- First pharyngeal arch
-
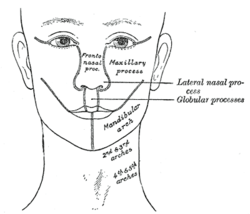
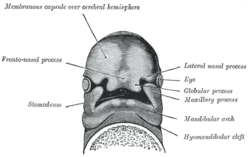
First branchial arch Diagram showing the regions of the adult face and neck related to the fronto-nasal process and the branchial arches. Under surface of the head of a human embryo about twenty-nine days old. Latin arcus pharyngeus primus Gray's subject #13 66 Code TE E5.0.2.1.5.0.1 MeSH Branchial+Region The first branchial arch, also called the first pharyngeal arch and mandibular arch, is the first of six branchial arches that develops in fetal life during the fourth week of development.[1] It is located between the stomodeum and the first pharyngeal groove.
Contents
Processes
This arch divides into a maxillary process and a mandibular process, giving rise to structures including the bones of the lower two-thirds of the face and the jaw. The maxillary process becomes the maxilla (or upper jaw), and palate while the mandibular process becomes the lower jaw. This arch also gives rise to the muscles of mastication.
Meckel's cartilage
Meckel's cartilage forms in the mesoderm of the mandibular process and eventually regresses to form the incus and malleus of the middle ear; the anterior ligament of the malleus and the sphenomandibular ligament. The mandible or lower jaw forms by perichondral ossification using Meckel's cartilage as a 'template', but the mandible does not arise from direct ossification of Meckel's cartilage.
Derivatives
The skeletal elements and muscles are detrived from mesoderm of the pharyngeal arches.
Derivatives of the first arch:
Skeletal elements
- Malleus & Incus of the middle ear
- maxilla & mandible
- spine of sphenoid bone
- Sphenomandibular ligament
- palatine bone
- squamous part of temporal bone
- Anterior ligament of malleus
Muscles
- Muscles of mastication (chewing)
- Masseter
- medial & lateral Pterygoid muscles
- Temporalis muscles
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Digastric muscle, anterior belly
- Tensor palati muscle
- Tensor tympani muscle
Other derivatives
Mucous membrane and glands of the anterior two thirds of the tongue are derived from ectoderm and endoderm of the arch.
Nerve supply
The mandibular and maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) innervate the structures derived from the corresponding processes of the first arch.[2] In some lower animals ,each arch is supplied by two cranial nerves.The nerve of the arch itself runs along the cranial side of the arch and is called post-trematic nerve of the arch.Each arch also receives a branch from the nerve of the succeeding arch called the pre-trematic nerve which runs along the caudal border of the arch.In human embryo,a double innervation is seen only in the first pharyngeal arch.The mandibular nerve is the post-trematic nerve of the first arch and chorda tympani (branch of facial nerve) is the pre-trematic nerve.This double innervation is reflected in the nerve supply of anterior two-thirds of tongue which is derived from the first arch.[3]
Blood supply
The artery of the first arch is the first aortic arch,[4] which partially persists as the maxillary artery.
Additional images
References
- ^ William J. Larsen (2001). Human embryology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06583-7
- ^ Harris, Edward F., 2002.Craniofacial Growth and Development.
- ^ Inderbir Sing,G.P Pal-Human Embryology
- ^ McMinn, R., 1994. Last's anatomy: Regional and applied (9th ed).
External links
- hednk-011 — Embryology at UNC
- Overview at University of Newcastle
- Overview at Howard University
- Mnemonic:First branchial arch
Human development of head and neck (GA 1.65, TE E5.3, 5.4) Face Nasal placode · Nasal pit · nasal prominences (Lateral, Medial) · Intermaxillary segment
Frontonasal prominence · Maxillary prominence · Mandibular prominence (Meckel's cartilage)Oral cavity Primary palate · Secondary palateLateral lingual swelling · Tuberculum impar · Copula linguae · Hypopharyngeal eminence · Gustatory placodeGeneral
branchial apparatusCategories:- Embryology
- Head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.