- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
-
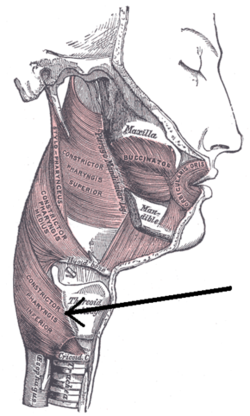
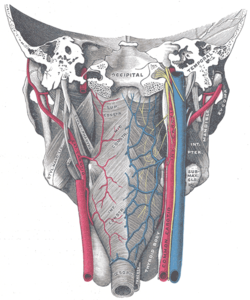
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle Muscles of the pharynx and cheek. (Constrictor pharyngis inferior visible at bottom left.) Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves. (Inf. const. labeled at bottom center.) Latin musculus constrictor pharyngis inferior Gray's subject #244 1142 Origin cricoid and thyroid cartilage Insertion pharyngeal raphe Artery Nerve Pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve Actions Swallowing The Inferior pharyngeal constrictor, the thickest of the three constrictors, arises from the sides of the cricoid and thyroid cartilage. Similarly to the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles, it is innervated by the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X), specifically, by branches from the pharyngeal plexus and by neuronal branches from the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Contents
Origin and insertion
The muscle is composed of two parts. The first (and more superior) arising from the thyroid cartilage (thyropharyngeal part) and the second arising from the cricoid cartilage (cricopharyngeal part). [1]
- On the thyroid cartilage it arises from the oblique line on the side of the lamina, from the surface behind this nearly as far as the posterior border and from the inferior cornu.
- From the cricoid cartilage it arises in the interval between the Cricothyreoideus in front, and the articular facet for the inferior cornu of the thyroid cartilage behind.
From these origins the fibers spread backward and medialward to be inserted with the muscle of the opposite side into the fibrous pharyngeal raphe in the posterior median line of the pharynx.
The inferior fibers are horizontal and continuous with the circular fibers of the esophagus; the rest ascend, increasing in obliquity, and overlap the Constrictor medius.
Action
As soon as the bolus of food is received in the pharynx, the elevator muscles relax, the pharynx descends, and the constrictores contract upon the bolus, and convey it downward into the esophagus.
Role in human disease
Uncoordinated contraction, and/or Cricopharyngeal Spasm and/or impaired relaxation of this muscle are currently considered the main factors in development of a Zenker's diverticulum.
Motor incoordination of the cricopharyngeus can cause difficulty swallowing.
See also
Additional images
References
External links
- -375783347 at GPnotebook
- lesson8 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (latpharyngealitems3)
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of head and neck: the neck (TA A04.2, GA 4.387) Cervical Suboccipital Suprahyoid CN V3 (medial): mylohyoid · anterior belly of digastric
CN VII (lateral): stylohyoid · posterior belly of digastric
C1 (deep): geniohyoidInfrahyoid/strap Fasciae Pharynx pharyngeal constrictor (superior, middle, inferior) · longitudinal (stylopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus)Larynx cricothyroid · cricoarytenoid (posterior, lateral) · arytenoid (oblique arytenoid/aryepiglottic, transverse arytenoid) · thyroarytenoid (vocal, thyroepiglottic)Categories:- Muscle stubs
- Muscles of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.