- Zvezda (ISS module)
-
For other uses, see Zvezda (disambiguation).
ISS Zvezda 
The Zvezda service module of the ISS with Zarya to the right and a docked Soyuz spacecraft to the left 
Station statistics Call sign International Space Station Launch July 12, 2000
Docked with ISS on July 26.Launch pad LC-81/23, Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan Mass 19,051 kilograms (42,000 lb) Length 13.1 metres (43 ft) Width 29.7 metres (97 ft) Diameter 4.15 m Atmospheric pressure 101.3 kPa (29.91 inHg) Perigee 319.6 kilometres (172.6 nmi) Apogee 346.9 kilometres (187.3 nmi) Orbital inclination 51.63 degrees Typical orbit altitude 333.3 kilometres (180.0 nmi) Average speed 27,743.8 kilometres per hour (17,239.2 mph) Orbital period 91.20 minutes Orbits per day 15.79 Days in orbit 2534 days Days occupied 2316 days Number of orbits 40,010 Statistics as of June 20, 2007 References: [1][2][3] Configuration 
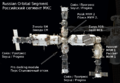
On-orbit configuration of the Zvezda service module Zvezda (Russian: Звезда, meaning "star"), DOS-8, also known as the Zvezda Service Module, is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provides all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the USOS, as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian portion of the station - the Russian Orbital Segment.
The module was manufactured by S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia. Zvezda was launched on a Proton rocket on July 12, 2000 and docked with the Zarya module on July 26. The rocket used for the launch was one of the first to carry advertising; it was emblazoned with the logo of the fast food chain Pizza Hut,[4] for which the company is reported to have paid more than US$1 million.[5]
Contents
Origins
Main article: Mir-2The basic structural frame of Zvezda, known as "DOS-8", was initially built in the mid-1980s to be the core of the Mir-2 space station. This means that Zvezda is similar in layout to the core module (DOS-7) of the Mir space station. It was in fact labeled as "Mir-2" for quite some time in the factory. Its design lineage thus extends back to the original Salyut stations. The space frame was completed in February 1985 and major internal equipment was installed by October 1986.
The MIR-2 space station was redesigned after the failure of the Polyus core module to reach orbit. Zvezda is around 1/4 the size of polyus, and has no armaments.
Design
Zvezda consists of a cylindrical "Work Compartment" where the crews work and live, a cylindrical "Transfer Chamber" which has one docking port, an unpressurized "Assembly Compartment" surrounding the Transfer Chamber, and a spherical "Transfer Compartment" with three docking ports. The component weights 18,051 kg (39,800 lb)) and had a length of 13.1 metres (43 ft). The solar panels extend 29.7 metres (97 ft).
The "Transfer Compartment" attaches to the Zarya module, and has docking ports intended for the Science Power Platform and the Universal Docking Module. As in the early days of Mir, the transfer compartment provides a suitable EVA airlock where spacewalkers in Orlan suits removed a hatch after closing a few that connected the compartment to the rest of the station. It was used only during Expedition 2, where two men put a docking cone on the nadir port. Currently the lower port contains the Pirs Docking Compartment and the other contains Mini-Research Module 2. In December 2011, Pirs will be deorbited and replaced by the Multipurpose Laboratory Module.
The "Assembly Compartment" holds external equipment such as thrusters, thermometers, antennas, and propellant tanks.
The "Transfer Chamber" is equipped with automatic docking equipment and is used to service Soyuz and Progress spacecraft.
Zvezda contains sleeping quarters for two cosmonauts, a NASA-provided Treadmill with Vibration Isolation System and a bicycle for exercise, toilet and other hygiene facilities and a galley with a refrigerator and freezer. It contains the primary Russian computers for guidance and navigation. It has a total of 14 windows—three 9-inch-diameter (230 mm) windows in the forward Transfer Compartment, a 16-inch window in the Working Compartment, one in each crew compartment, and several more. It also contains the Elektron system that electrolyzes condensed humidity and waste water to provide hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is expelled into space and the oxygen is used for breathing air. The condensed water and the waste water can be used for drinking in an emergency, but ordinarily fresh water from Earth is used. There are 16 small thrusters and two large thrusters for propulsion, and eight batteries for storing power.
The Elektron system has required significant maintenance work, having failed several times and requiring the crew to use Solid Fuel Oxygen Generator canisters (commonly called "Oxygen Candles", which were the cause of a fire on Mir) when it has been broken for extended amounts of time. It also contains the Vozdukh, a system which removes carbon dioxide from the air based on the use of regenerable absorbers of carbon dioxide gas. Zvezda has been criticized for being excessively noisy and the crew has been observed wearing earplugs inside it.
Connection to the ISS
On July 26, 2000, Zvezda became the third component of the ISS when it docked at the aft port of Zarya. (Zarya had already been attached to the U.S. Unity module.) Later in July, the computers aboard Zarya handed over ISS commanding functions to computers on Zvezda.[6]
On September 11, 2000, two members of the STS-106 Space Shuttle crew completed final connections between Zvezda and Zarya; during a 6 hour, 14 minute EVA, astronaut Ed Lu and cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko connected nine cables between Zvezda and Zarya, including four power cables, four video and data cables and a fiber-optic telemetry cable.[7] The next day, STS-106 crew members floated into Zvezda for the first time, at 05:20 UTC on September 12, 2000.[8]
Zvezda provided early living quarters, a life support system, a communication system (Zvezda introduced a 10 Mbit/s Ethernet network to the ISS[9]), electrical power distribution, a data processing system, a flight control system, and a propulsion system. These quarters and some, but not all, systems have since been supplemented by additional ISS components.
The two main engines on Zvezda can be used to raise the station's altitude. This was done on April 25, 2007. This was the first time the engines had been fired since Zvezda arrived in 2000.[10]
Launch risks
Due to Russian financial problems, Zvezda was launched with no backup and no insurance. Due to this risk, NASA had constructed an Interim Control Module in case it was delayed significantly or destroyed on launch.
Gallery
References
- ^ "The ISS to Date". NASA.gov. 2007-02-22. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/station/isstodate.html. Retrieved 2007-06-24.
- ^ "International Space Station Status Report #06-7". NASA.gov. 2006-02-17. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/spacenews/reports/issreports/2006/iss06-7.html. Retrieved 2007-06-24.
- ^ "NASA - Zvezda Service Module". NASA.gov. 2006-10-14. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/sm.html. Retrieved 2007-07-10.
- ^ Space.com, September 30, 1999. Pizza Hut Puts Pie in the Sky with Rocket Logo. Accessed June 27, 2006.
- ^ "THE MEDIA BUSINESS; Rocket to Carry Pizza Hut Logo". New York Times. October 1, 1999. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9B0CE1DB123EF932A35753C1A96F958260. Retrieved January 21, 2009.
- ^ "STS-106". NASA. http://science.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-106/mission-sts-106.html.
- ^ "STS-106 Report # 07". NASA. http://science.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-106/news/sts-106-mcc-07.txt.
- ^ "STS-106 Report # 10". NASA. http://science.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/missions/sts-106/news/sts-106-mcc-09.txt.
- ^ ISS and STS Commercial Off-The-Shelf Router Testing, Ivancic, Bell and Shell, NASA Technical Memo TM-2002-211310
- ^ "International Space Station Status Report: SS07-23". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2007/apr/HQ_SS0723_station_status.html.
Components of the International Space Station Overview Assembly · US Orbital Segment · Russian Orbital Segment · Expeditions · Spacewalks · ISS Program · Scientific Research · Major Incidents
Major components
in orbitZarya (Functional Cargo Block) · Zvezda (Service Module) · Unity (Node 1) · Harmony (Node 2) · Tranquility (Node 3) · Destiny (Laboratory) · Columbus (Laboratory) · Kibō (PM, ELM-PS, EF) · Quest (Airlock) · Pirs (Airlock / Docking Module) · Rassvet (MRM 1) · Poisk (MRM 2) · Leonardo (PMM) · Cupola · Integrated Truss Structure (ITS)Subsystems
in orbitFlight-ready hardware
with no launch planScheduled for launch
by ProtonProposed module Cancelled Support vehicles Current: Soyuz · Progress · Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) · H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV)
Future: Dragon · Cygnus · Orion · Rus · CST-100
Former: Space ShuttleMission control centers Salyut program Salyut stations (DOS) 
Almaz stations (OPS) Successors Mir (DOS-7) · Zvezda (DOS-8)TKS spacecraft Support craft Soyuz · ProgressLists Expeditions · Spaceflights (manned · unmanned) · Visitors · Spacewalks← 1999 · Orbital launches in 2000 · 2001 → USA-148 | Galaxy 10R | Feng Huo 1 | JAWSAT · FalconSAT-1 · ASUSat-1 · OCSE · OPAL (STENSAT · MEMS 1A · MEMS 1B · MASAT · Thelma · Louise) | Progress M1-1 | Kosmos 2369 | Hispasat 1C | Globalstar 60 · Globalstar 62 · Globlastar 63 · Globalstar 64 | Gruzovoy Maket · IRDT-1 | ASTRO-E | STS-99 | Garuda 1 | Superbird-B2 | Ekspress A2 | MTI | ICO F1 | Dumsat | INSAT-3B · AsiaStar | IMAGE | Soyuz TM-30 | SESAT 1 | Galaxy 4R | Progress M1-2 | GOES 11 | Kosmos 2370 | USA-149 | USA-150 | SimSat 1 · SimSat 2 | STS-101 | Eutelsat W4 | Gorizont #45L | TSX-5 | Ekspress A3 | Feng Yun 2B · Nadezhda 6 · Tsinghua 1 · SNAP-1 | TDRS-8 | Sirius FM-1 | Kosmos 2371 | Zvezda | EchoStar VI | CHAMP · MITA · Rubin-1 | USA-151 | Samba · Salsa | Sindri (MEMS 2A · MEMS 2B) | PAS-9 | Progress M1-3 | Rumba · Tango | Brazilsat B4 · Nilesat 102 | USA-152 | DM-F3 | Globus #16L | Zi Yuan 2 | Sirius FM-2 | Eutelsat W1 | STS-106 | Astra 2B | GE-7 | NOAA-16 | Kosmos 2372 | Megsat 1 · Unisat 1 · Saudisat 1A · Saudisat 1B · Tiungsat 1 | Kosmos 2373 | GE-1A | N-Sat 110 | HETE-2 | STS-92 (ITS Z1 · PMA-3) | Kosmos 2374 · Kosmos 2375 · Kosmos 2376 | Progress M-43 | USA-153 | Thuraya 1 | GE-6 | Europe*Star 1 | Beidou 1A | Soyuz TM-31 | USA-154 | PAS-1R · AMSAT-P3D · STRV 1C · STRV 1D | Progress M1-4 | QuickBird-1 | EO-1 · SAC-C · Munin | Anik F1 | Sirius FM-3 | STS-97 (ITS P6) | Eros 1A | USA-155 | Astra 2D · GE-8 · LDREX | Beidou 1B | Gonets-D1 #7 · Gonets-D1 #8 · Gonets-D1 #9 · Strela-3 #125 · Strela-3 #126 · Strela-3 #127Payloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Manned flights are indicated in bold text. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in brackets.Categories:- Components of the International Space Station
- Russian components of the International Space Station
- 2000 in spaceflight
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.