- Chilean Antarctic Territory
-
Not to be confused with Antarctica.
The Chilean Antarctic Territory (Spanish: Territorio Antártico Chileno) is the territory in Antarctica claimed by Chile. The Chilean Antarctic Territory ranges from 53°W to 90°W and from the South Pole to 60°S, partially overlapping Argentine and British Antarctic claims. It is administered by the Cabo de Hornos municipality in the South American mainland.
Within Chilean territorial organization Antártica is name of the commune that administers the territory. The comune of Antártica is managed by the minicpality of Cabo de Hornos with seat in Puerto Williams in southernmost Chile and belongs to Antártica Chilena Province, which is part of Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region. The commune of Antártica was created on July 11, 1961, and was dependent on the Magallanes Province until 1975, when the Antártica Chilena Province was created, making it dependent administratively on Puerto Williams, the province capital.
Contents
Antártica commune
Antártica — Commune — Night view of Villa Las Estrellas, the only civil settlement Foundation July 11, 1961 Government[1][2] - Type Municipality - Alcalde Hugo Henriquez Matus (PRSD) Area[3] - Total 1,250,000 km2 (482,627.7 sq mi) Population (2002 Census)[3] - Total 130 - Density 0/km2 (0/sq mi) - Urban 0 - Rural 130 Sex[3] - Men 115 - Women 15 Time zone CLT [4] (UTC-4) - Summer (DST) CLST [5] (UTC-3) Website Municipality of Cape Horn 1 As mayor of the commune of Cabo de Hornos Antártica is a Chilean commune in Antártica Chilena Province, Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region, which covers all of the Territorio Chileno Antártico—the territory in Antarctica claimed by Chile. It ranges from 53°W to 90°W and from the South Pole to 60°S, overlapping the Argentine and British Antarctic claims. It is administered by the Cabo de Hornos municipality in the South American mainland.
Antártica was created on July 11, 1961, and was dependent on the Magallanes Province until 1975, when the Antártica Chilena Province was created, making it dependent administratively on Puerto Williams, the province capital.
Demographics
According to the 2002 census of the National Statistics Institute, Antártica spans an area of 1,250,000 km2 (482,628 sq mi) and has 130 inhabitants (115 men and 15 women), making the commune an entirely rural area. The population fell by 0.8% (1 person) between the 1992 and 2002 censuses.[3] Its population has increased since then to about 1,000. This does not include the staff of non-Chilean bases in the area.[citation needed]
Census districts
The commune consists of two census districts:[6]
- Piloto Pardo (pop. 114), consisting of the South Shetland Islands and named after Luis Pardo, with the only civil settlement, Villa Las Estrellas.
- Tierra O´Higgins (the Antarctic mainland) (pop. 16), with communal capital Puerto Covadonga (O'Higgins Station).
Permanent Chilean stations and settlements
The largest population center is located on King George Island and consists of Frei Montalva Station, which has an airport (Teniente Rodolfo Marsh Martin Aerodrome, ICAO Code SCRM [1]), and which is connected to the communal capital, the village of Villa Las Estrellas, which has a town hall, hotel, day-care center, school, scientific equipment, hospital, post office and bank. This enclave is a center of logistical support for the other eight countries with scientific bases on King George Island.
Nearby Professor Julio Escudero Base, controlled by the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH), under the Ministry of Foreign Relations, is the main Chilean scientific facility in Antarctica.
Captain Arturo Prat Base is a Chilean Antarctic research base located on Greenwich Island. Opened February 6, 1947, it is the oldest Chilean Antarctic station. Until March 1, 2006, it was a base of the Chilean Navy, on which date it was handed over to the regional government of Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region. Until February, 2004, it had been a permanent base. Afterwards, it had served as a summer base of ionospheric and meteorologic research. There have been plans to reopen the station for permanent occupation starting March, 2008.
The only permanent Chilean station on the Antarctic mainland (Antarctic Peninsula), O'Higgins Station has been in operation since February 18, 1948. It is located on Puerto Covadonga and it is the official communal capital.[citation needed]
Seasonal Chilean bases
- Dr. Guillermo Mann Base (formely "Shirreff Base") 62°28′2″S 60°46′3″W / 62.46722°S 60.7675°W; summer base of the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH), under the Ministry of Foreign Relations, in Livinsgton Island. Weather and ecological research station. Archaeological research site about former sealers. Another former Chilean refuge also called "Dr. Guillermo Mann" (or Spring-INACH), located in P. Spring (Pen. Palmer), is in ruins.[7]
- Luis Risopatrón Base (formerly "Copper Mine Naval Refuge") 62°22′17″S 59°42′53″W / 62.37139°S 59.71472°W; summer station of the Chilean Navy in Robert Island. Geodetic, geophysical and biological research station.
- Teniente (lieutenant) Parodi Base 80°18′20″S 81°20′39″W / 80.30556°S 81.34417°W; known as Patriot Hills Base, is a semi-permanent station. The base is located in Mts. Patriot, in Ellsworth Land. It's being next to Antonio Huneeus Refuge (INACH). This base is provided by the Chilean Antarctic Institute and the Air Force of Chile to study glaciology, meteorology, geology and mapping since 1996.
- Julio Ripamondi Base 62°12′37″S 58°56′7″W / 62.21028°S 58.93528°W; little summer station of the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH), located in Ardley Island, next to Frei Montalva Station and Professor Julio Escudero Base (nearby located in the King George Island). The Ripamondi Base conducts research on geodesy and cartography (since 1997), terrestrial biology (since 1988) and studies of penguins (since 1988). The base is located near a large colony of gentoo penguins.
- González Videla Base 64°49′26″S 62°51′27″W / 64.82389°S 62.8575°W; station of the Chilean Air Force on the Antarctic mainland's Waterboat Point in Paradise Bay. It is now an "inactive" base, with fuel and supplies in storage in the buildings for emergency use, or in case the base were to be reactivated in the future. Occasional summer visits are made by Chilean scientifics and tourists. The base was recently used (2011) in researchs of the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH)
- Teniente (lieutenant) Carvajal Base (formely "Station T") 67°46′25″S 68°53′36″W / 67.77361°S 68.89333°W; station of the Chilean Air Force. Previously the British Antarctic Survey Station T - Adelaide Base, between 1961 and 1977. The base was transferred to Chile in 1984 and renamed Teniente Carvajal. Chile has used the station as a summer facility since this time. In the last few years the skiway has deteriorated further, leading to the death of a Chilean air mechanic, when he fell down a crevasse. Since then the Chilean Air Force have ceased operations at Carvajal. The Chilean Navy continues to visit the base during the summer to ensure it is in good order. The base was recently used (2011) in researchs of the Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH).
Administration
The commune is governed from Puerto Williams in the Cabo de Hornos commune from its municipal office located at O'Higgins 165.[1] Chilean law allows a municipality to govern more than one commune, however, this is the only such case. As a commune, Antártica is a third-level administrative division of Chile administered by a municipal council, headed by an alcalde who is directly elected every four years. The 2008-2012 alcalde is Hugo Henriquez Matus (PRSD).[2]
Within the electoral divisions of Chile, Antártica is represented in the Chamber of Deputies by Carolina Goic (PDC) and Miodrag Marinovic (Ind.) as part of the 60th electoral district, which includes the entire Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region. The commune is represented in the Senate by Carlos Bianchi Chelech (Ind.) and Pedro Muñoz Aburto (PS) as part of the 19th senatorial constituency (Magallanes Region).
References
- ^ a b (Spanish) "Asociación Chilena de Municipalidades". http://www.imcabodehornos.cl. Retrieved 27 January 2011.
- ^ a b (Spanish) "Municipality of Cabo de Hornos". http://www.imcabodehornos.cl. Retrieved 27 January 2011.
- ^ a b c d (Spanish) "National Statistics Institute". http://www.ine.cl/canales/chile_estadistico/censos_poblacion_vivienda/censo_pobl_vivi.php. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ^ "Chile Time". WorldTimeZones.org. http://www.world-time-zones.org/zones/chile-time.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-28.
- ^ "Chile Summer Time". WorldTimeZones.org. http://www.world-time-zones.org/zones/chile-summer-time.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-28.
- ^ "Territorial division of Chile" (PDF). http://www.ine.cl/canales/chile_estadistico/territorio/division_politico_administrativa/pdf/DPA_COMPLETA.pdf. Retrieved 11 September 2010.
- ^ Paul Jeffrey. Cristian Donoso and Claudio Scaletta completes historic journey in Antarctica
External links
- Gobierno Regional Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Official website (in Spanish)
- Gobernación Provincia de Antártica Chilena Official website (in Spanish)
- Chilean Antarctic Institute Official website (in Spanish)
- (Spanish) Municipality of Cape Horn
Coordinates: 75°00′S 71°30′W / 75°S 71.5°W
< Communes and municipalities in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region Última Esperanza Province 
Magallanes Province Tierra del Fuego Province Antártica Chilena Province Chilean Antarctic Territory · Cabo de HornosAntarctic territorial claims Current 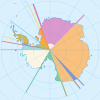
Proposed Former Antártica Chilena 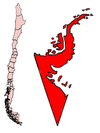
Bases
Research stations: Bernardo O'Higgins · Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva · Professor Julio Escudero · González Videla*
Civilian settlements: Villa Las EstrellasInstitutions
INACH · Navy of Chile (Icebreaker)Overlapping claims
Argentine Antarctica · British Antarctic Territory
Antarctica Main articles - Antarctic
- History
- Geography
- Climate
- Expeditions
- Research stations
- Field camps
- Territorial claims
- Antarctic Treaty System
- Telecommunications
- Demographics
- Economy
- Tourism
- Transport
- Military activity in the Antarctic
Geographic regions - Antarctic Peninsula
- East Antarctica
- West Antarctica
- Extreme points of the Antarctic
- List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
- Antarctica ecozone
Waterways Famous explorers  Portal:AntarcticaCategories:
Portal:AntarcticaCategories:- Chilean Antarctica
- Antarctic territorial claims
- Communes of Chile
- Magellan and Chilean Antarctica Region
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



