- Mylohyoid muscle
-
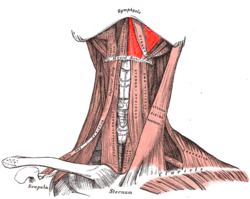
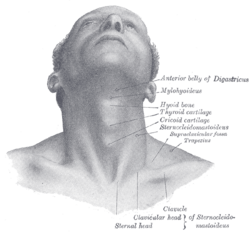
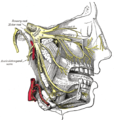
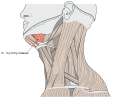
Mylohyoid muscle Muscles of the neck. Anterior view. Mylohyoid muscle colored in bright red. Front view of neck. (Mylohyoideus labeled at right, second from top.) Latin musculus mylohyoideus Gray's subject #112 393 Origin Mylohyoid line (mandible) Insertion body of hyoid bone and median raphe Artery mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery Nerve mylohyoid nerve, from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] Actions Raises oral cavity floor, elevates hyoid, elevates tongue, depresses mandible The mylohyoid muscle is a muscle running from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity. It is named for its two attachments, with the prefix "mylo" coming from the Greek word for "molar".[1] These muscles are mesodermal in origin. The mylohyoid muscle is derived from the first pharyngeal arch.
Contents
Structure
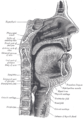
The mylohyoid muscle is flat and triangular, and is situated immediately above the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It forms, with its fellow of the opposite side, a muscular floor for the cavity of the mouth.
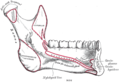
It arises from the whole length of the mylohyoid line of the mandible, extending from the symphysis in front to the last molar tooth behind. The posterior fibers pass inferomedially to insert into the body of the hyoid bone. It thus belongs to the suprahyoid muscles.
The middle and anterior fibers are inserted into a median fibrous raphé extending from the symphysis menti to the hyoid bone, where they joint at an angle with the fibers of the opposite muscle. This median raphé is sometimes absent; the fibers of the two muscles are then continuous.
Innervation
Along with the anterior belly of the digastric muscle, the mylohyoid muscle is innervated by the mylohyoid nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve, which is a branch of the mandibular nerve, a division of the trigeminal nerve.
Actions
The mylohyoid depresses the mandible and elevates the hyoid, the floor of the oral cavity, and the tongue. This is particularly important during swallowing and speaking.
Variations
It may be united to or replaced by the anterior belly of the digastric muscle; accessory slips to other hyoid muscles are frequent.
Additional images
References
External links
- LUC myl
- -1456144304 at GPnotebook
- Mylohyoid+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 25420.000-1
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of head and neck: the neck (TA A04.2, GA 4.387) Cervical Suboccipital Suprahyoid CN V3 (medial): mylohyoid · anterior belly of digastric
CN VII (lateral): stylohyoid · posterior belly of digastric
C1 (deep): geniohyoidInfrahyoid/strap Fasciae Pharynx pharyngeal constrictor (superior, middle, inferior) · longitudinal (stylopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus)Larynx cricothyroid · cricoarytenoid (posterior, lateral) · arytenoid (oblique arytenoid/aryepiglottic, transverse arytenoid) · thyroarytenoid (vocal, thyroepiglottic)Categories:- Muscle stubs
- Muscles of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.