resource Centre (GEF IWRC)
- The Integrated Management of Transboundary Waters in Europe (TransCat)
- The International Water Law Project
- The International Water Resources Association (IWRA)
- FAO
- Ocean Atlas
- Transboundary Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) article
- OneFish fisheries research portal
- Regional Fisheries Bodies of the World portal
- The UNDP-GEF article describing international waters from which this article has been adapted.
- UNEP freshwater thematic portal on transboundary waters
- UNESCO thematic portals for oceans, water, coasts and small islands
- WaterWiki: A new Wiki-based on-line knowledge map and collaboration tool for Water-practitioners in the Europe & CIS region
Categories:- Law of the sea
- International waters
- International water transport
- Water and politics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.