- Copula linguae
-
Copula linguae 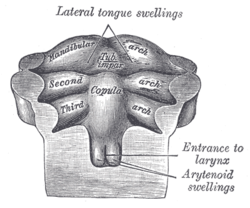
Floor of pharynx of human embryo of about the end of the fourth week. 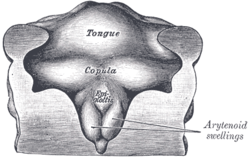
Floor of pharynx of human embryo about thirty days old. Latin copula linguae Gray's subject #241 1103 Also known as the hypobranchial eminence.
The furcula is at first separated from the tuberculum impar by a depression, but later by a ridge, the copula, formed by the forward growth and fusion of the ventral ends of the second, third, and part of the fourth branchial arches.
External links
- copula at eMedicine Dictionary
- hednk-024 — Embryology at UNC
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human development of head and neck (GA 1.65, TE E5.3, 5.4) Face Nasal placode · Nasal pit · nasal prominences (Lateral, Medial) · Intermaxillary segment
Frontonasal prominence · Maxillary prominence · Mandibular prominence (Meckel's cartilage)Oral cavity Lateral lingual swelling · Tuberculum impar · Copula linguae · Hypopharyngeal eminence · Gustatory placodeGeneral
branchial apparatusCategories:- Developmental biology stubs
- Anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
