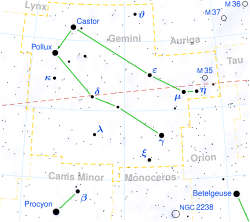
- Delta Geminorum
-
δ Geminorum Observation data
Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000Constellation Gemini Right ascension 07h 20m 07.38s[1] Declination +21° 58′ 56.42″ Apparent magnitude (V) +3.5[1] Characteristics Spectral type F0[1] Delta Geminorum (δ Gem, δ Geminorum) is a star in the constellation Gemini. It has the traditional name Wasat. The traditional name comes from the Arabic word for "middle".
In Chinese, 天樽 (Tiān Zūn), meaning Celestial Wine Cup, refers to an asterism consisting of δ Geminorum, 57 Geminorum and ω Geminorum.[2] Consequently, δ Geminorum itself is known as 天樽二 (Tiān Zūn èr, English: the Second Star of Celestial Wine Cup.)[3]. From this Chinese name, the name Ta Tsun was appeared.[4]
Properties
The star has an apparent magnitude of +3.5 and belongs to the spectral class F0.[1] It is 59 light years distant.
Wasat is only two-tenths of a degree south of the ecliptic, and therefore is occasionally occulted by the Moon and, more rarely, by a planet. The last occultation by a planet was by Saturn on June 30, 1857, and the next will be by Venus on August 12, 2420.
Wasat is actually a binary star, having a cooler class K companion which is not apparent to the naked eye but clearly visible in a small telescope. Wasat and its companion take 1200 years to orbit about each other.[5]
References
- ^ a b c d "Delta Geminorum (Wasat)". SIMBAD Astronomical Database. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=Delta+Geminorum. Retrieved 2011-06-03.
- ^ (Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ^ Richard Hinckley Allen: Star Names — Their Lore and Meaning: Gemini
- ^ http://www.astro.uiuc.edu/~kaler/sow/wasat.html
External links
- Delta Geminorum on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
Star systems within 50–60 light-years from Earth with brightest member's absolute magnitude of +8.5 or brighter. Castor (51.6 ± 1.0 ly; 6 stars) • Delta Leonis «Zosma» (57.7 ± 0.9 ly; 2 stars) • Iota Centauri «Alhakim» (58.6 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star) • Beta Arietis «Sheratan» (59.6 ± 0.8 ly; 2 stars)‡Delta Aquilae «Denebokab» (50.1 ± 0.6 ly; 3 stars)‡ • I Carinae (52.9 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star) • Beta Cassiopeiae «Caph» (54.5 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • Xi Geminorum «Alzirr» (57.2 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star) • Psi Velorum (59.7 ± 1.0 ly; 2 stars)‡ • Mu Virginis (60.9 ± 1.1 ly; 1 star)‡Sigma Boötis «Hemelein Secunda» (50.4 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)‡ • Tau Boötis (50.9 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars, 1 planet: planet b) • Alpha Circini (53.5 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • q¹ Eridani (56.6 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • g Lupi (57.1 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star) • Alpha Comae Berenices «Diadem» (58.3 ± 1.5 ly; 3 stars) • Delta Geminorum «Wasat» (58.8 ± 0.9 ly; 3 stars) • Chi Cancri (59.2 ± 1.0 ly; 1 star)‡ • Eta Corvi «Avis Satyra» (59.4 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star)‡ • Delta Equulei «Pherasauval» (60.0 ± 1.0 ly; 2 stars)‡Chi Eridani (57.0 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)Mu Arae (49.8 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 4 planets: planet d • planet e • planet b • planet c)‡ • 51 Pegasi (50.1 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b «Bellerophon»)‡ • HR 7368 (50.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 2 brown dwarfs: brown dwarf C • brown dwarf B) • HR 2007 (50.8 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b)‡ • HR 8323 (51.0 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • HR 7670 (51.8 ± 0.5 ly; 3 stars, 2 planets: planet c • planet b) • Psi⁵ Aurigae (53.9 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • HR 3538 (55.8 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star) • Iota Horologii (56.2 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • 37 Geminorum (56.3 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star) • Rho Coronae Borealis (56.8 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • GJ 3021 (57.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • 15 Sagittae (57.6 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 brown dwarf) • HR 7644 (57.8 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • HR 5534 (58.5 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star, 2 brown dwarfs) • Gliese 651 (58.9 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • 70 Virginis (59.1 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • Pi Mensae (59.4 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b)83 Leonis (57.6 ± 1.5 ly; 2 stars, 2 planets: planet Bb • planet Bc) • Epsilon Reticuli (59.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b)‡GJ 3860 (54.0 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star, 2 planets) • Gliese 56.5 (54.9 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • HD 87883 (58.9 ± 1.0 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • Gliese 652 (59.0 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b) • 14 Herculis (59.2 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b)In left column are stellar classes of primary members of star systems. ‡Distance error margin extends out of declared distance interval. Italic are systems possibly located within declared distance interval, but probably not. Bayer α (Castor) • β (Pollux) • γ (Alhena) • δ (Wasat) • ε (Mebsuta) • ζ (Mekbuda) • η (Tejat Prior) • θ • ι • κ • λ • μ (Tejat Posterior) • ν • ξ (Alzirr) • ο • π • ρ • σ • τ • υ • φ • χ • ω • b • c • d • e • f • g • AFlamsteed 1 (Propus) • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 (η, Tejat Prior) • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 (μ, Tejat Posterior) • 14 • 15 • 16 • 18 (ν) • 19 • 20 • 22 • 23 • 24 (γ, Alhena) • 25 • 26 • 27 (ε, Mebsuta) • 28 • 30 • 31 (ξ, Alzirr) • 32 • 33 • 34 (θ) • 35 • 36 (d) • 37 • 38 (e) • 39 • 40 • 41 • 42 (ω) • 43 (ζ, Mekbuda) • 44 • 45 • 46 (τ) • 47 • 48 • 49 • 51 • 52 • 53 • 54 (λ) • 55 (δ, Wasat) • 56 • 57 (A) • 58 • 59 • 60 (ι) • 61 • 62 (ρ) • 63 • 64 • 65 (b) • 66 (α, Castor) • 67 • 68 • 69 (υ) • 70 • 71 (ο) • 74 (f) • 75 (σ) • 76 (c) • 77 (κ) • 78 (β, Pollux) • 79 • 80 (π) • 81 (g) • 82 • 83 (φ) • 84 • 85 • 3 Lyn • 141 TauNearby Gliese 251 • GJ 1093 • Gl 232 • 2MASS 0727+1710List Categories:- Bayer objects
- Binary stars
- Gemini constellation
- Stars with proper names
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.