- Cervical sinus
-
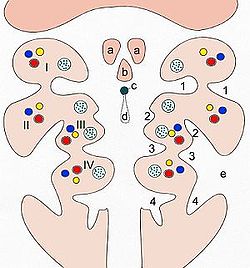
Cervical sinus Pattern of the branchial arches. I-IV branchial arches, 1-4 branchial pouches (inside) and/or pharyngeal grooves (outside)
a Tuberculum laterale
b Tuberculum impar
c Foramen cecum
d Ductus thyreoglossus
e Sinus cervicalisLatin sinus cervicalis Gray's subject #13 67 The mandibular and hyoid arches grow more rapidly than those behind them, with the result that the latter become, to a certain extent, telescoped within the former, and a deep depression, the cervical sinus, is formed on either side of the neck.
This sinus is bounded in front by the hyoid arch, and behind by the thoracic wall; it is ultimately obliterated by the fusion of its walls.
Additional images
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human development of head and neck (GA 1.65, TE E5.3, 5.4) Face Nasal placode · Nasal pit · nasal prominences (Lateral, Medial) · Intermaxillary segment
Frontonasal prominence · Maxillary prominence · Mandibular prominence (Meckel's cartilage)Oral cavity Lateral lingual swelling · Tuberculum impar · Copula linguae · Hypopharyngeal eminence · Gustatory placodeGeneral
branchial apparatusCategories:- Embryology
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.