- Cracked tooth syndrome
-
Cracked tooth syndrome Classification and external resources 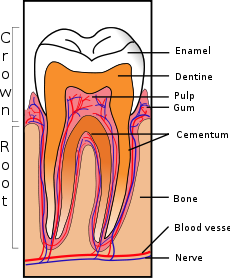
Cross-section of a posterior tooth.ICD-9 521.81 Cracked tooth syndrome (abbreviated CTS) is a medical condition in which a partial crack extends through the dentin, and occasionally through the pulp of a tooth.[1]
Contents
Classification
Since there is a fairly extensive list of classifications for cracked teeth, it is often difficult for doctors to find a correct diagnosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary, however CTS is characterized by sharp fleeting pain intitiated only when biting on an object, not just when the tooth contacts another tooth. The pain is inconsistent, and frequently hard to reproduce.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing cracked tooth syndrome, a doctor takes many factors into consideration. A bite-test is commonly performed to confirm the diagnosis, in which the patient bites down on either a Q-tip, cotton roll, or a medical instrument called the Tooth Slooth.[1][2]
Treatments
- Root Canal
- Stabilization (a band is placed around the tooth to minimize flexing)
- Crown tooth
References
- ^ a b The Cracked Tooth Syndrome, 68, Canadian Dental Association, September 2002, http://www.cda-adc.ca/jcda/vol-68/issue-8/470.pdf
- ^ Patient Education about Cracked Teeth, Tooth Slooth, 12 December 2005, http://www.toothslooth.com/Education.html
Acquired tooth disease (K02–K05, 521–525) Hard tissues Caries (tooth decay) · Attrition · Abrasion · Erosion · Hypercementosis · tooth resorption (External resorption, Internal resorption, Root resorption)Pulp/periapical (Endodontal) PulpalPeriapicalAcute apical periodontitis · Chronic apical periodontitis · Combined periodontic-endodontic lesions · Fistula · Periapical abscess · Phoenix abscess · Vertical root fractureUngroupedGingiva/periodontal
(Periodontal)Bone cyst Other Toothache · Cracked tooth syndromeTo be grouped
from periodontologyDiagnosesChronic periodontitis · Localized aggressive periodontitis · Generalized aggressive periodontitis · Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease · Necrotizing periodontal diseases · Abscesses of the periodontium · Combined periodontic-endodontic lesionsPathogenesisA. actinomycetemcomitans · Capnocytophaga sp. · F. nucleatum · P. gingivalis · P. intermedia · T. forsythia · T. denticolaPathologic entitiesCalculus · Edentulism · Fremitus · Furcation defect · Gingival enlargement · Gingival pocket · Gingivitis · Horizontal bony defect · Linear gingival erythema · Occlusal trauma · Periodontal pocket · Periodontal disease · Periodontitis · Plaque · Recession · Vertical bony defectCategories:- Dental disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
