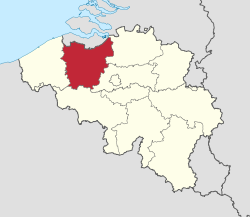
- East Flanders
-
East Flanders — Province of Belgium — Name transcription(s) – Dutch Oost-Vlaanderen – French Flandre-Orientale – German Ostflandern 
Flag
Coat of armsCountry  Belgium
BelgiumRegion  Flemish Region
Flemish RegionCapital Ghent Government – Governor André Denys Area – Total 2,991 km2 (1,154.8 sq mi) Population (1 January 2010)[1] – Total 1,432,326 – Density 478.9/km2 (1,240.3/sq mi) Website Official site East Flanders (Dutch: Oost-Vlaanderen [ˈoːst ˈvlaːndərə(n)] (
 listen), French: (Province de) Flandre-Orientale, German: Ostflandern) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the North) on the Netherlands and in Belgium on the provinces of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant (both in Flanders), of Hainaut (Wallonia) and of West Flanders (Flanders). It has an area of 2,991 km² which is divided into six administrative districts (arrondissementen in Dutch) containing 65 municipalities. The provincial population is 1,408,484 and the capital is Ghent.
listen), French: (Province de) Flandre-Orientale, German: Ostflandern) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the North) on the Netherlands and in Belgium on the provinces of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant (both in Flanders), of Hainaut (Wallonia) and of West Flanders (Flanders). It has an area of 2,991 km² which is divided into six administrative districts (arrondissementen in Dutch) containing 65 municipalities. The provincial population is 1,408,484 and the capital is Ghent.The flag has a black lion with red tongue and claws, on a background of horizontal white and green stripes. This is a recent adaptation. The flag of East-Flanders used to be the same as that of the Flanders region; a black lion on a yellow background. The old flag is still publicly used, e.g. for road signs.
Contents
Government
The provincial parliament, Provincieraad, has 84 members.[2] Six people chosen by and from the parliament are the deputies, bestendige deputatie, and form the daily government. The daily government is led by the governor, who is appointed by the Flemish government.
André Denys (VLD) has been the governor of East Flanders since 26 November 2004.[3]
The provincial deputies are:[4]
- 1st Deputy: Alexander Vercamer (CD&V)
- 2nd Deputy: Marc De Buck (CD&V)
- 3rd Deputy: Peter Hertog (SP.A-Spirit)
- 4th Deputy: Jozef Dauwe (CD&V)
- 5th Deputy: Carina Van Cauter (CD&V)
- 6th Deputy Eddy Couckuyt (CD&V)
The province has a yearly budget of approximately 300 million euro.
Governors
- Pierre De Ryckere (1830)
- Werner de Lamberts-Cortenbach (1830–1834)
- Charles Vilain XIIII (1834–1836)
- Louis de Schiervel (1837–1843)
- Leander Desmaisières (1843–1848)
- Edouard De Jaegher (lib.) (1848–1871)
- Emile de T'Serclaes De Wommersom (1871–1879)
- Léon Verhaeghe de Naeyer (lib.) (1879–1885)
- Raymond de Kerchove d'Exaerde (1885–1919)
- Maurice Lippens (lib.) (1919–1921)
- André de Kerchove de Denterghem (lib.) (1921–1929)
- Karel Weyler (lib.) (1929–1935)
- Jules Ingenbleek (lib.) (1935–1938)
- Louis Frederiq (lib) (1938–1939)
- Maurice Van den Boogaerde (1939–1954)
- Albert Mariën (lib.) (1954–1963)
- Roger de Kinder (BSP) (1963–1984)
- Herman Balthazar (SP.A) (1984–2004)
- André Denys (VLD) (2004-)
Timeline:

Sub divisions
Formal subdivisions: districts and municipalities
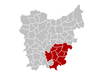
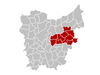
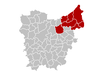
District Ghent District: Oudenaarde District: Eeklo District: Aalst District: Dendermonde District: Sint-Niklaas District: Location 
BE.OV.GT
BE234
44
512,407
944 km²BE.OV.OD
BE235
45
117,125
419 km²BE.OV.EK
BE233
43
80,574
334 km²BE.OV.AL
BE231
41
267,274
469 km²BE.OV.DM
BE232
42
189,638
343 km²BE.OV.SN
BE236
46
231,262
475 km²Municipalities Informal subdivisions
- Denderstreek
- Meetjesland
- Waasland (nl:Waasland)
- Flemish Ardennes (nl:Vlaamse Ardennen)
- Lys region (nl:Leiestreek)
 Subdivisions of Belgium
Subdivisions of BelgiumCommunities 
Regions · Provinces Municipalities
by regionArrondissements References
- ^ Population per municipality on 1 January 2010 (XLS; 221 KB)
- ^ "The provinical parliament, province East Flanders". http://www.oost-vlaanderen.be/public/over_provincie/beleid_bestuur/provincieraad/index.cfm. Retrieved 2006-03-14.
- ^ "The governor, province East Flanders". http://www.oost-vlaanderen.be/public/over_provincie/beleid_bestuur/gouverneur/index.cfm. Retrieved 2006-03-14.
- ^ "Who is who, province East Flanders". http://www.oost-vlaanderen.be/public/over_provincie/beleid_bestuur/deputatie/wieiswie/index.cfm. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
External links
- Official Website (in Dutch)
Categories:- East Flanders
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
- Flemish provinces
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.