- Mannitol salt agar
-
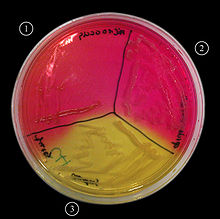
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. This medium is important in medical laboratories by distinguishing pathogenic microbes in a short period of time. [1] It contains a high concentration (~7.5%-10%) of salt (NaCl), making it selective for Staphylococci (and Micrococcaceae) since this level of NaCl is inhibitory to most other bacteria[2]. It is also a differential medium, containing mannitol and the indicator phenol red. Coagulase-positive Staphylococci produce yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas coagulase-negative Staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no color change to the medium.[3] If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that will cause the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow. [4] It is used for the selective isolation of presumptive pathogen (pp) Staphylococci.
Contents
Expected Results
- Gram + staphylococci fermenting mannitol: Media turns yellow
- Gram + staphylococci not fermenting mannitol: Media does not change color
- Gram + streptococci: inhibited growth
- Gram - : inhibited growth [5]
Typical composition
MSA typically contains[6]:
- 5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of casein
- 5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of animal tissue
- 1.0 g/L beef extract
- 10.0 g/L D-mannitol
- 75.0 g/L sodium chloride
- 0.025 g/L phenol red
- 15.0 g/L agar
- pH 7.4 ± 0.2 at 25°C
References
- ^ Bachoon, Dave S., and Wendy A. Dustman. Microbiology Laboratory Manual. Ed. Michael Stranz. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning, 2008. Exercise 8, "Selective and Differential Media for Isolation" Print.
- ^ Becton, Dickinson and Company, Mannitol salt agar, 2005, [1].
- ^ Neogen corp., Mannitol salt agar (7143), 2008, [2].
- ^ Bachoon, Dave S., and Wendy A. Dustman. Microbiology Laboratory Manual. Ed. Michael Stranz. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning, 2008. Exercise 8, "Selective and Differential Media for Isolation" Print.
- ^ Bachoon, Dave S., and Wendy A. Dustman. Microbiology Laboratory Manual. Ed. Michael Stranz. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning, 2008. Exercise 8, "Selective and Differential Media for Isolation" Print.
- ^ United States Pharmacopeial Convention. 1995. The United States Pharmacopeia, 23rd ed. The United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Rockville, MD.
Bachoon, Dave S., and Wendy A. Dustman. Microbiology Laboratory Manual. Ed. Michael Stranz. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning, 2008. Exercise 8, "Selective and Differential Media for Isolation" Print.
External links
Growth media / agar plates Selective media Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Hoyle's agar) · Enterococcus (Bile esculin agar) · Lactobacillus (MRS agar) · Staphylococcus (Mannitol salt agar)AlphaproteobacteriaBrucella abortus (Brucella agar)BetaproteobacteriaDifferential media Fungal media Nonselective media Other/ungrouped media Cysteine lactose electrolyte deficient agar · Cystine tryptic agar · Endo agar · LIA slant · Müller-Hinton agar/PNP agar · R2a agar · Simmons' citrate agar · Trypticase soy agar · TSI agarCategories:- Microbiological media
- Microbiology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.