- Liothyronine sodium
-
Liothyronine sodium 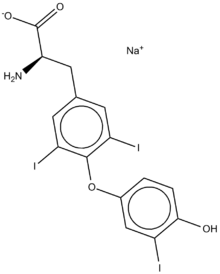
Systematic (IUPAC) name sodium (2S)-2-amino-3- [4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl] propanoate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682462 Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 99.7% Half-life 2.5 days Identifiers CAS number 6893-02-3 
ATC code H03AA02 PubChem CID 16218759 DrugBank APRD01074 ChemSpider 17346129 
UNII 06LU7C9H1V 
ChEBI CHEBI:6484 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201119 
Chemical data Formula C15H11I3NNaO4 Mol. mass 672.96 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) sodium (verify)
(what is this?) sodium (verify)Liothyronine sodium is the L-isomer of triiodothyronine (T3), a form of thyroid hormone used to treat hypothyroidism and myxedema coma. It is marketed under the brand name Cytomel (or Tertroxin in Australia).
Contents
Pharmacology
Liothyronine is the most potent form of thyroid hormone. As such, it acts on the body to increase the basal metabolic rate, affect protein synthesis and increase the body's sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline) by permissiveness. The thyroid hormones are essential to proper development and differentiation of all cells of the human body. These hormones also regulate protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism, affecting how human cells use energetic compounds.
In comparison to levothyroxine (T4), liothyronine has a faster onset of action as well as a shorter biological half-life, which may be due to less plasma protein binding to thyroxine-binding globulin and transthyretin.
Side effects
Liothyronine may cause a number of side effects, mostly similar to symptoms of hyperthyroidism, which include:[1]
- weight loss
- tremor
- headache
- upset stomach
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- stomach cramps
- nervousness
- irritability
- insomnia
- excessive sweating
- increased appetite
- fever
- changes in menstrual cycle
- sensitivity to heat
Black box warning
The package insert for Cytomel contains the following black box warning:[2]
Drugs with thyroid hormone activity, alone or together with other therapeutic agents, have been used for the treatment of obesity. In euthyroid patients, doses within the range of daily hormonal requirements are ineffective for weight reduction. Larger doses may produce serious or even life-threatening manifestations of toxicity, particularly when given in association with sympathomimetic amines such as those used for their anorectic effects.
Uses
Physicians can use this instead of levothyroxine (T4) for patients undergoing thyroid withdrawal. When a patient has thyroid cancer or Grave's, I-131 ablation therapy can be used to remove any trace thyroid tissue. In order for I-131 therapy to be effective, the trace thyroid tissue must be avid to iodine. The best method is to starve the tissue of iodine but this can lead to hypothyroid symptoms for the patient. Withdrawal from levothyroxine can be done but it takes 6 weeks of withdrawal for the remaining thyroid tissue to be completely starved. 6 weeks is needed owing to levothyroxine's long half life. 6 weeks can be inconvenient for the patient and delay treatment. Liothyronine instead can be taken and withdrawn from for 2 weeks to starve the thyroid tissue. This is much safer and more convenient than levothyroxine.
See also
References
- ^ MedlinePlus. "Liothyronine." Last accessed July 14, 2007.
- ^ United States Food & Drug Administration. "Cytomel." Last accessed July 14, 2007.
Thyroid therapy (H03) Thyroid hormones Antithyroid preparations Thiouracils: Propylthiouracil# • Methylthiouracil • Benzylthiouracil
Sulfur-containing imidazole derivatives: Carbimazole • MethimazoleSodium-iodide symporter
inhibitorOtherCategories:- Thyroid hormones
- Iodinated tyrosine derivatives
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
