- Greater Lebanon
-
State of Greater Lebanon
État du Grand LibanMandate of French Third Republic ← 
1920–1946  →
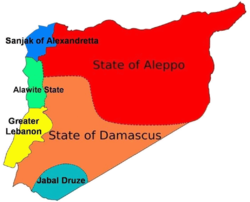
→Greater Lebanon (yellow) in the Mandate of Syria. Capital Beirut Language(s) French Religion Christianity, Islam Political structure League of Nations Mandate Historical era Interwar Period - Mandate issued 1920 - French left the country 1946 The state of Greater Lebanon, the predecessor of modern Lebanon, was created in 1920 as part of the French scheme of dividing the French Mandate of Syria into six states.
The French Mandate for Syria was a League of Nations Mandate created at the end of World War I. When the Ottoman Empire was formally split up by the Treaty of Sèvres in 1920, it was decided that four of its territories in the Middle East should be League of Nations mandates temporarily governed by the United Kingdom and France on behalf of the League. The British were given Palestine and Iraq, while the French were given a mandate over Syria, of which Lebanon was a part.
On September 1, 1920, General Gouraud proclaimed the establishment of State of Greater Lebanon (French: État du Grand Liban) with its present boundaries and with Beirut as its capital.[1] The new territory was granted a flag, merging the French flag with the Lebanese cedar.
The name Greater Lebanon refers to the incorporation of the former Ottoman districts of Tripoli and Sidon as well as the Bekaa Valley to the existing former autonomous region of Mount Lebanon, which had been established in 1861 to protect the local Christian population.
The first Lebanese constitution was promulgated on May 23, 1926, and subsequently amended several times. Modeled after that of the French Third Republic, it provided for a bicameral parliament with Chamber of Deputies and a Senate (although the latter was eventually dropped), a President, and a Council of Ministers, or cabinet. The president was to be elected by the Chamber of Deputies for one six-year term and could not be reelected until a six-year period had elapsed; deputies were to be popularly elected along confessional lines.
History of Lebanon 
This article is part of a seriesAncient History Phoenicia Arab rule Ottoman rule French Rule Modern Lebanon 1958 Lebanon crisis Lebanese Civil War Cedar Revolution 2006 Lebanon War
Lebanon Portal
A custom of selecting major political officers, as well as top ranks within the public administration, according to the proportion of the principal sects in the population was strengthened during this period. Thus, for example, the president ought to be to be a Maronite Christian, the prime minister a Sunni Muslim, and the speaker of the Chamber of Deputies a Shia Muslim. Theoretically, the Chamber of Deputies performed the legislative function, but in fact bills were prepared by the executive and submitted to the Chamber of Deputies, which passed them virtually without exception. Under the Constitution, the French high commissioner still exercised supreme power, an arrangement that initially brought objections from the Lebanese nationalists. Nevertheless, Charles Debbas, a Greek Orthodox, was elected the first president of Lebanon three days after the adoption of the Constitution.
At the end of Debbas's first term in 1932, Bishara al-Khuri and Émile Eddé competed for the office of president, thus dividing the Chamber of Deputies. To break the deadlock, some deputies suggested Shaykh Muhammad al Jisr, who was chairman of the Council of Ministers and the Muslim leader of Tripoli, as a compromise candidate. However, French high commissioner Henri Ponsot suspended the constitution on May 9, 1932, and extended the term of Debbas for one year; in this way he prevented the election of a Muslim as president. Dissatisfied with Ponsot's conduct, the French authorities replaced him with Comte Damien de Martel, who, on January 30, 1934, appointed Habib Pacha Es-Saad as president for a one-year term (later extended for an additional year).
Émile Eddé was elected president on January 30, 1936. A year later, he partially reestablished the Constitution of 1926 and proceeded to hold elections for the Chamber of Deputies. However, the Constitution was again suspended by the French high commissioner in September 1939, at the outbreak of World War II.
Lebanon gained its independence in 1943 and the French left the country in 1946.
See also
- Emir Majid Arslan II
- Sykes-Picot Agreement
- Patriarch Elias Hoayek
- San Remo conference
- Mount Lebanon
- French Mandate of Syria
- Battle of Maysalun - 1920
- Syria-Lebanon Campaign - 1941
- List of French possessions and colonies
- French colonial empire
References
External links
- A concise history of Lebanon
- Glossary -- Lebanon
- Milestone Dates in Lebanon's Modern History
- Library of Congress - Research - Country Studies - Lebanon- The French Mandate
Categories:- Former countries in the Middle East
- League of Nations mandates
- States and territories established in 1920
- States and territories disestablished in 1946
- 1943 disestablishments
- History of Lebanon
- 20th century in Lebanon
- Fertile Crescent
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.